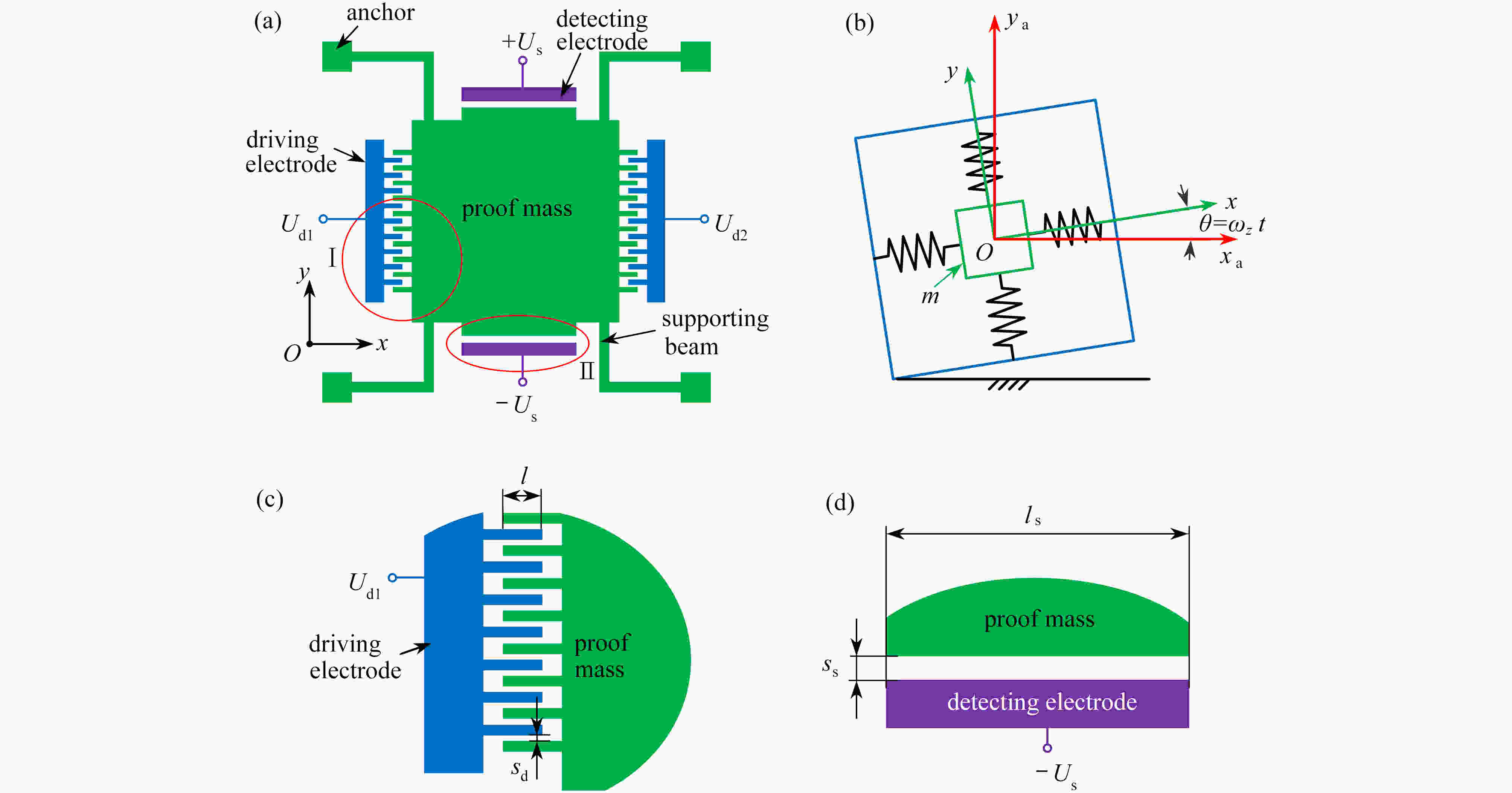
Effects of Structure Parameters on Dynamic Performances of Electrostatic Drive Micro-Machined Gyroscopes
-
摘要:
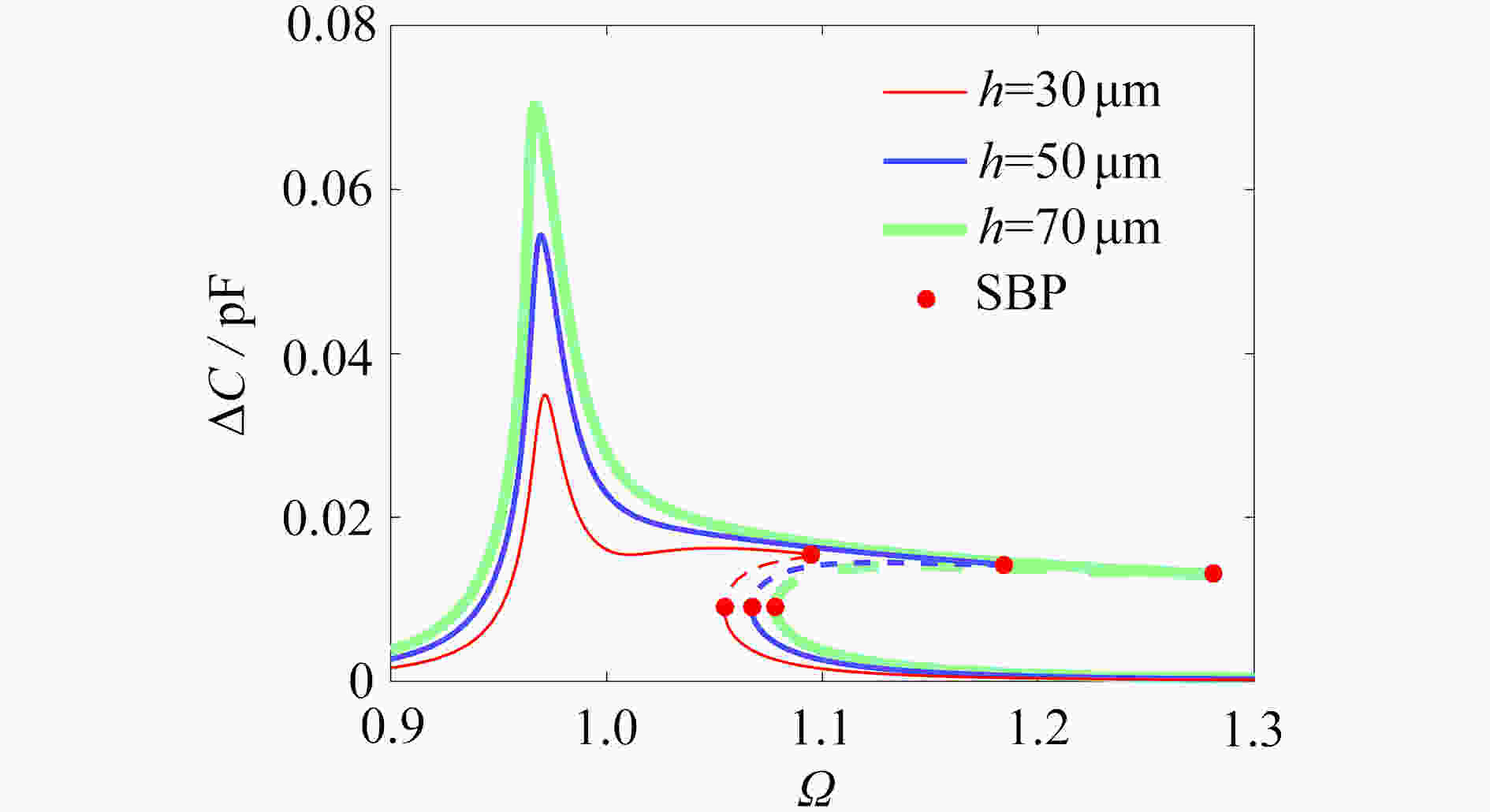
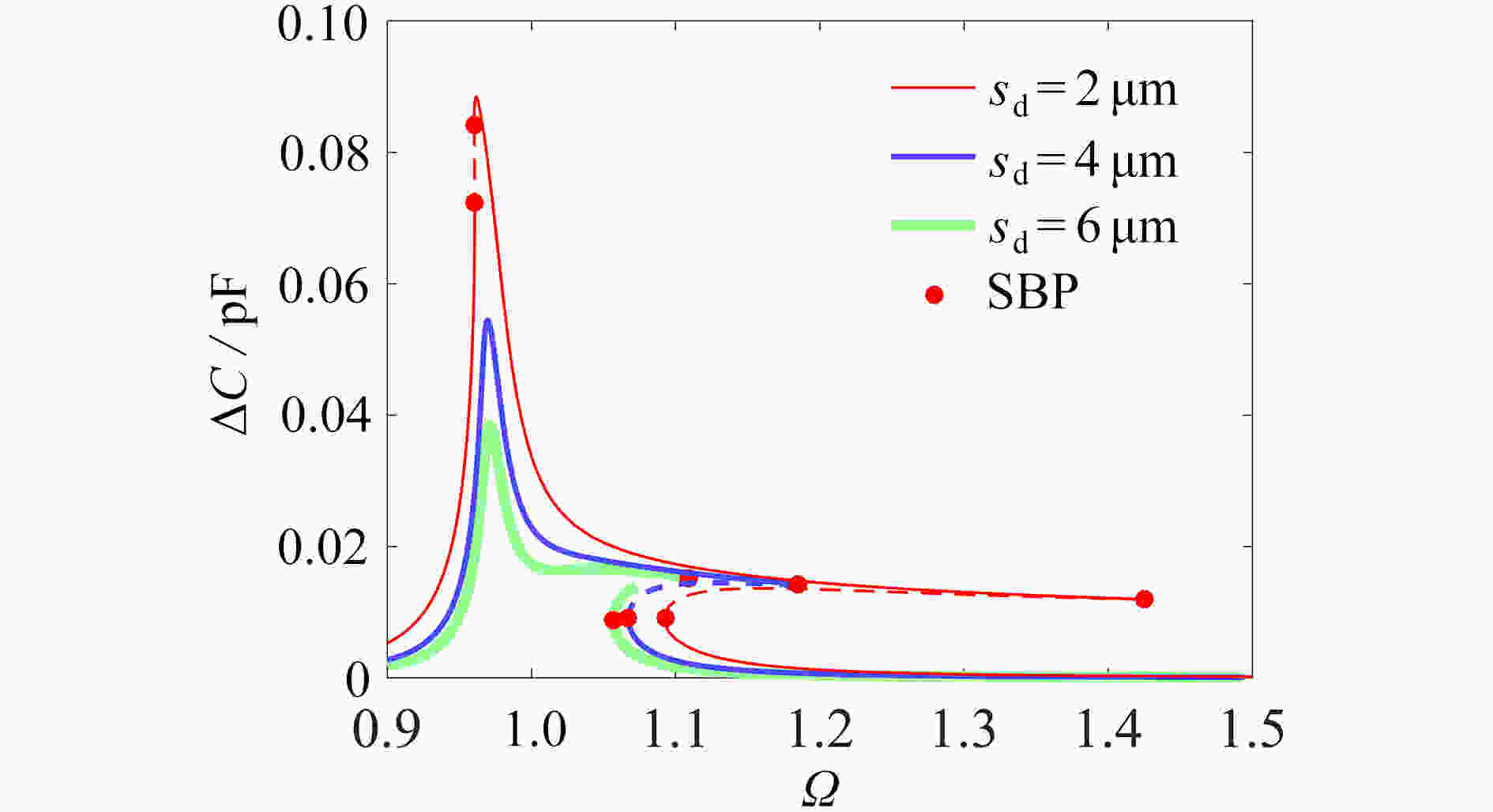
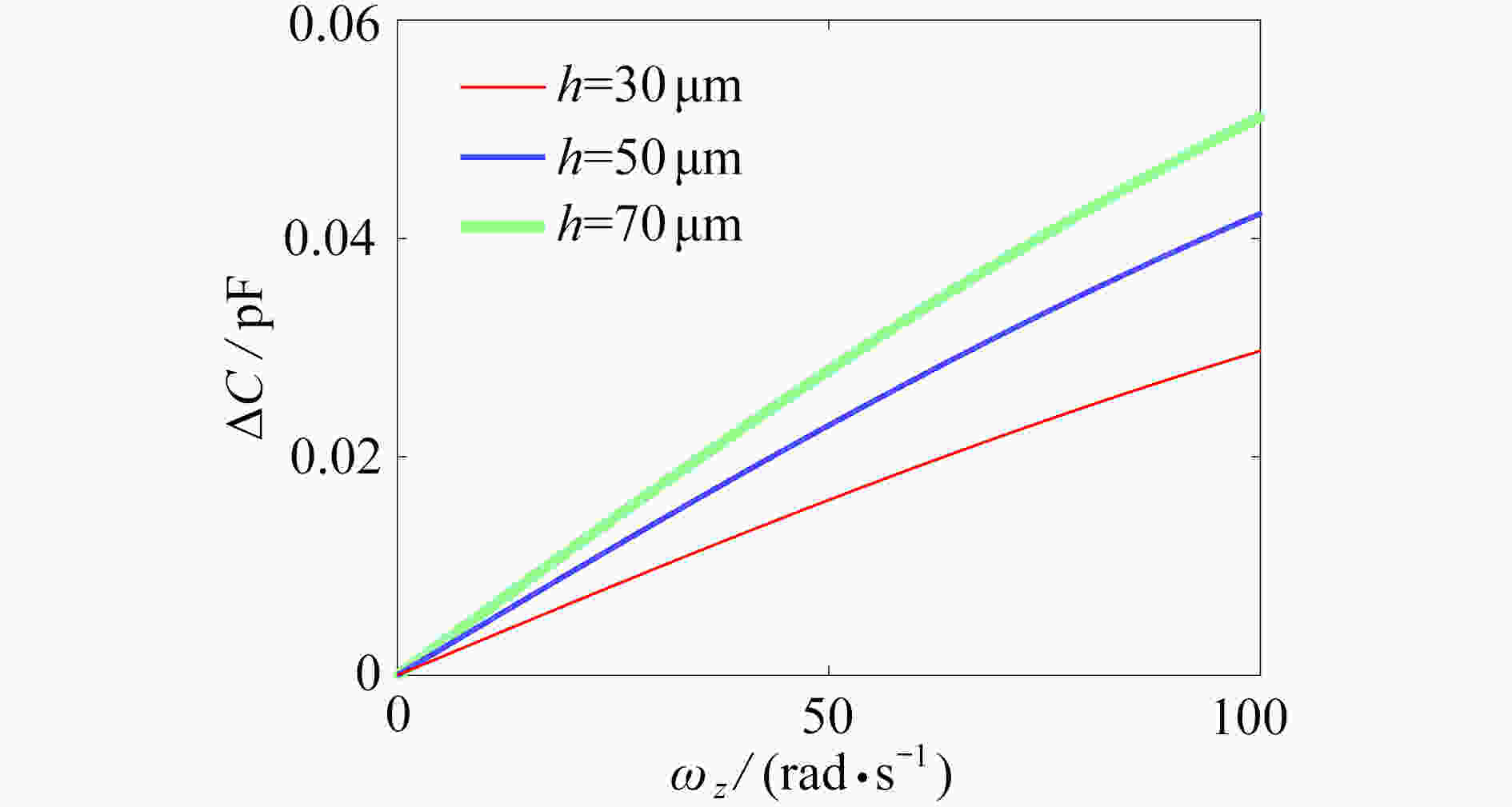
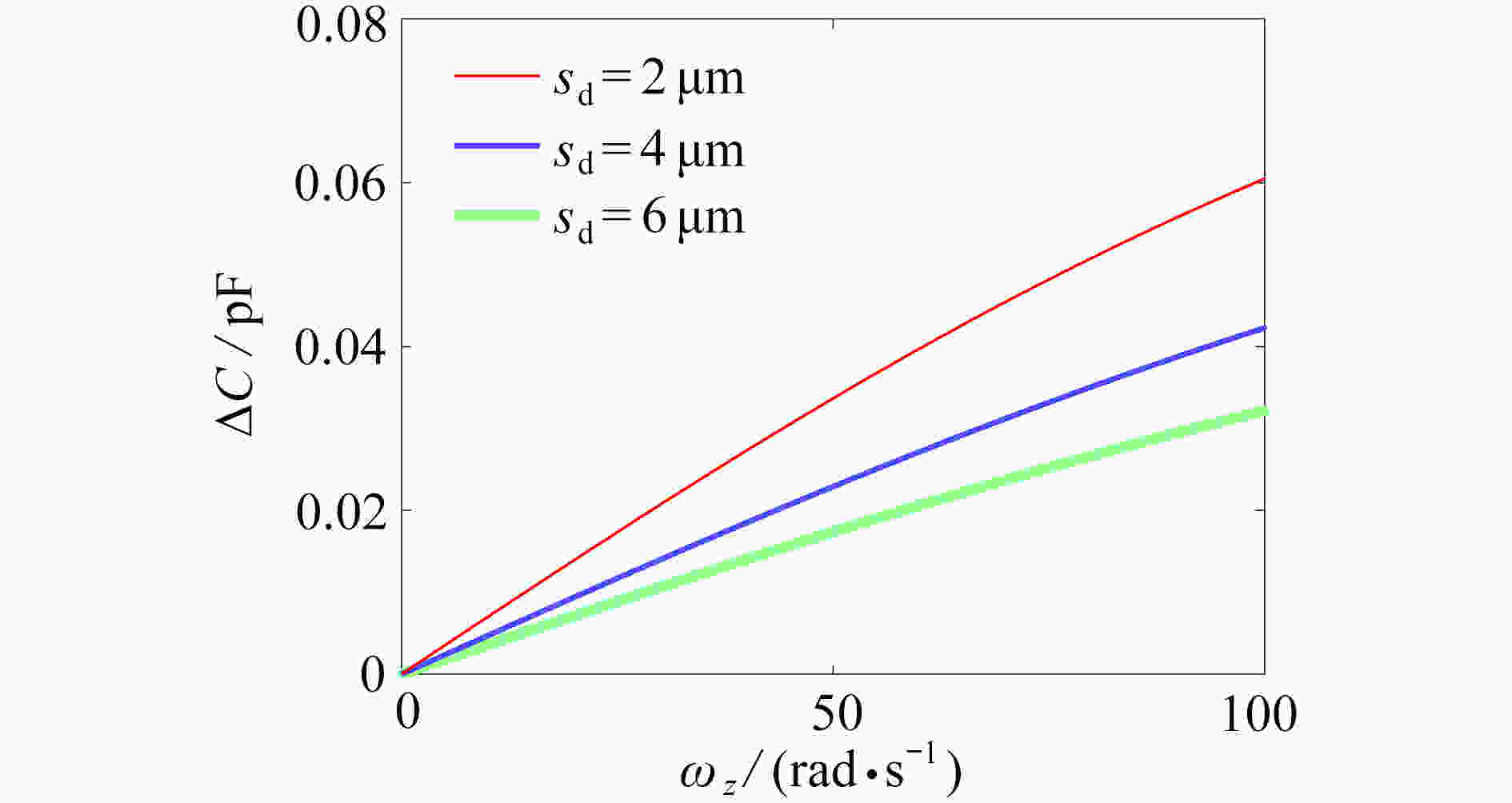
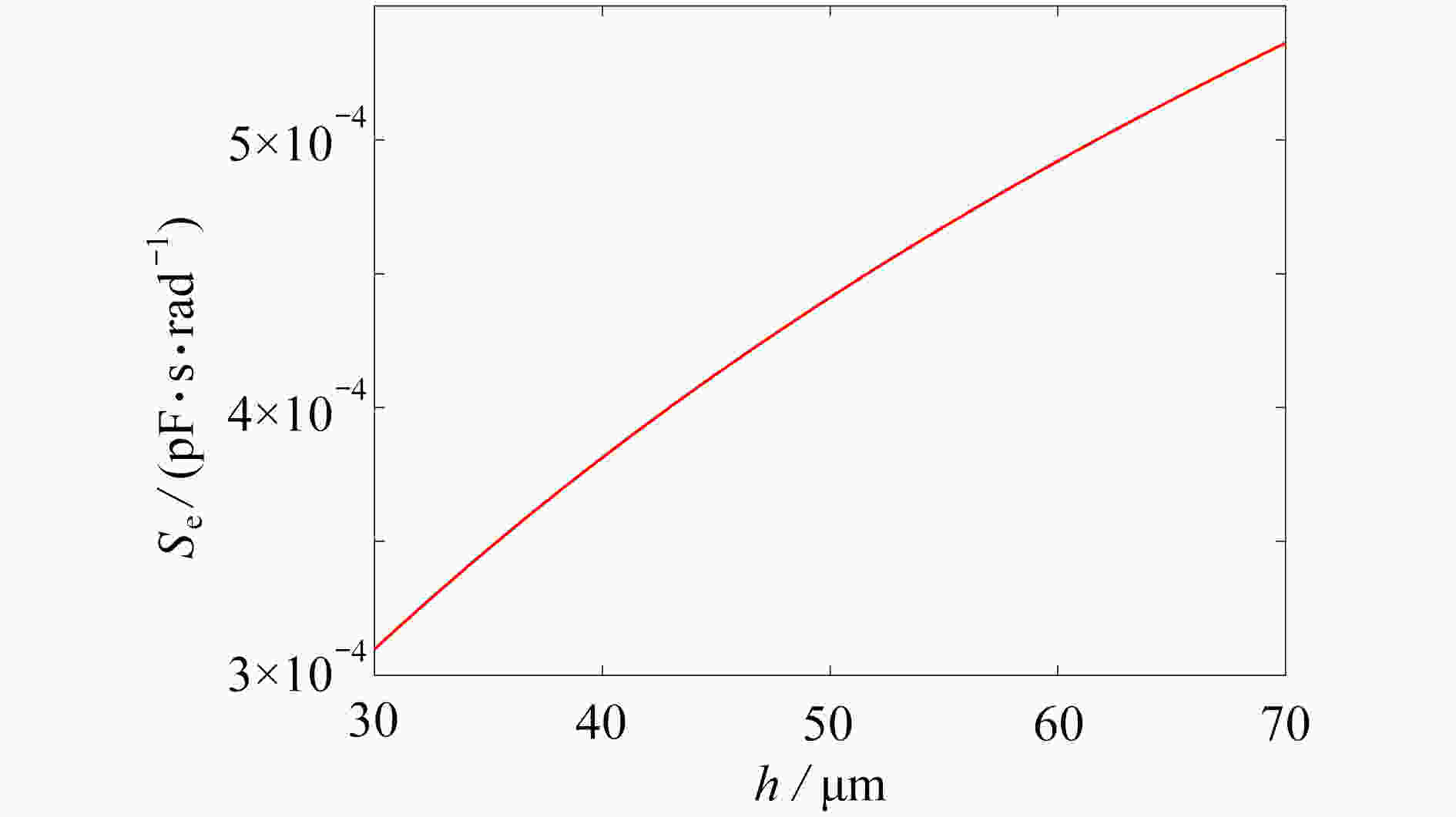
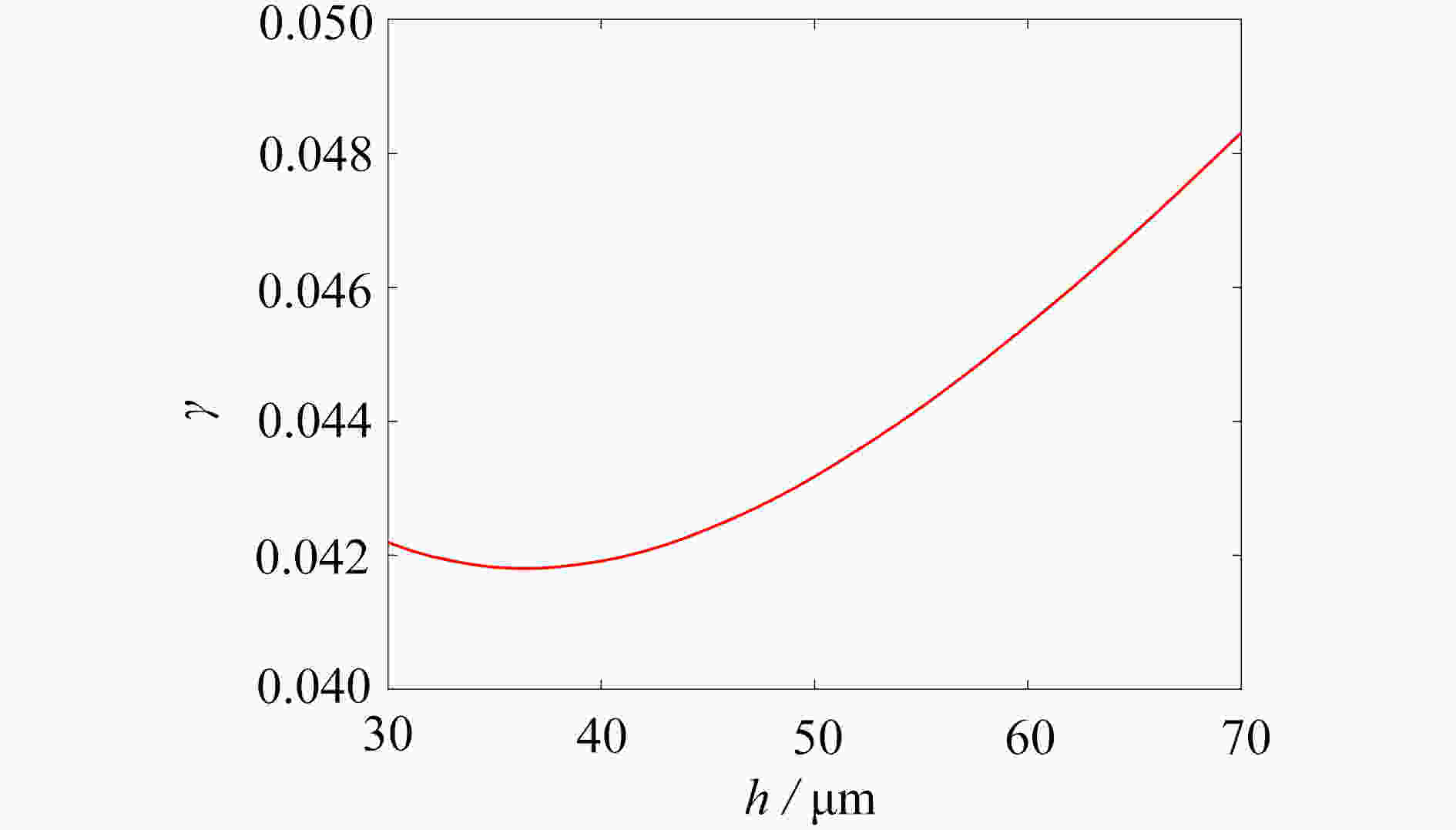
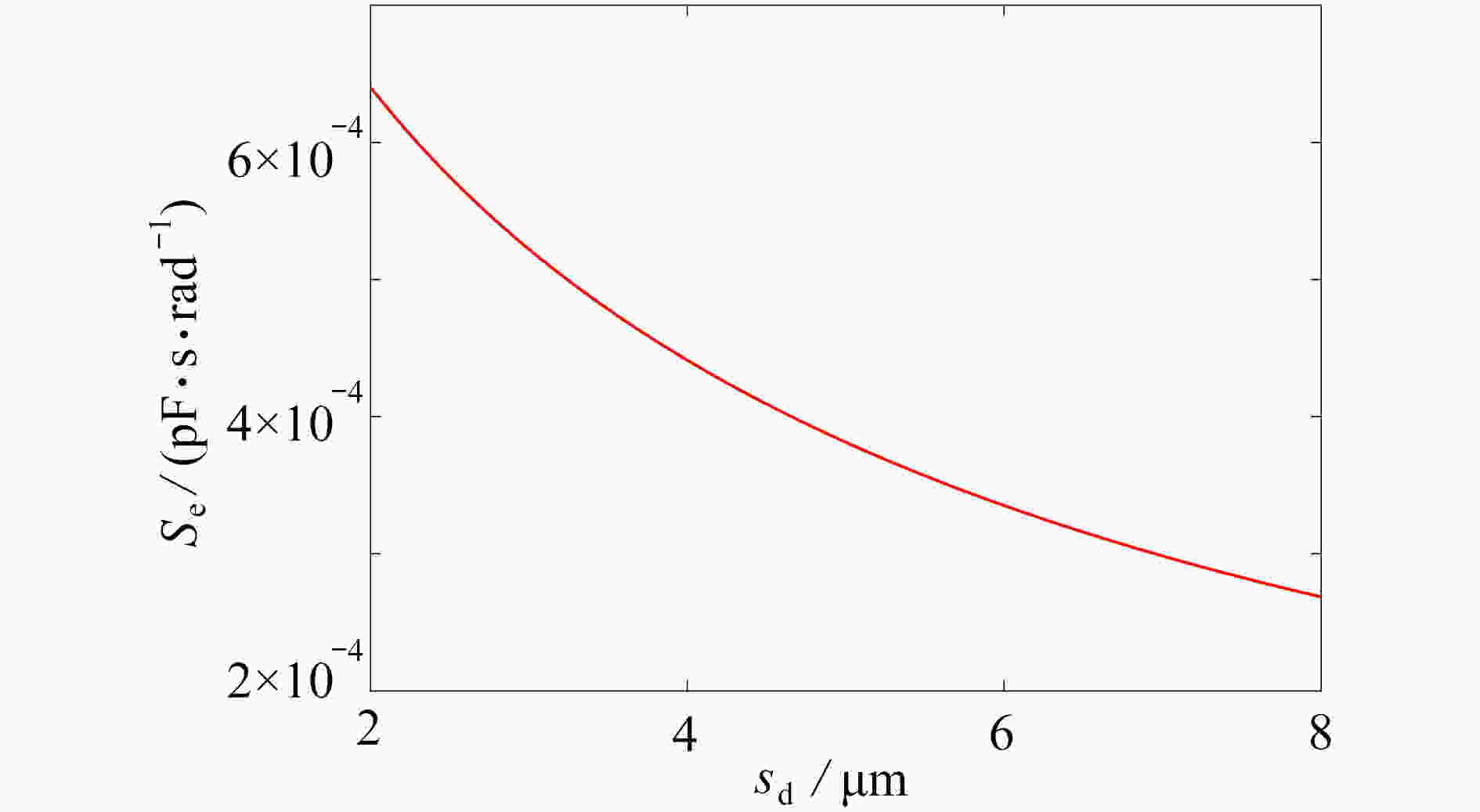
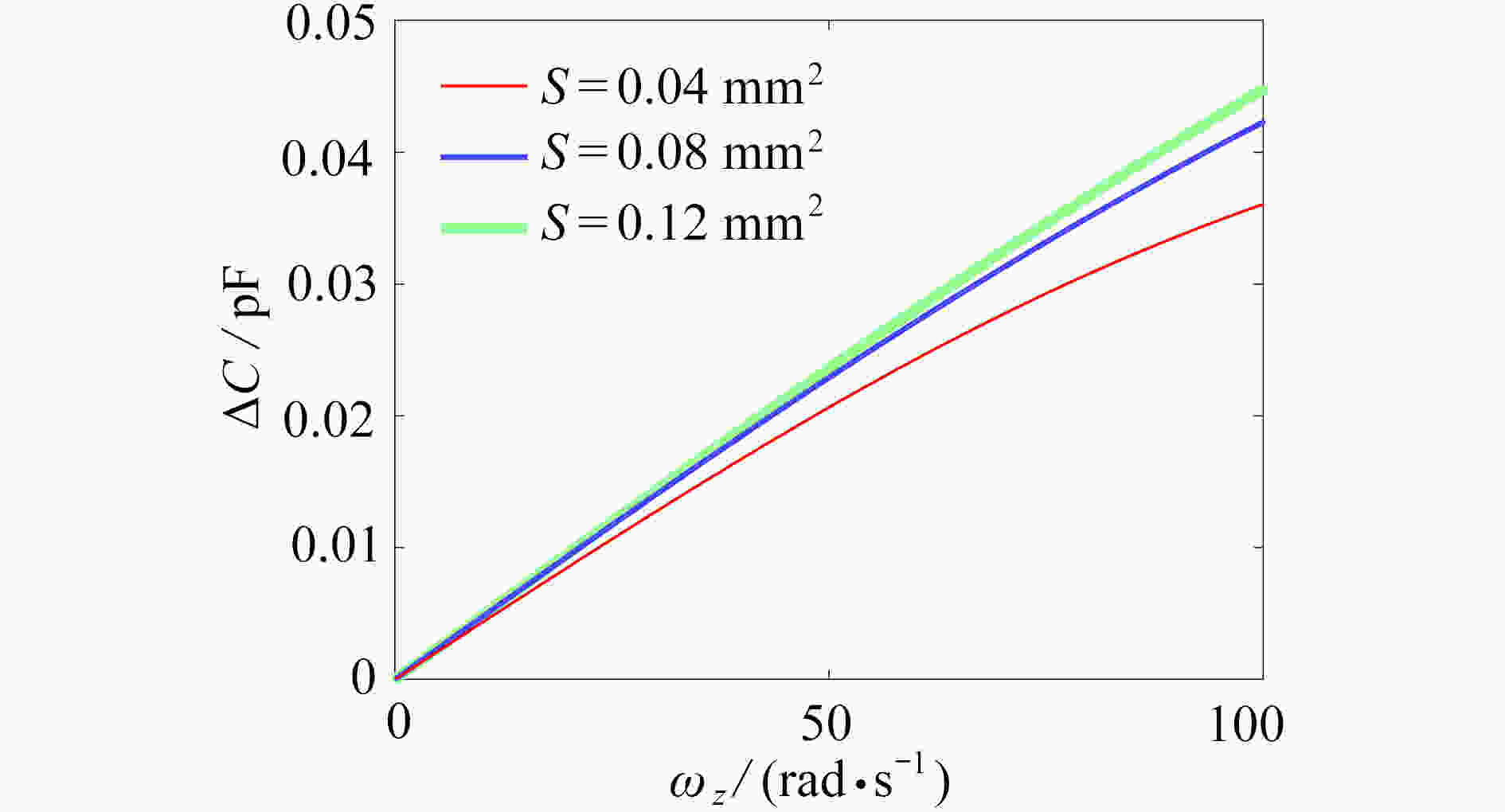
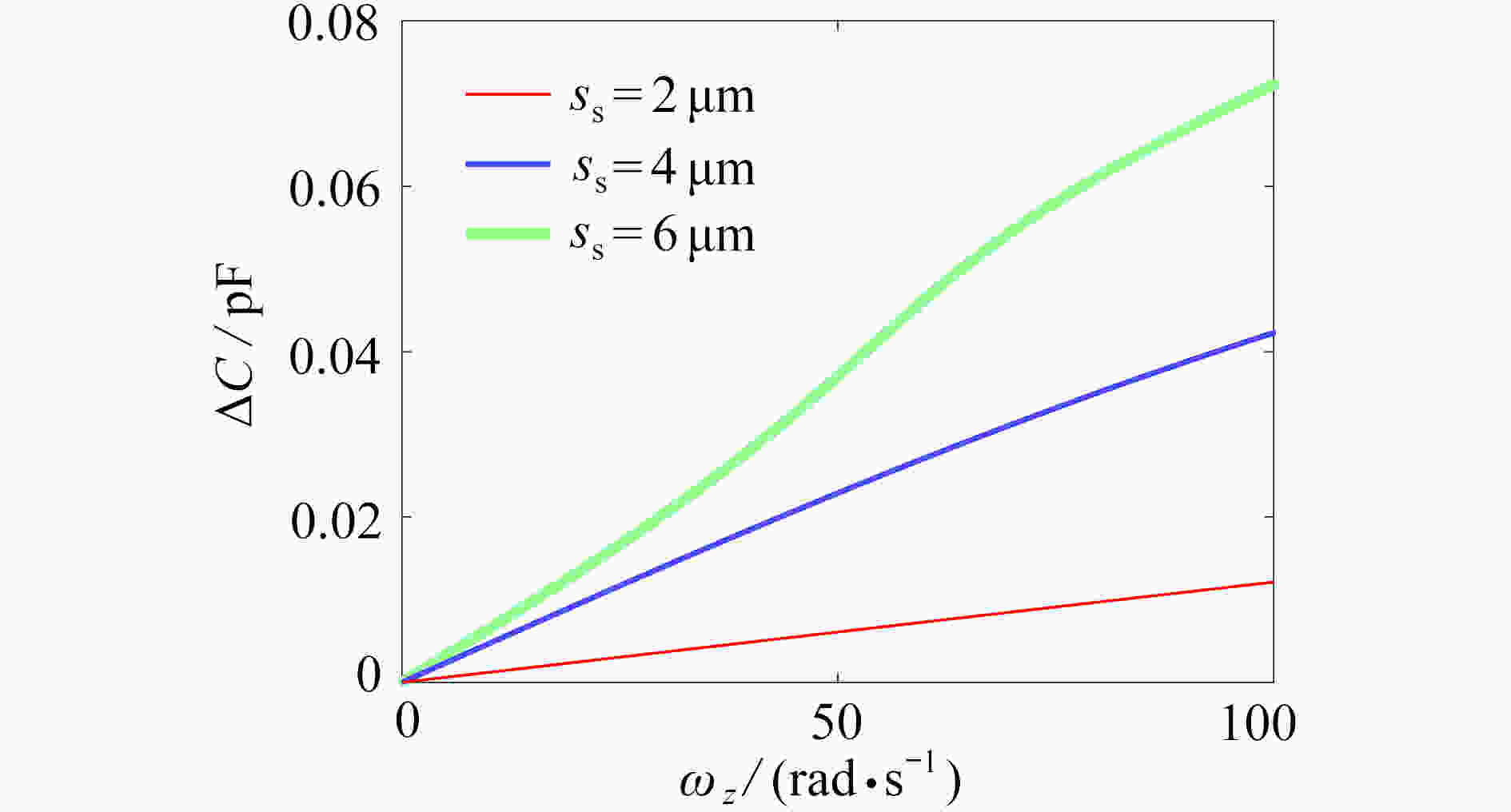
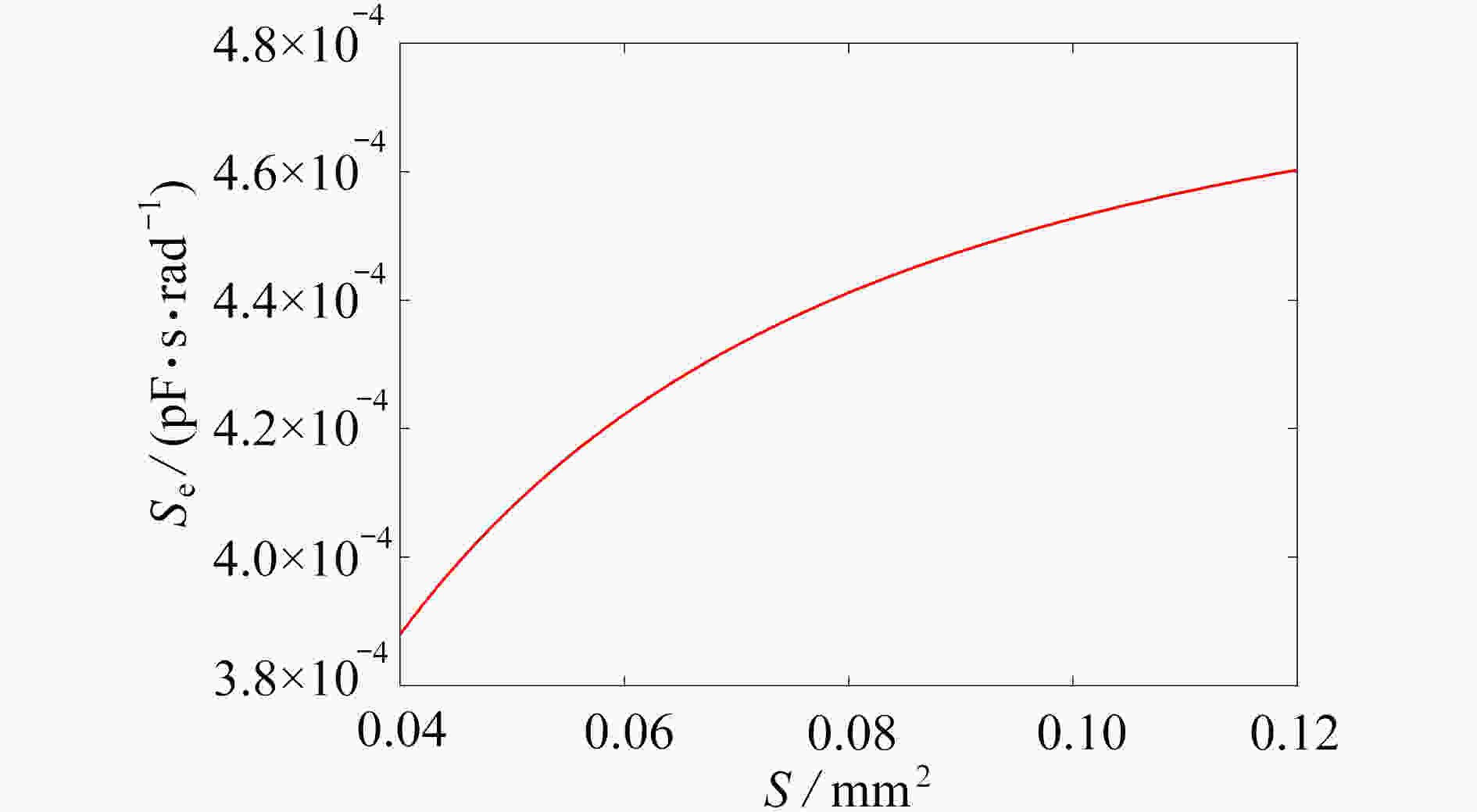
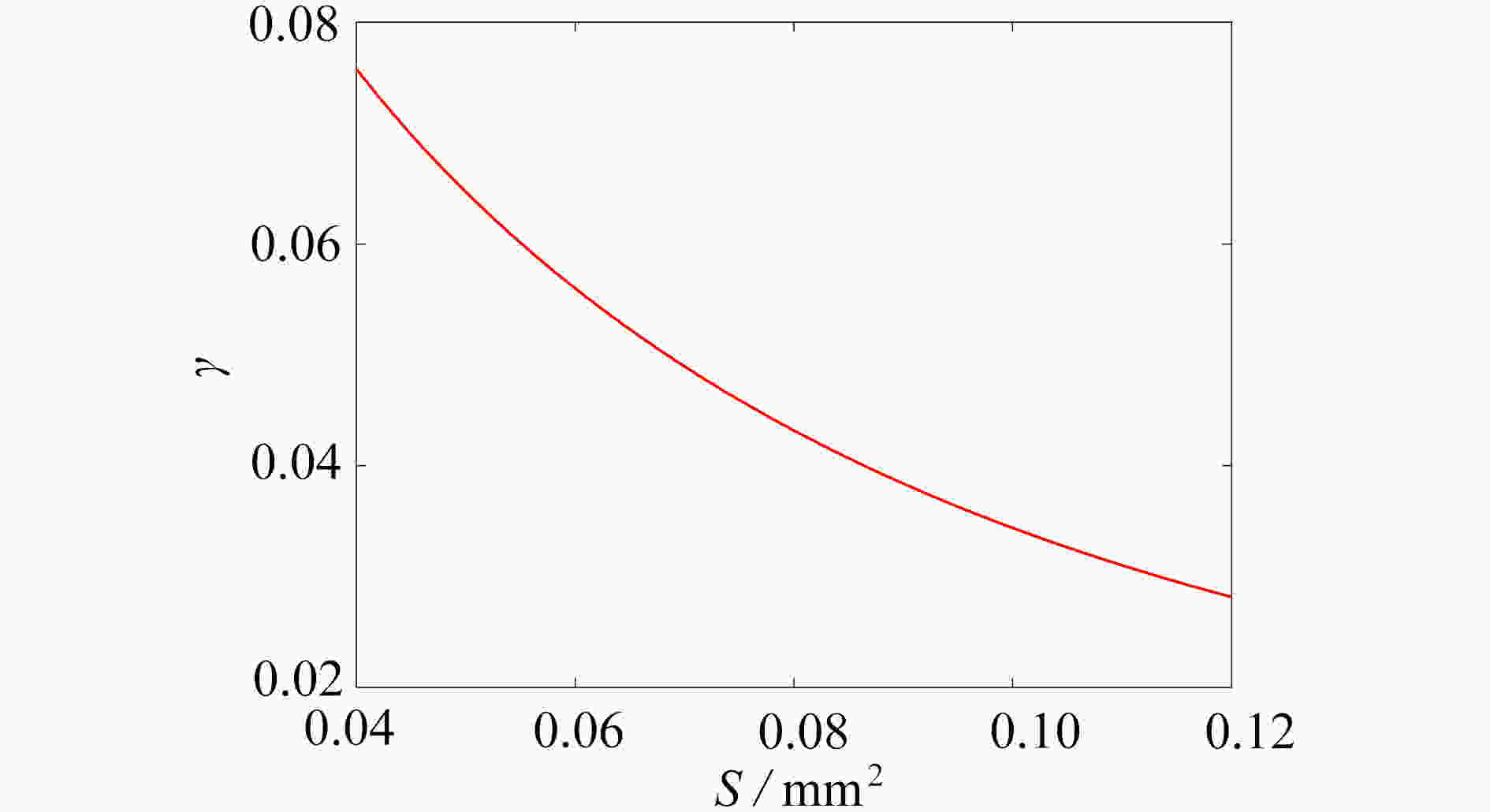
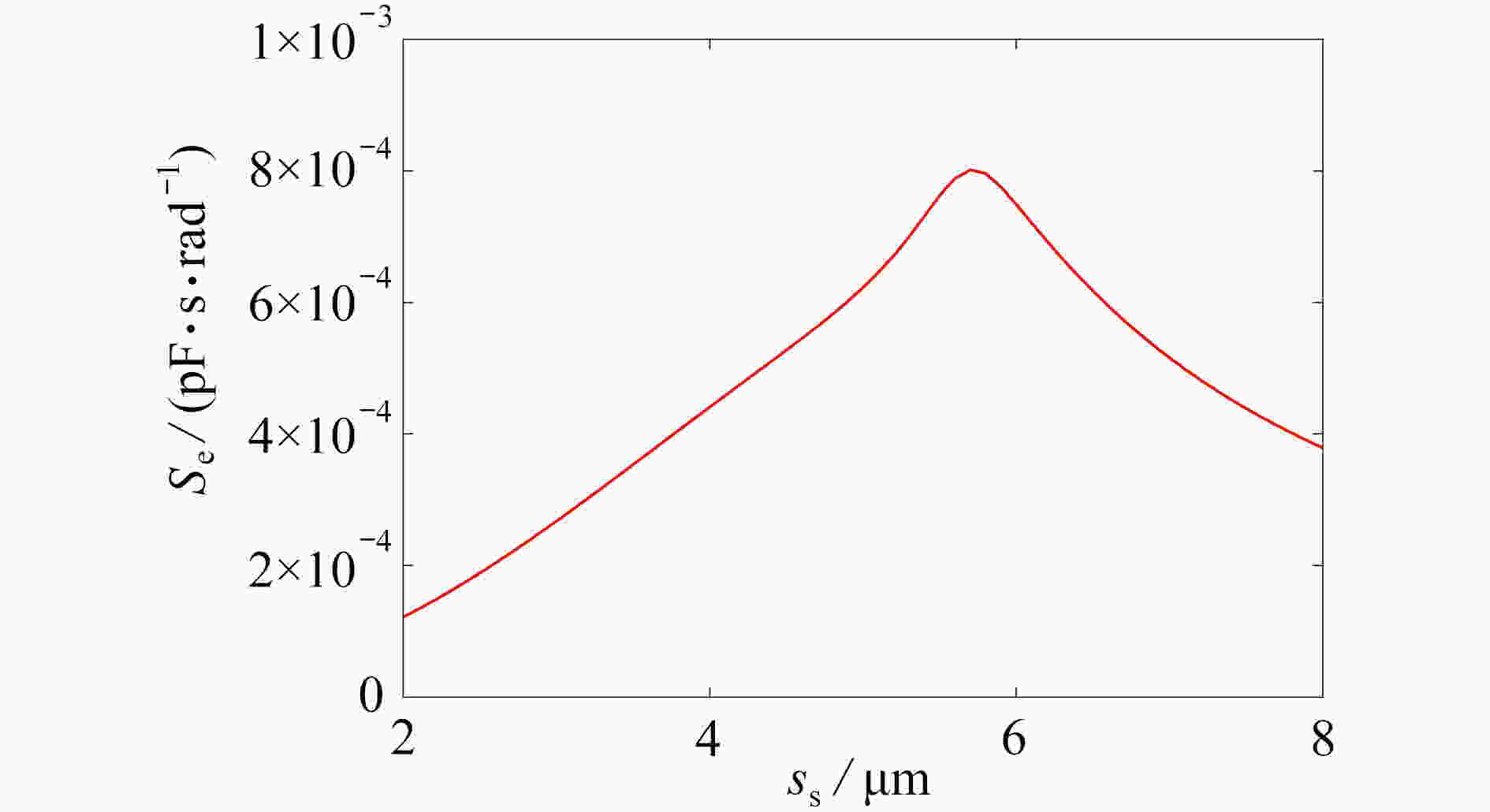
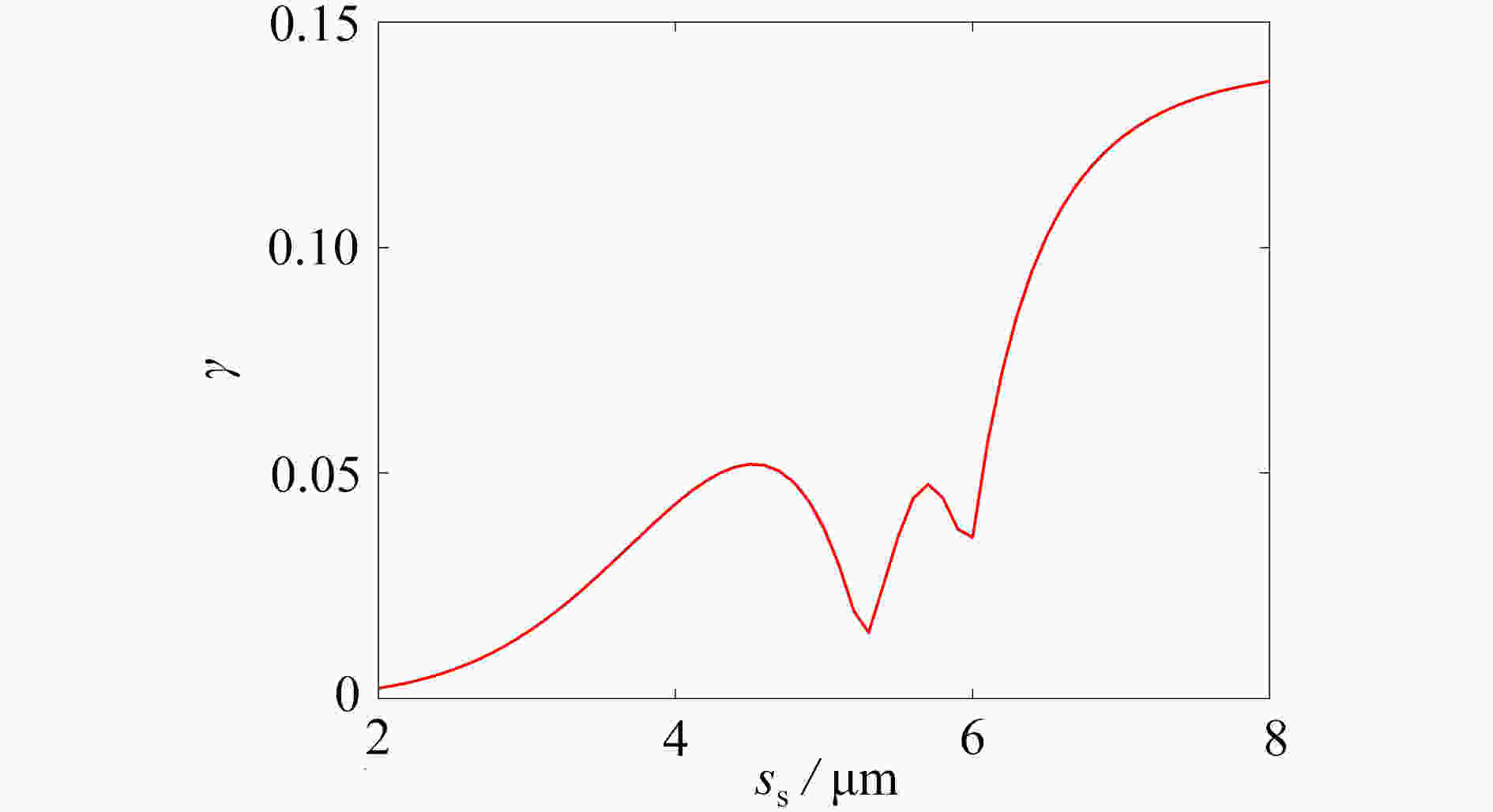
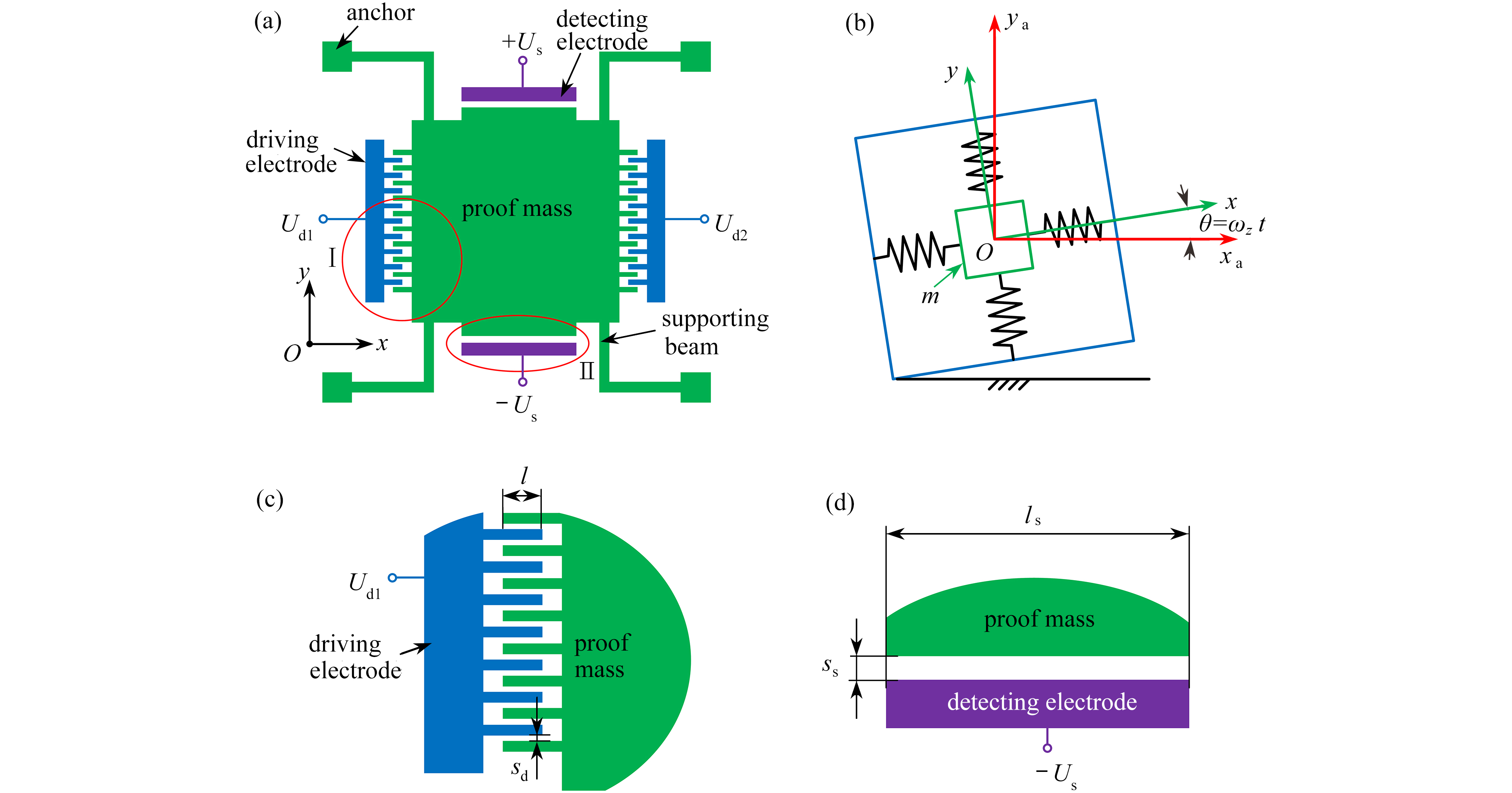
为研究结构参数对静电驱动微机械陀螺动态性能的影响,考虑支承刚度的三次非线性和静电力的分式非线性,基于两自由度动力学模型,利用谐波平衡法结合留数定理求解了系统的周期响应,得到了驱动电极的梳齿厚度、梳齿间隙以及检测电极的极板面积、极板间隙变化时电容变化量随驱动力频率和载体角速度的变化曲线,以及电容灵敏度和非线性度随这些参数的变化曲线。结果表明,检测电容变化量随驱动力频率的变化曲线会呈现明显的非线性特征,即第二个峰向右倾斜,从而引起跳跃现象。