引 言
在过去的几十年中,神经网络的稳定性分析、周期振荡以及混沌行为得到了广泛的研究.因此神经网络可应用于自动控制、信号处理、模式识别和优化计算等领域[1-5].神经网络在实际应用中越来越受欢迎,因为其可以通过大规模的集成或数字电路来实现.由于放大器有限的转换速度以及信号传输过程中出现的拥塞现象等因素,使得时间延迟现象不可避免地存在.这种时滞是导致神经网络不稳定或振荡的原因之一,因此具有时滞的神经网络的稳定性与同步问题引起了许多学者的关注,同时获得了许多的成果 [6-7].中立型神经网络是一种特殊类型的时滞神经网络,时滞不仅出现在系统现在的状态,而且出现在系统状态的导数中.因此时滞中立型神经网络的稳定性分析已获得了大量的研究成果[4,7-9].
在生物神经系统中突触的信号传递可被视为一个噪声过程,这种噪声主要源于神经传导物质的释放及一些概率性的因素带来的随机波动.在一般情况下,Gauss噪声经常被视为在神经网络中所引起的干扰.另外,许多神经网络可能会受到某些现象的影响而出现在结构和参数的突然变化,从而改变子系统之间的相互关联以及突然的环境变化.在这种情况下,神经网络可被视为具有有限模态的系统,这些模态在不同的时间从一个跳变到另一个,这种跳变可以用Markov链来描述.因此,带有Markov跳变的神经网络的应用十分广泛[10-15].文献[10]研究了具有Markov中立型延迟神经网络的驱动响应同步.文献[11]通过使用自适应控制方法,考虑了具有Markov耦合中立型复杂动力网络的指数同步.
在网络无法自行同步的情况下,已经研究出许多控制技术来驱动网络实现同步,如线性状态反馈控制[16]、脉冲控制[17-18]、自适应控制[19-20]、采样数据控制[21]以及它们之间的组合方法,已被广泛运用于混沌系统.这些方法中多数是通过控制网络的全部节点来实现同步的,但是真实世界的网络是由大量的节点构成的,将控制器添加到大规模网络中的所有节点是非常困难的.为了减少受控节点的数量,引入了牵制控制,其中控制器仅适用于部分节点,通过节点之间的耦合作用,从而控制整个网络[22].另外,为了有效获得适当的控制增益,自适应牵制控制方法涌现了大量的研究成果[23-25].
本文利用Lyapunov稳定性理论和自适应牵制控制方法,给出了保证中立型神经网络与Markov切换参数自适应同步的准则.最后给出了一个数值例子来说明所提方法的有效性.
1 系统模型及预备知识
{r(t),t≥0}是在完全概率空间上(Ω,F,{Ft}t≥0,P)的一个右连续的Markov链,它包含满足一般条件(即当F0包含P-空集时单调递增且右连续)的自然流.
{Ft}t≥0在有限状态空间S={1,2,…,κ}中取值.概率转移矩阵为Π=(π)κ×κ:
其中,δ>0且γij≥0是i到j的转移率,如果i≠j,则γii=-∑j≠iγij.为简单起见,令r(t)=m,m∈S.
考虑到如下具有Markov的中立型时滞神经网络模型:
d[s(t)-Dms(t-τ(t))]=
[-Cms(t)+Amf(s(t))+Bmf(s(t-τ(t)))+J]dt,
(1)
其中,s(t)=[s1(t),s2(t),…,sn(t)]T∈Rn是与n个神经元相关联的状态向量,Am∈Rn×n为连接权矩阵,Bm∈Rn×n为时滞连接权矩阵,Cm=diag{c1,c2,…,cn}是正定对角矩阵,Dm∈Rn×n, f(·)是神经元激活函数且有界,τ(t)是时变时滞且满足
(2)
其中,![]() 为常数.
为常数.
