Identification of Crack Tip Positions Based on the Scaled Boundary Finite Element Method and the Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm
-
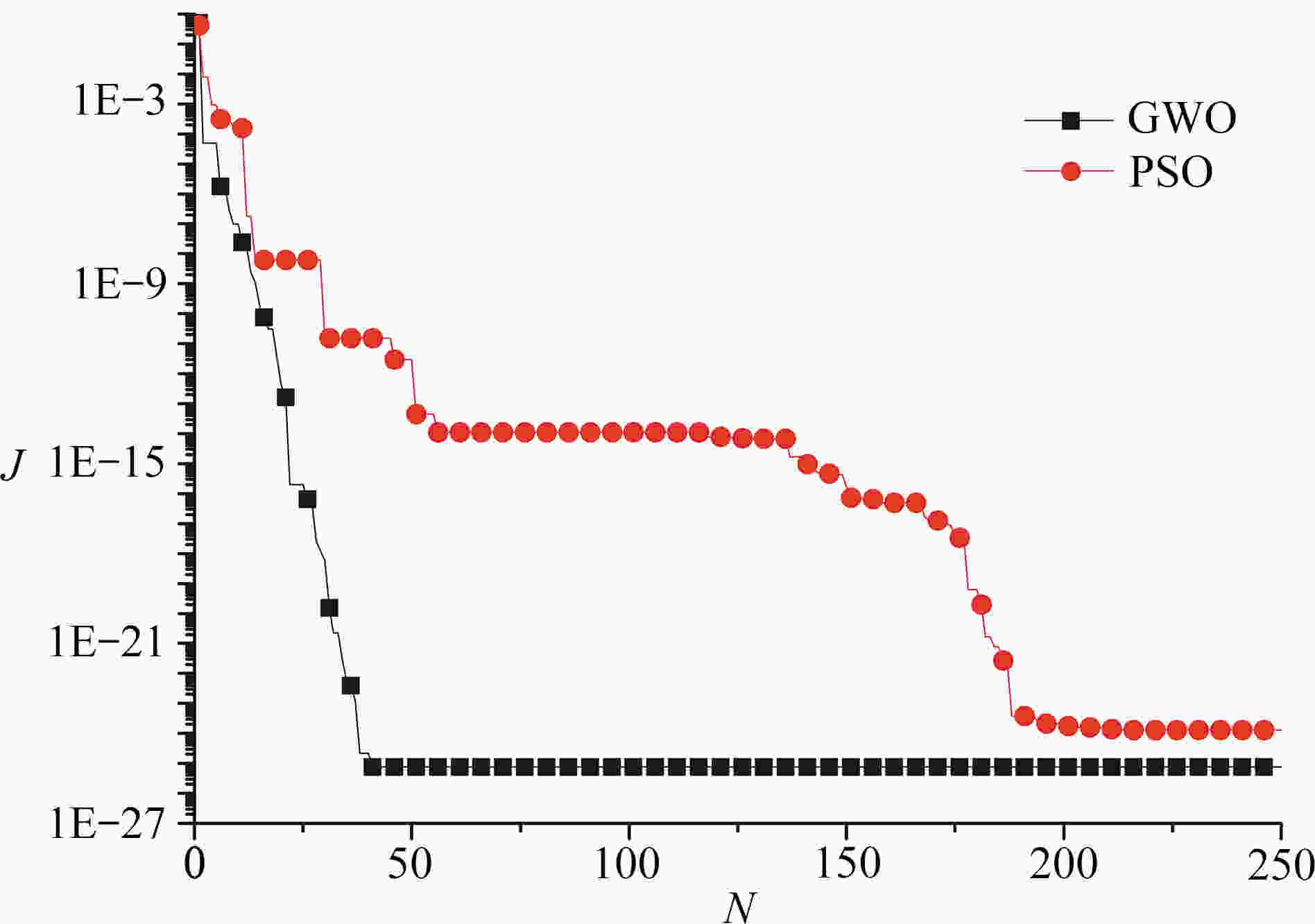
摘要: 基于比例边界有限元法(SBFEM)和灰狼优化(GWO)算法,提出了一种裂纹尖端识别方法。首先,借助SBFEM解决断裂力学问题特有的优势,快速准确地计算出反演所需的测点位移,并验证了正问题求解的正确性。其次,建立与裂纹尖端位置有关的目标函数,将求解裂纹尖端位置转换为求解目标函数最小值的优化问题。最后,采用GWO算法对目标函数进行了优化,进而搜索裂纹尖端的最佳位置。