驱动电极的梳齿厚度、梳齿间隙和检测电极的极板间隙对检测电容变化量随载体角速度的变化影响较大,而检测电极的极板面积的影响很小。驱动电极梳齿厚度、梳齿间隙以及检测电极的极板面积对电容灵敏度和非线性度的影响基本上是线性的,但检测电极的极板间隙对电容灵敏度和非线性度的影响是非线性的。
Abstract:In view of the cubic nonlinear stiffness and the nonlinear electrostatic force in fraction form, a 2DOF model was analyzed with the harmonic balance method and the residue theorem, and the effects of structure parameters on dynamic performances of micro-machined gyroscopes were studied. The variations of the capacitance with the driving force frequency and the carrier angular velocity were obtained for different thicknesses and gaps of driving electrode comb teeth, different electrode plate areas and different detecting electrode gaps. In addition, the variations of sensitivity and nonlinearity with these structure parameters were also presented. It is found that, the variation curves of the detection capacitance with the driving force frequency show obvious nonlinear characteristics. In other words, the 2nd peak leans rightward, which results in jumping. The effects of thicknesses and gaps of driving electrode comb teeth, and gaps between detecting electrode plates on the variation curves of the capacitance with the carrier angular velocity are much greater than those of detecting electrode plate areas. The variations of sensitivity and nonlinearity with thicknesses and gaps of driving electrode comb teeth and detecting electrode plate areas, are approximately linear, however, those with gaps between detecting electrode plates are nonlinear.
-
-
[1] GUO Z S, CHENG F C, LI B Y, et al. Research development of silicon MEMS gyroscopes: a review[J]. Microsystem Technologies, 2015, 21(10): 2053-2066. doi: 10.1007/s00542-015-2645-x [2] 杨波, 吴磊, 周浩, 等. 