考虑到式(1)中s(t)是作为同步动态,研究了具有随机扰动和Markov跳变的n维中立型神经网络.如下所示的随机延迟差分方程表达了它的动态行为:
d[xi(t)-Dmxi(t-τ(t))]=
i=1,2,…,N,
(3)
其中,x(t)=(x1(t),x2(t),…,xn(t))T∈Rn是第i个节点的神经元状态向量,系统参数Am,Bm,Cm,Dm与式(1)定义相同,Ri(t)是控制输入向量,c是耦合强度,Γ=diag{γ1,γ2,…,γn}是对角矩阵,描述的是在时间t、两个互连节点i和j之间的内耦合,ei(t)=xi(t)-s(t)表示节点i的状态和状态向量s(t)之间的误差,ω(t)=(ω1(t),ω2(t),…,ωn(t))T是定义在完备概率空间(Ω,{Ft}t≥0,P)上具有自然流{Ft}t≥0的m维Brown运动,σ是满足σ:R+×Rn×Rn→Rn×m的噪声强度函数,![]() 是外耦合转置矩阵,表示中立型神经网络的耦合强度和拓扑结构,对于i=1,2,…,N,则
是外耦合转置矩阵,表示中立型神经网络的耦合强度和拓扑结构,对于i=1,2,…,N,则
由矩阵Gm的性质能够得到
由式(3)减去式(1),得到如下的误差系统:
d[ei(t)-Dmei(t-τ(t))]=
i=1,2,…,N,
(4)
其中
f(ei(t))=f(xi(t))-f(s(t))=f(ei(t)+s(t))-f(s(t)),
f(ei(t-τ(t)))=f(xi(t-τ(t)))-f(s(t-τ(t)))=
f(ei(t-τ(t))+s(t-τ(t)))-f(s(t-τ(t))).
为证明我们的主要结果,则需要下面的假设、定义和引理.
假设1 对于任意x,y∈Rn,存在常数li,函数f(·)满足下面Lipschitz条件:
‖ f(x)-f(y)‖≤li‖x-y‖.
令L=diag{η1,η2,…,ηn},可以从假设1中得出结论:
fT(e(t))M f(e(t)),
其中,M=diag{m1,m2,…,mn}是任意正对角矩阵.
假设2 噪声强度矩阵σ(·,·,·)满足有界条件,对于任意x,y∈Rn,存在两个已知常数h1和h2,满足
trace[σT(r(t),e(t),e(t-τ(t)))σ(r(t),e(t),e(t-τ(t)))]≤
eT(t)h1e(t)+eT(t-τ(t))h2e(t-τ(t)).
引理1(广义It 公式) 令V∈(Rn×R+×S;R)且0≤τ1≤τ2是有界停止时间.如果V(t,i,x(t))和LV(t,i,x(t))在t∈[τ1,τ2]上是有界的,故
公式) 令V∈(Rn×R+×S;R)且0≤τ1≤τ2是有界停止时间.如果V(t,i,x(t))和LV(t,i,x(t))在t∈[τ1,τ2]上是有界的,故
EV(τ2,r(τ2),x(τ2))=EV(τ1,r(τ1),x(τ1))+E![]() LV(s,r(s),x(s))ds.
LV(s,r(s),x(s))ds.
引理2 对于任意的![]() 和r0=m∈S,若误差系统(3)是稳定的,则系统(1)和系统(2)则是同步的,
和r0=m∈S,若误差系统(3)是稳定的,则系统(1)和系统(2)则是同步的,
E![]() ‖e(t;ζ(0),r0)‖2dt<∞.
‖e(t;ζ(0),r0)‖2dt<∞.