数值算例结果表明:利用SBFEM的高精度、半解析的优点,在反演过程中采用其求解正问题是非常有效的;GWO算法具有良好的全局收敛性,且相比经典的粒子群算法,能够更快速准确地搜索出裂纹尖端的位置;GWO算法具有较好的抗噪性。Abstract: Based on the scaled boundary finite element method (SBFEM) and the grey wolf optimization algorithm (GWO), an identification method for crack tips was proposed. Firstly, the special advantages of the SBFEM were used to solve the fracture mechanics problem, the displacements of measurement points required in the inversion process were quickly and accurately calculated, and the correctness of the solution to the forward problem was verified in advance. Then, the objective function related to the crack tip position was established, and the identification of the crack tip position was converted to the optimization problem of solving the minimum value of the objective function. Finally, the GWO was used to optimize the objective function, that is, to search for the optimal position of the crack tip. The numerical example results show that, it is very effective to solve forward problems in the inversion process with the high precision and semi-analytical advantages of the SBFEM. The grey wolf optimization algorithm has good global convergence property, and can search for the crack tip position more quickly and accurately compared with the classical particle swarm optimization. The grey wolf optimization algorithm has good noise resistance.
-
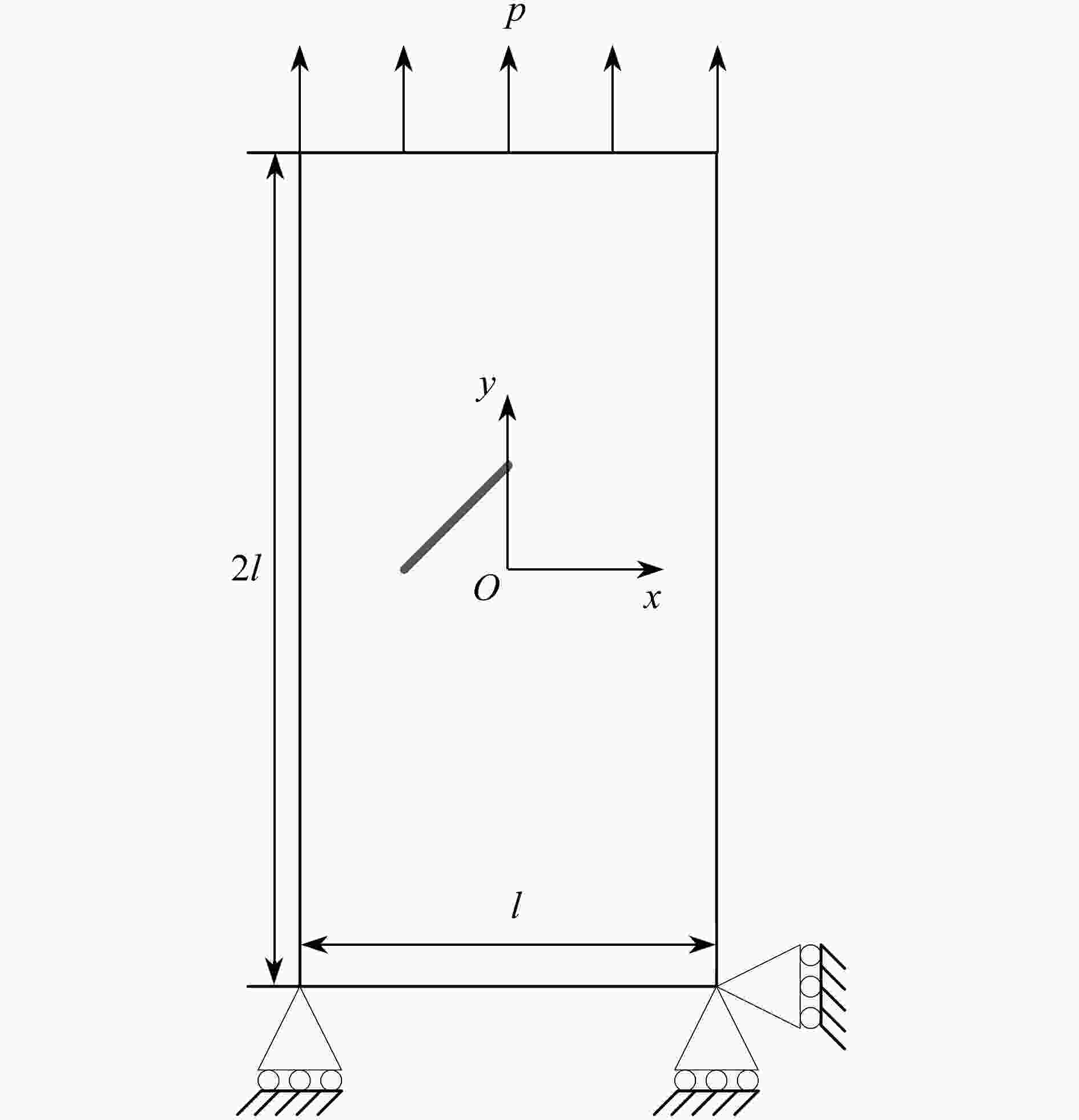
表 1 中心裂纹应力强度因子
Table 1. The stress intensity factor of the center crack
SBFEM
KI / (MPa·m1/2)analytical solution KI / (MPa·m1/2) relative error
δ / %1.4886 1.4819 0.452 表 2 中心裂纹尖端识别结果
Table 2. Identification results of center crack tips
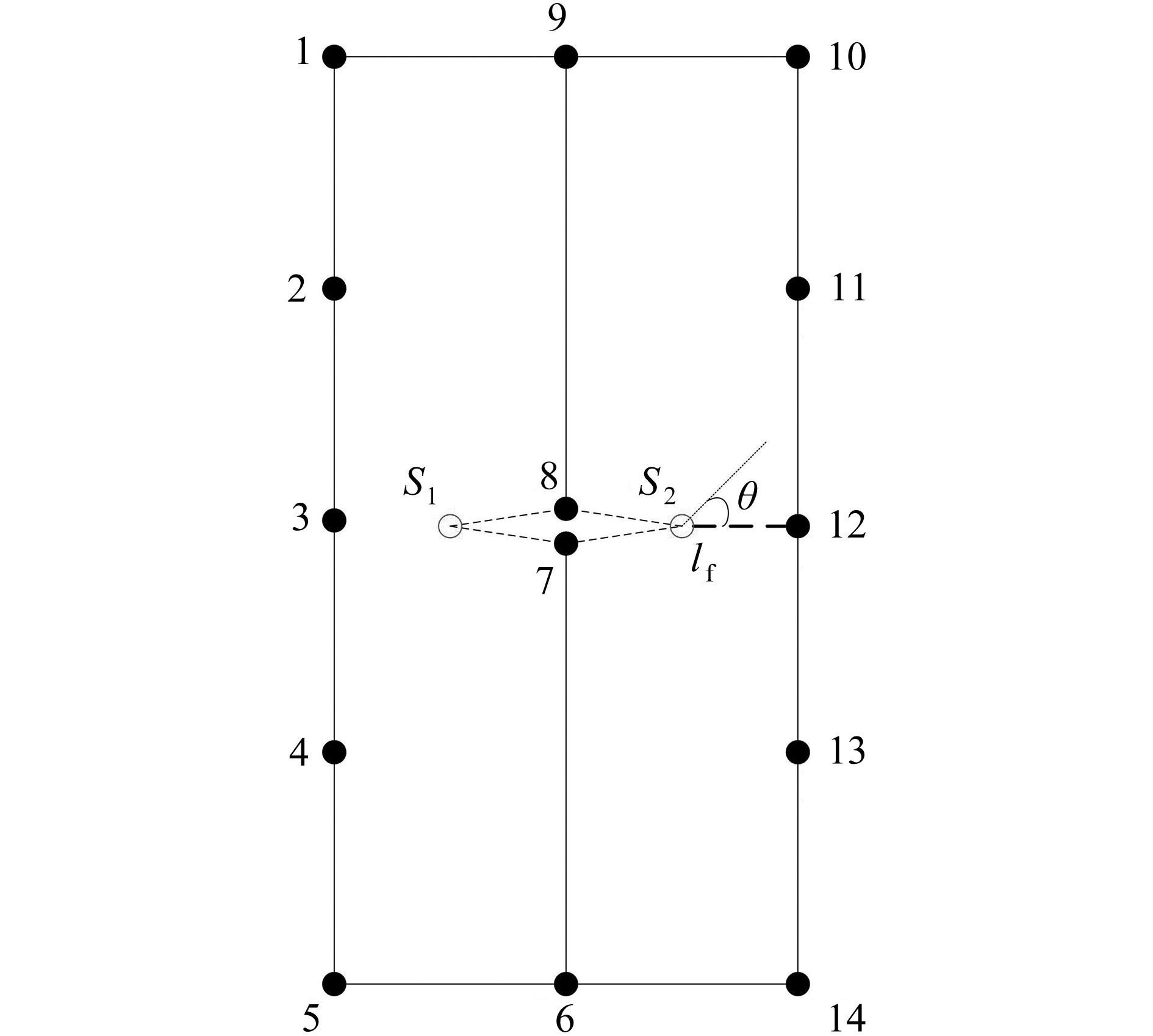
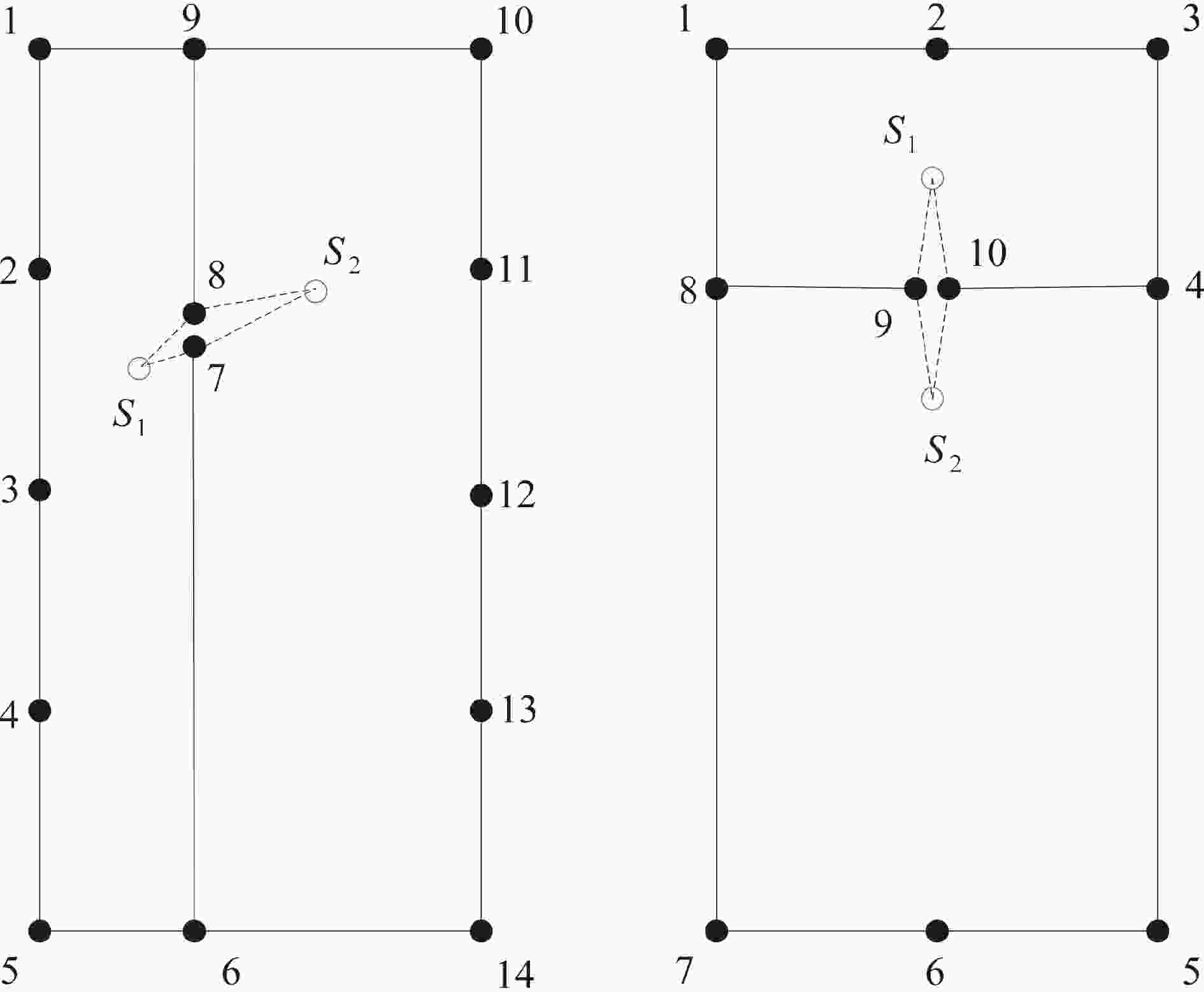