双质量解耦硅微陀螺仪的非理想解耦特性研究和性能测试[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2015, 23(6): 794-799. (YANG Bo, WU Lei, ZHOU Hao, et al. Non-ideal decoupled characteristics’ research and system performance test of dual-mass decoupled silicon micro-gyroscope[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2015, 23(6): 794-799.(in Chinese) [3] ASOKANTHAN S F, WANG T. Nonlinear instabilities in a vibratory gyroscope subjected to angular speed fluctuations[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2008, 54(1/2): 69-78. doi: 10.1007/s11071-008-9347-1 [4] BRAGHIN F, RESTA F, LEO E, et al. Nonlinear dynamics of vibrating MEMS[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2007, 134(1): 98-108. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2006.10.041 [5] MARTYNENKO Y G, MERKURIEV I V, PODALKOV V V. Dynamics of a ring micromechanical gyroscope in the forced-oscillation mode[J]. Gyroscopy and Navigation, 2010, 1(1): 43-51. doi: 10.1134/S2075108710010074 [6] MOJAHEDI M, AHMADIAN M T, FIROOZBAKHSH K. The oscillatory behavior, static and dynamic analyses of a micro/nano gyroscope considering geometric nonlinearities and intermolecular forces[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2013, 29(6): 851-863. doi: 10.1007/s10409-013-0083-5 [7] KACEM N, HENTZ S, BAGUET S, et al. Forced large amplitude periodic vibrations of non-linear Mathieu resonators for microgyroscope applications[J]. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 2011, 46(10): 1347-1355. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnonlinmec.2011.07.008 [8] LAJIMI S A M, HEPPLER G R, ABDEL-RAHMAN E M. Primary resonance of an amplitude-frequency-modulation beam-rigid body microgyroscope[J]. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 2015, 77: 364-375. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnonlinmec.2015.07.002 [9] 尚慧琳, 张涛, 文永蓬. 