为了使中立型神经网络能够实现指数同步,设计一个自适应牵制控制器,控制器被添加到一部分节点上.不失一般性,让前l个节点被控制,控制器的设计如下:
(5)
所以,误差系统(4)被描述如下:
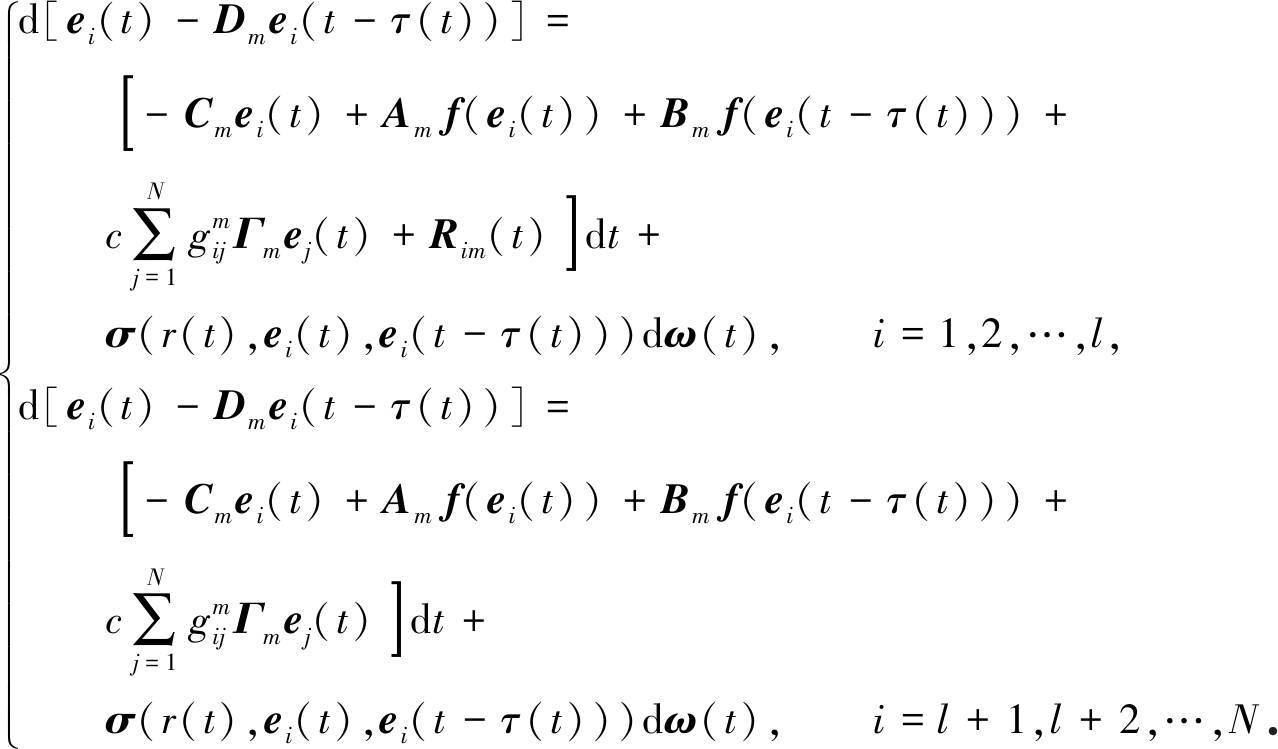
(6)
通过使用Kronecker内积,系统(4)重新定义为
d[e(t)-(IN⊗Dm)e(t-τ(t))]=
[-(IN⊗Cm)e(t)+(IN⊗Am) f(e(t))+(IN⊗Bm) f(e(t-τ(t)))+
(cGm⊗Γm)e(t)+Rm]dt+σ(r(t),e(t),e(t-τ(t)))dω(t).
(7)
2 主 要 结 果
设计一个自适应控制器使得中立型耦合神经网络(1)和(3)实现同步,主要结果如下.
定理1 在假设1、2成立的条件下,如果存在常数ρm>0,对称矩阵 Pm>0,Q1>0,Q2>0,L>0,M>0,R>0,使得下列LMIs成立:
Pm<ρmI,
(8)

(9)
其中
k*⊗Pm+cGm⊗PmΓm,
W33=-IN⊗Q1, W44=IN⊗(R-2M),
选择的自适应更新定律如下所示:
αi>0, i=1,2,…,l.
(10)
证明 构建如下的Lyapunov函数:
V2(t,X)=![]() eT(s)(IN⊗Q1)e(s)ds+
eT(s)(IN⊗Q1)e(s)ds+![]() eT(s)(IN⊗Q2)e(s)ds,
eT(s)(IN⊗Q2)e(s)ds,
V3(t,X)=![]() fT(e(s))(IN⊗R)f(e(s))ds.
fT(e(s))(IN⊗R)f(e(s))ds.