case crack tip position (x, y) / m objective function value 1 (−0.5001, 0.0096),(0.4999, 0.0086) 2.49×10−13 2 (−0.5000, 0.0119),(0.5007, 0.0273) 2.87×10−12 3 (−0.5013, 0.0419),(0.5008, 0.0131) 6.03×10−12 4 (−0.4997, 0.0245),(0.5003, 0.0473) 1.02×10−11 表 3 GWO和PSO算法识别边缘裂纹尖端位置结果
Table 3. The position of the edge crack tip identified with GWO and PSO algorithm
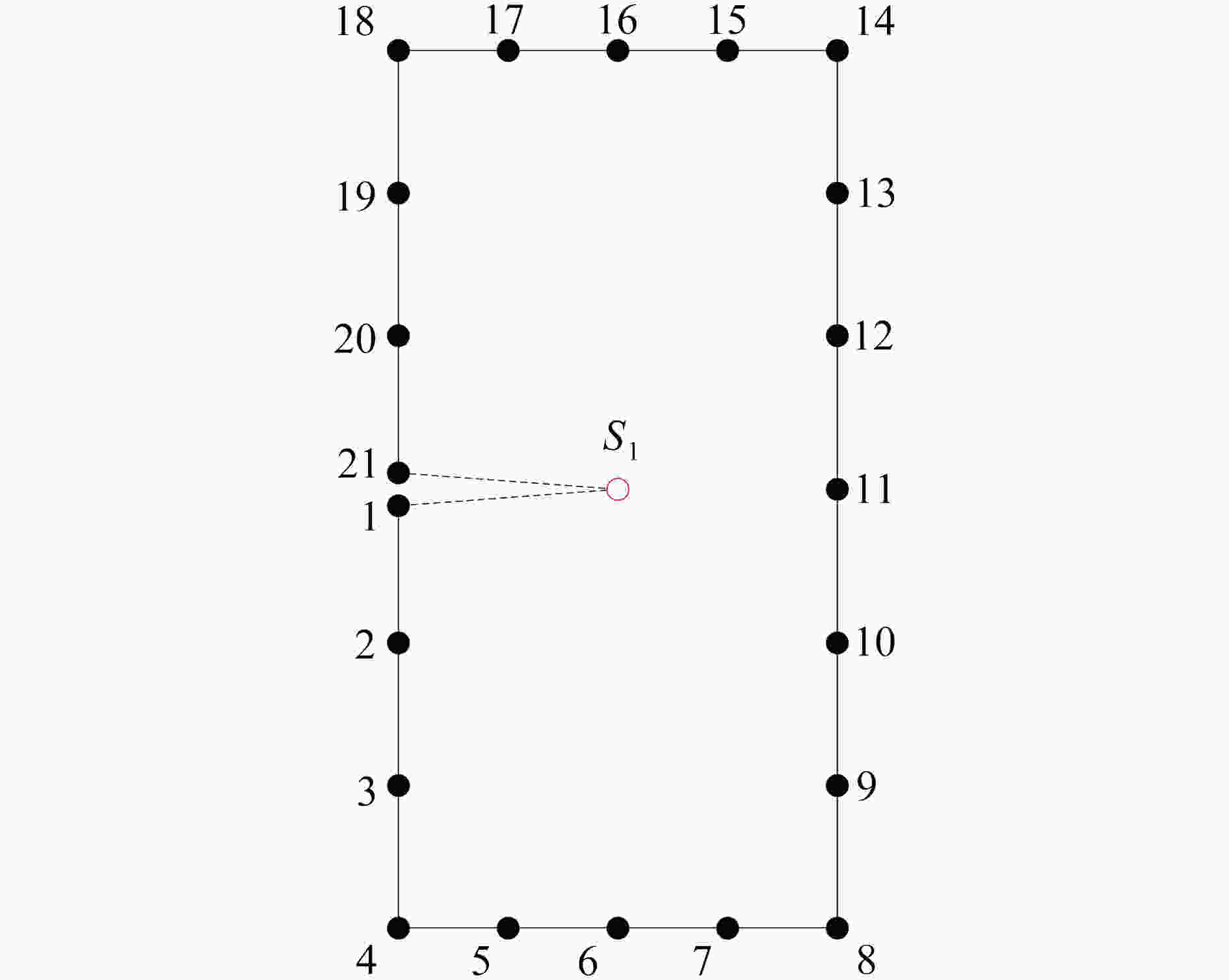
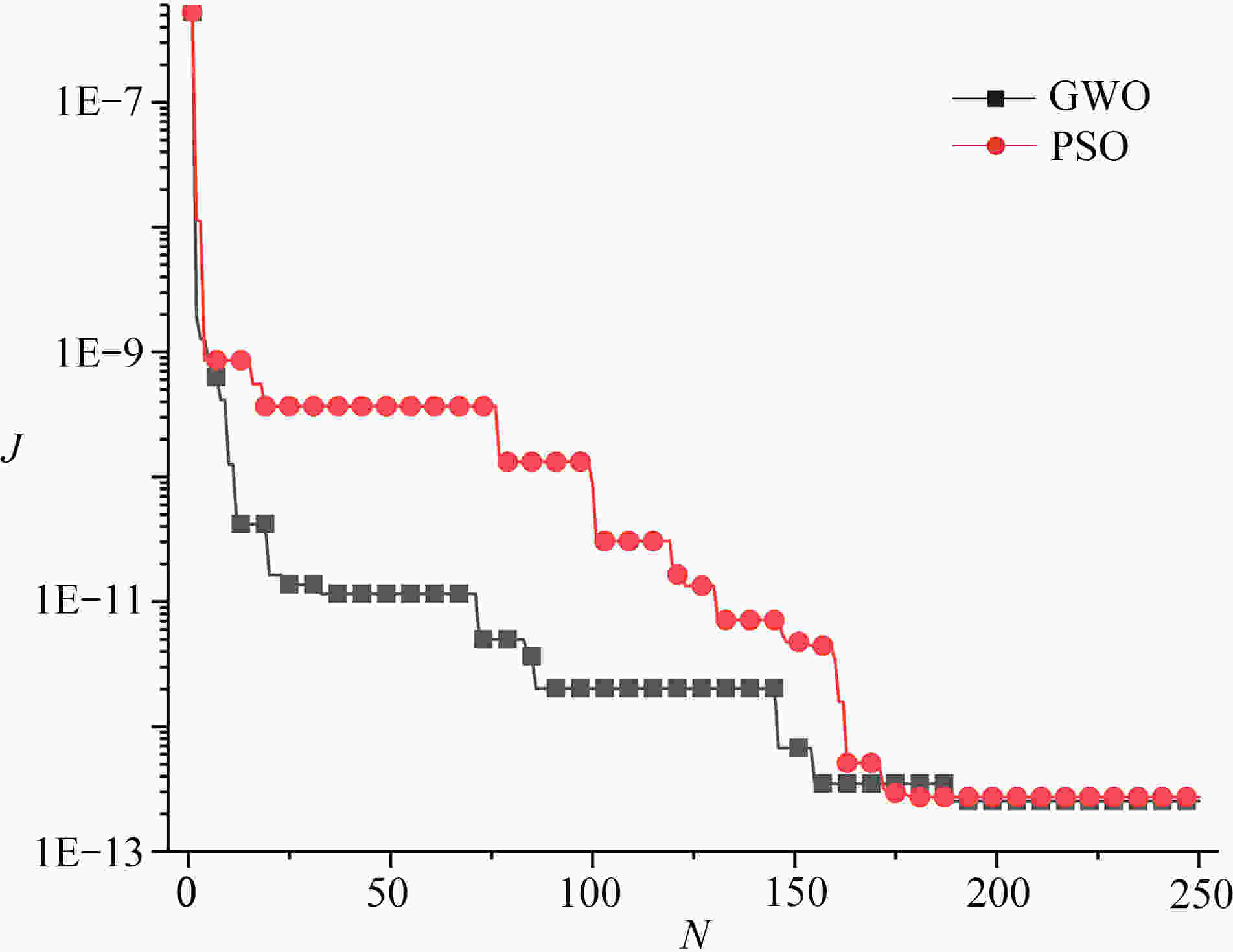