参数激励驱动微陀螺系统的非线性振动特性研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2017, 36(1): 102-107. (SHANG Huilin, ZHANG Tao, WEN Yongpeng. Nonlinear vibration behaviors of a micro-gyroscope system actuated by a parametric excitation[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(1): 102-107.(in Chinese) [10] 文永蓬, 尚慧琳. 微陀螺动力学建模与非线性分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2015, 34(4): 69-73. (WEN Yongpeng, SHANG Huilin. Dynamic modeling and nonlinear analysis for a microgyroscope[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(4): 69-73.(in Chinese) [11] 郝淑英, 李会杰, 张辰卿, 等. 检测刚度非线性对双检测微陀螺灵敏度稳定性影响[J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(24): 46-52. (HAO Shuying, LI Huijie, ZHANG Chenqing, et al. Influence of sense stiffness nonlinearity on the sensitivity stability of a double-sense micro-gyroscope[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(24): 46-52.(in Chinese) [12] 郝淑英, 李伟雄, 李会杰, 等. 驱动刚度非线性对双检测微陀螺性能的影响[J]. 振动与冲击, 2019, 38(14): 131-137. (HAO Shuying, LI Weixiong, LI Huijie, et al. Effect of driving stiffness nonlinearity on the performance of a double sense-mode micro gyroscope[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2019, 38(14): 131-137.(in Chinese) [13] HAMED Y S, EL-SAYED A T, EL-ZAHAR E R. On controlling the vibrations and energy transfer in MEMS gyroscope system with simultaneous resonance[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2016, 83(3): 1687-1704. doi: 10.1007/s11071-015-2440-3 [14] AWREJCEWICZ J, STAROSTA R, SYPNIEWSKA-KAMIŃSKA G. Complexity of resonances exhibited by a nonlinear micromechanical gyroscope: an analytical study[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2019, 97(3): 1819-1836. doi: 10.1007/s11071-018-4530-5 [15] TSAI N C, SUE C Y. Stability and resonance of micro-machined gyroscope under nonlinearity effects[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2009, 56(4): 369-379. doi: 10.1007/s11071-008-9404-9 [16] NITZAN S H, TAHERI-TEHRANI P, DEFOORT M, et al. Countering the effects of nonlinearity in rate-integrating gyroscopes[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(10): 3556-3563. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2016.2533480 [17] LESTEV M A, TIKHONOV A A. Nonlinear phenomena in the dynamics of micromechanical gyroscopes[J]. Vestnik St Petersburg University: Mathematics, 2009, 42(1): 53-57. doi: 10.3103/S1063454109010087 [18] LEE K B. Principles of Micro Electromechanical System[M]. Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons International Rights, 2011. [19] 钟玉泉. 复变函数论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2013.ZHONG Yuquan. Complex Variable Theory[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2013. (in Chinese) -




 下载:
下载:





 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号