沿着误差系统(7)的轨迹对V1(t,X)求无穷小算子:
XT(IN⊗Pm)[-(IN⊗Cm)e(t)+(IN⊗Am)f(e(t))+
c(Gm⊗Γm)e(t)+(IN⊗Bm)f(e(t-τ(t)))]+
(11)
由式(8)和假设2,有
(12)
由于
(13)
(14)
对V2(t,X)求无穷小算子,可得
LV2(t,X)≤eT(t)(IN⊗(Q1+Q2))e(t)-eT(t-τ)(IN⊗Q1)eT(t-τ)-
(15)
根据假设1,有
LV3(t,X)≤fT(e(t))(IN⊗R)f(e(t))-
2eT(t)[(IN⊗LM)f(e(t))-fT(e(t))(IN⊗M)f(e(t))]=
fT(e(t))[IN⊗(R-2M)]f(e(t))+2eT(t)(IN⊗LM)f(e(t))-
(16)
由式(11)~(16)相加,可得
eT(t-τ)(IN⊗Q1)e(t-τ)+eT(t)[IN⊗(PmAm+2LM)]f(e(t))+
fT(e(t))[IN⊗(R-2M)]f(e(t))-
ξT(t)Ωξ(t),
(17)
其中
考虑Ω≤0,可得
LV(t,X)≤0.
由式(9)和引理2,有
E(LV(t,X))≤-βi‖ξ(t)‖2≤-β‖ξ(t)‖2≤-β‖e(t)‖2,
(18)
其中,-βi=λmax(Ω),βi>0,i∈S和-β=maxi∈S{-βi}.由Dynkin公式,可以得到
EV(τ,r(τ),x(τ))-EV(0,r(0),x(0))=
E![]() LV(s,r(s),x(s))ds≤-β
LV(s,r(s),x(s))ds≤-β![]() ‖e(t)‖2ds.
‖e(t)‖2ds.
(19)
因此由式(19),有
β![]() ‖e(t)‖2ds≤
‖e(t)‖2ds≤
-EV(τ,r(τ),x(τ))+EV(0,r(0),x(0))≤EV(0,r(0),x(0)).
(20)
由式(18)~(20)可得
根据引理4,系统(1)和系统(3)是同步的,证毕.
3 数 值 仿 真
在这部分,通过给出实例来证明结果的有效性.Markov链进程{r(t),t≥0}在S={1,2}中取值.给出概率转移矩阵,产生一个Markov链.考虑给出的概率转移矩阵如下:
考虑具有四个节点的中立型神经网络(3):
d[xi(t)-Dmxi(t-τ(t))]=
σ(r(t),xi(t),xi(t-τ(t)))dω(t), i=1,2,3,4,
(21)
其中,xi(t)=[xi1(t),xi2(t)]T是第i节点的状态变量,
同时其他参数如下所示:
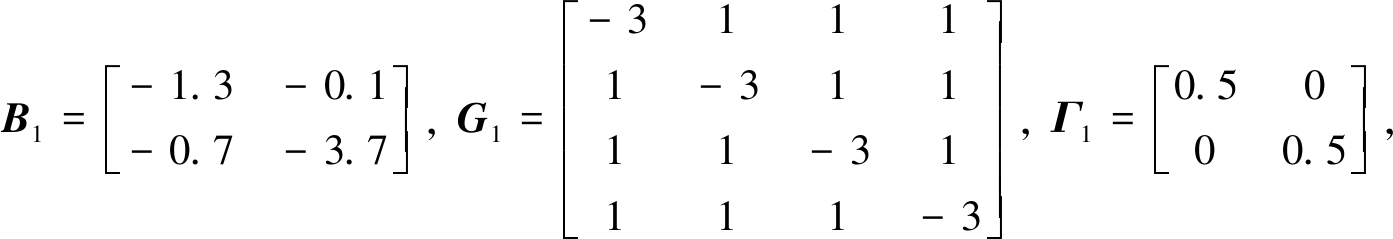

噪声强度矩阵为
噪声强度矩阵σ(·,·,·)满足有界条件,且h1=h2=0.45.当r(t)=1时,将控制器添加到第一个节点,k*=diag{30,0,0,0};当r(t)=2时,将控制器添加到前三个节点中,k*=diag{30,30,30,0}.使用LMI工具箱,获得下列的可行解:
ρ1=202.867 9, ρ2=135.599 6,
表1给出了最大时滞上界.图1~6所展示的仿真结果给定的系统初始值条件为x1=[1.6.-0.5], x2=[1.1,1.1], x3=[1.3,1.7], x4=[3.7,-1.5], s=[-3.0,2.2]以及α1=α2=1.图1为Markov链的变化曲线;图2是控制器增益的变化曲线,可以看到控制增益在几秒内达到稳定;图3、4表示的是xi(t)(i=1,2,3,4)和si(t)的状态变化,可以看出式(21)和式(1)达到同步;图5、6是误差的变化曲线,随着时间的流逝,状态演化误差迅速接近零.
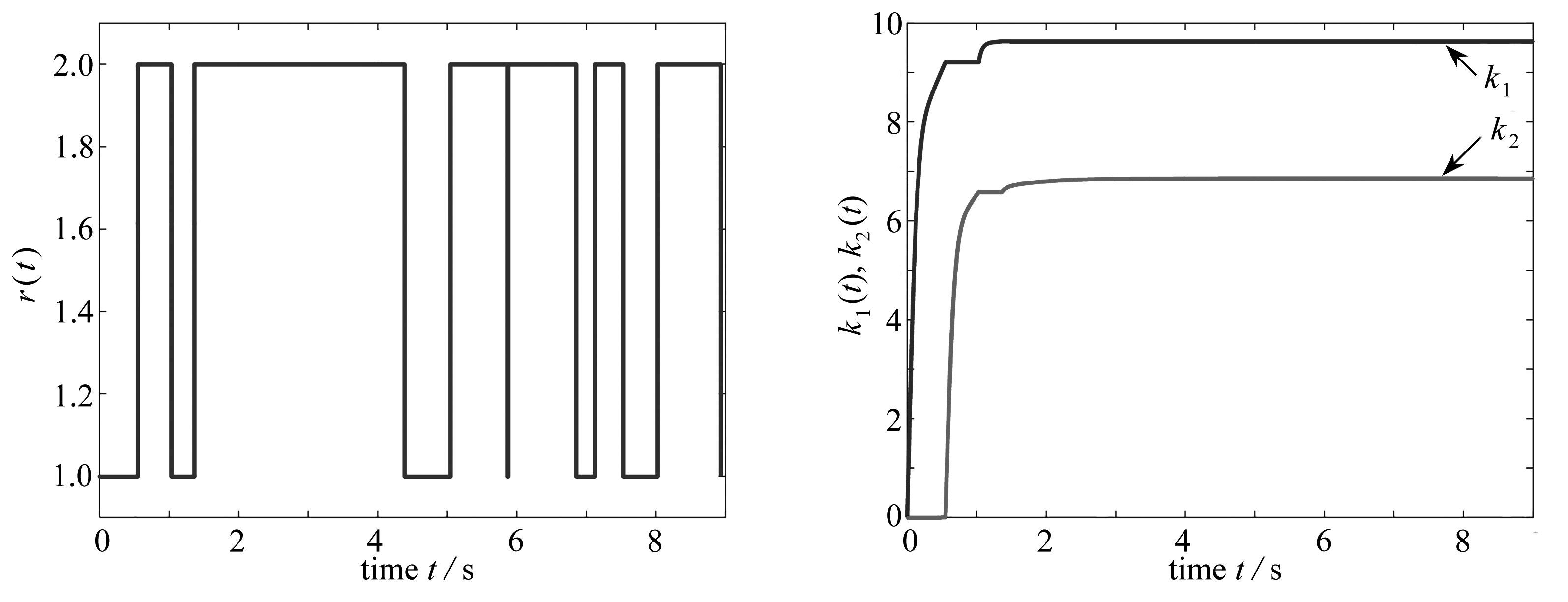
图1 Markov链的轨迹变化 图2 控制器增益的时间演变
Fig. 1 Markovian chain trajectory changes Fig. 2 Time evolution of the adaptive strengths
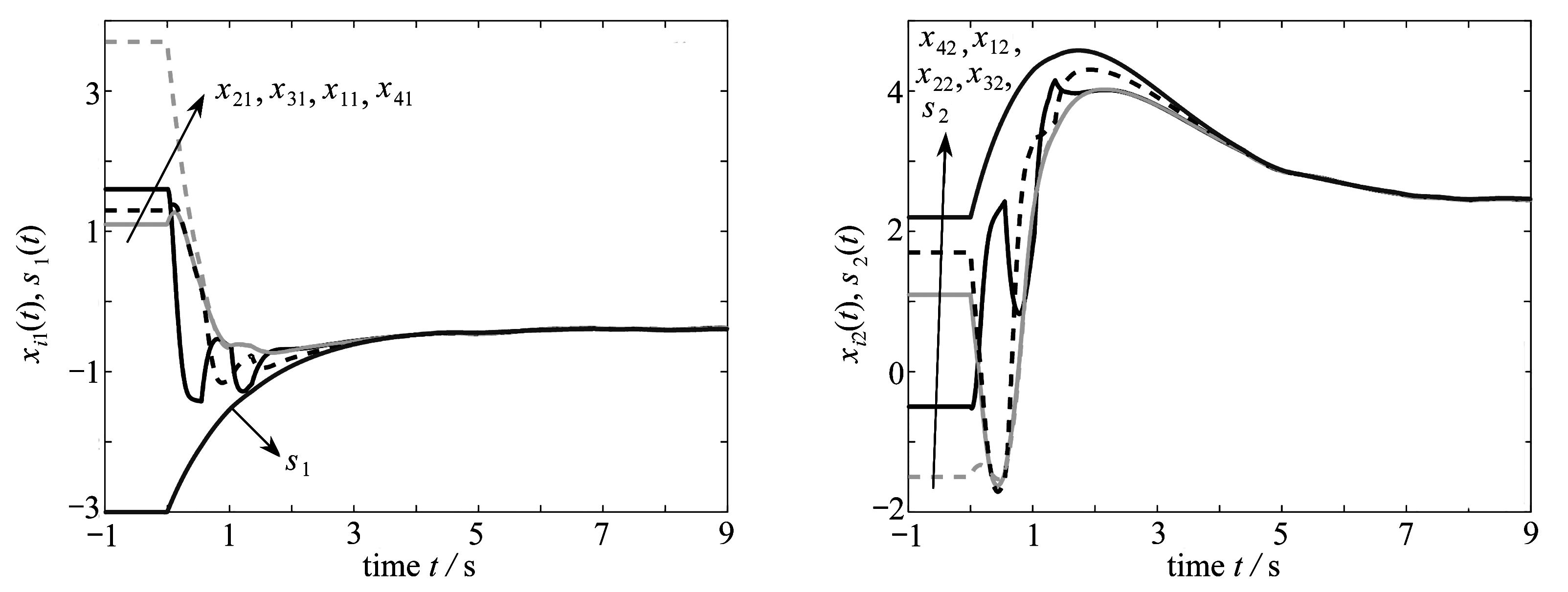
图3 控制网络(21)xi1(t)(i=1,2,3,4)轨迹变化 图4 控制网络(21)xi2(t)(i=1,2,3,4)轨迹变化
Fig. 3 The trajectories of the state variables of xi1(t)(i=1,2,3,4) in controlled network (21) Fig. 4 The trajectories of the state variables of xi2(t)(i=1,2,3,4) in controlled network (21)
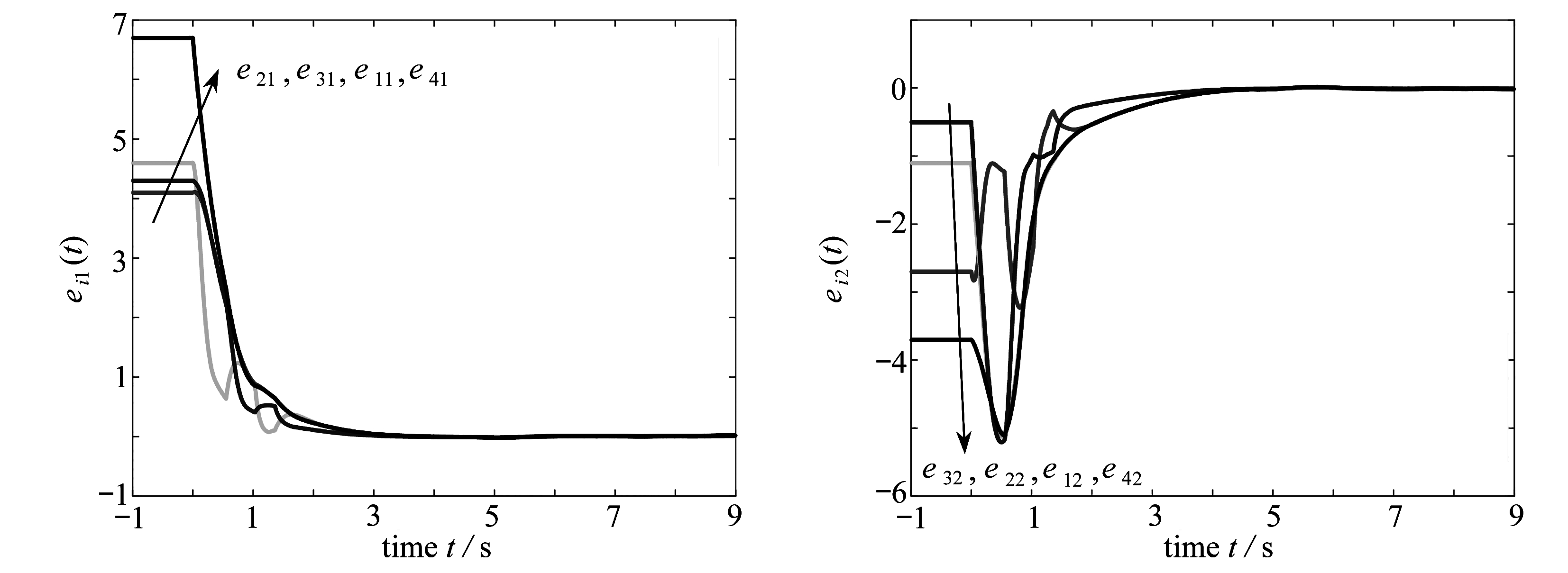
图5 误差ei1(t)轨迹变化 图6 误差ei2(t)状态变化
Fig. 5 The trajectories of the state variables of ei1(t) Fig. 6 The trajectories of the state variables of ei2(t)
表1 最大时滞上界
Table 1 The maximum delay bounds
methodref. [1]ref. [2]ref. [26]theorem 1max(τ(t))0.549 30.549 60.671 01
4 结 论
本文研究了具有Markov和随机扰动的中立型耦合神经网络的自适应同步问题.将自适应牵制控制运用到中立型耦合神经网络中,即通过控制网络中的部分节点,以达到控制整个网络的目的,降低了控制的成本.通过构造合适的Lyapunov函数,得到了误差中立型耦合神经网络的稳定性判据,数值仿真算例验证了理论分析的有效性.在未来的研究工作中: 1) 我们将研究更简单的控制器,确保具有时变时滞和Markov切换的中立型系统的同步; 2) 将进一步研究带有混合时滞的中立型系统的同步问题.
[1] ZUO Z Q, YANG C L, WANG Y J. A new method for stability analysis of recurrent neural networks with interval time-varying delay[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2010, 21(2): 339-344.
[2] BAI Y Q, CHEN J. New stability criteria for recurrent neural networks with interval time-varying delay[J]. Neurocomputing, 2013, 121(9): 179-184.
[3] HE Y, LIU G, REES D. New delay-dependent stability criteria for neural networks with time-varying delay[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2007, 18(1): 31-314.
[4] ZHOU W, ZHU Q, SHI P, et al. Adaptive synchronization for neutral-type neural networks with stochastic perturbation and Markovian switching parameters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2014, 44(12): 2848-2860.
[5] WANG J L, WU H N, GUO L. Novel adaptive strategies for synchronization of linearly coupled neural networks with reaction-diffusion terms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(2): 429-440.
[6] 周军, 童东兵, 陈巧玉. 基于事件触发控制带有多时变时滞的主从系统同步[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2019, 40(12): 1389-1398. (ZHOU Jun, TONG Dongbing, CHEN Qiaoyu. Synchronization of master-slave systems with multiple time-varying delays based on the event-trigger[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2019, 40(12): 1389-1398. (in Chinese))
[7] SAMIDURAI R, RAJAVEL S, SRIRAMAN R, et al. Novel results on stability analysis of neutral-type neural networks with additive time-varying delay components and leakage delay[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2017, 15(4): 1888-1900.
[8] BALASUBRAMANIAM P, VEMBARASAN V. Asymptotic stability of BAM neural networks of neutral-type with impulsive effects and time delay in the leakage term[J]. International Journal of Computer Mathematics, 2011, 88(15): 3271-3291.
[9] WANG X H, LI S Y, XU D V. Globally exponential stability of periodic solutions for impulsive neutral-type neural networks with delays[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2011, 64(1/2): 65-75.
[10] ZHOU W N, GAO Y, TONG D B, et al. Adaptive exponential synchronization in pth moment of neutral-type neural networks with time delays and Markovian switching[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2013, 11(4): 845-851.
[11] ZHANG Y, GU D, XU S. Global exponential adaptive synchronization of complex dynamical networks with neutral-type neural network nodes and stochastic disturbances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅰ: Regular Papers, 2013, 60(10): 2709-2718.
[12] RAO R F, ZHONG S M, WANG X R. Stochastic stability criteria with LMI conditions for Markovian jumping impulsive BAM neural networks with mode-dependent time-varying delays and nonlinear reaction-diffusion[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2014, 19(1): 258-273.
[13] WU T, XIONG L I, CAO JINDE, et al. New stability and stabilization conditions for stochastic neural networks of neutral type with Markovian jumping parameters[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2018, 355(17): 8462-8483.
[14] HUANG H Y, DU Q S, KANG X B. Global exponential stability of neutral high-order stochastic Hopfield neural networks with Markovian jump parameters and mixed time delays[J]. ISA Transactions, 2013, 52(6): 759-767.
[15] MAHARAJAN C, RAJA R, CAO J D, et al. Global exponential stability of Markovian jumping stochastic impulsive uncertain BAM neural networks with leakage, mixed time delays, and α-inverse Hölder activation functions[J]. Advances in Difference Equations, 2018, 2018(1): 1-31.
[16] JIANG G, TANG W K, CHEN G. A state-observer-based approach for synchronization in complex dynamical networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅰ: Regular Papers, 2006, 53(12): 2739-2745.
[17] 阿子阿英, 饶若峰, 赵锋, 等. 具概率延迟反馈金融系统的脉冲控制[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2019, 40(12): 1409-1416. (AZI Aying, RAO Ruofeng, ZHAO Feng, et al. Impulse control of financial systems with probabilistic delay feedback[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2019, 40(12): 1409-1416. (in Chinese))
[18] YANG X, CAO J, LU J. Stochastic synchronization of complex networks with nonidentical nodes via hybrid adaptive and impulsive control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅰ: Regular Papers, 2012, 59(2): 371-384.
[19] ZHANG Q, LU J, TSE C K. Adaptive feedback synchronization of a general complex dynamical network with delayed nodes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅱ: Express Briefs, 2008, 55(2): 183-187.
[20] SHI M, LI J M, HE C, et al. Synchronization of complex dynamical networks with nonidentical nodes and derivative coupling via distributed adaptive control[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2013, 2013(10): 172608.
[21] LEE T H, WU Z G, PARK J H. Synchronization of a complex dynamical network with coupling time-varying delays via sampled-data control[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2012, 219(3): 1354-1366.
[22] SUN X J, FENG Z H, LIU X L. Pinning adaptive synchronization of neutral-type coupled neural networks with stochastic perturbation[J]. Advances in Difference Equations, 2014, 2014(1): 1-13.
[23] PAN L J, CAO J, AI-JUBOORI U A, et al. Cluster synchronization of stochastic neural networks with delay via pinning impulsive control[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 366(13): 109-117.
[24] WANG Y L, CAO J D, HU J Q. Stochastic synchronization of coupled delayed neural networks with switching topologies via single pinning impulsive control[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2015, 26(7): 1739-1749.
[25] WU X, XU C. Cluster synchronization of nonlinearly coupled neural networks with hybrid time-varying delays and stochastic perturbations via pinning control[J]. Journal of Convergence Information Technology, 2012, 7(6): 101-111.
[26] ZENG H B, PARK H J, ZHANG C F, et al. Stability and dissipativity analysis of static neural networks with interval time-varying delay[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2015, 352(3): 1284-1295.