real position (x, y) / m (x, y)GWO / m (x, y)PSO / m (0, 0) (−1.953×10−12, 3.621×10−12) (−2.877×10−12, 2.886×10−12) 表 4 GWO和PSO算法识别斜裂纹尖端位置
Table 4. The position of the oblique crack tips identified with GWO algorithm and PSO algorithm
real position (x, y) / m (x, y)GWO / m (x, y)PSO / m (−0.5, 0) (−0.499 8, −9.2407×10−3) (−0.499 8, −1.0472×10−3) (0, 0.5) (2.2318×10−4, 0.503 0) (5.1873×10−4, 0.504 2) 表 5 考虑正则化时裂纹尖端识别结果
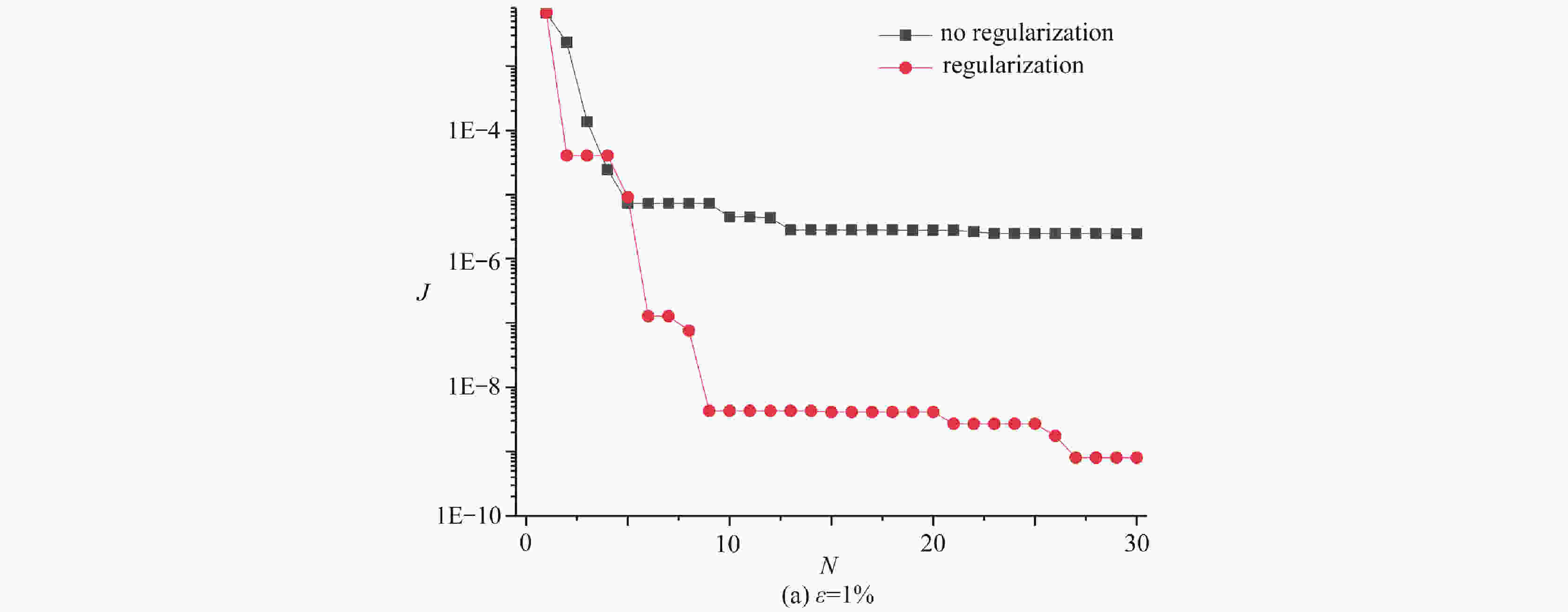
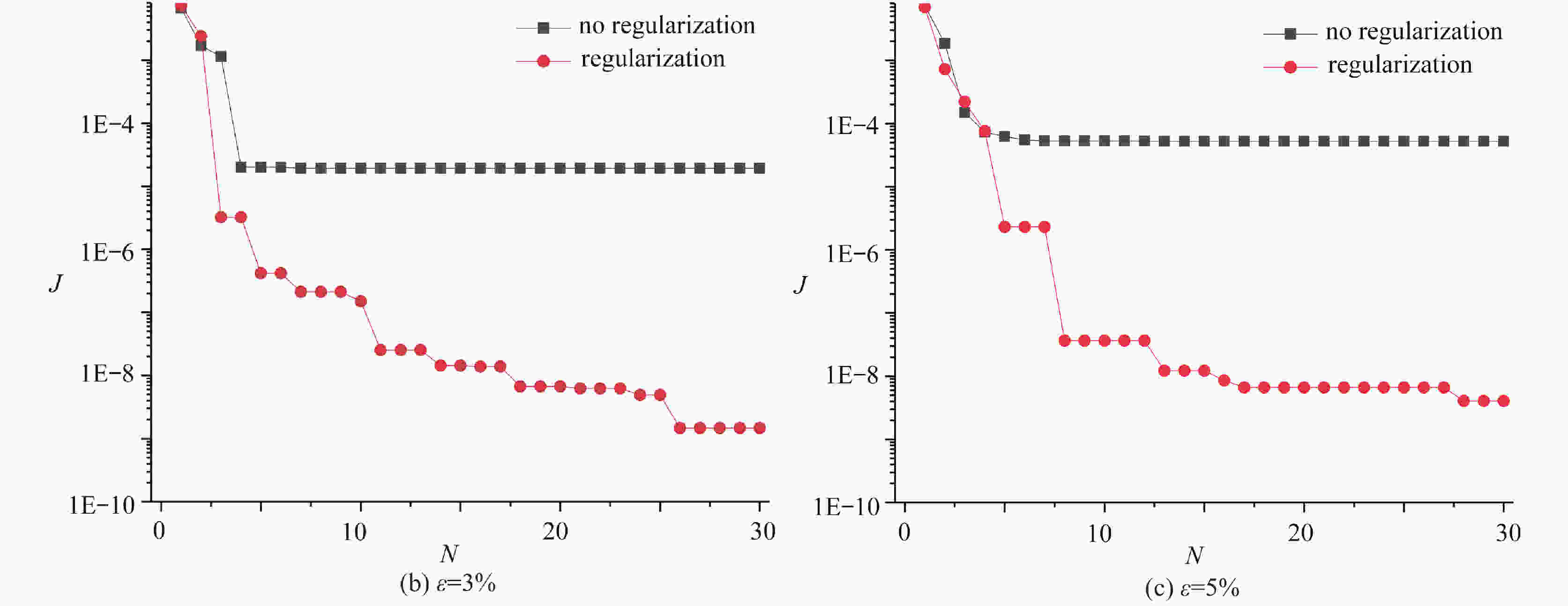
Table 5. Identification results of the crack tip in view of the regularization scheme
error ε 1% 3% 5% objective function value of GWO result 4.537×10−13 3.153×10−12 4.109×10−11 objective function value of PSO result 6.501×10−10 2.088×10−9 1.030×10−8 crack tip position of GWO result (x,y)GWO /cm (1.904×10−4, −4.229×10−5) (8.294×10−4, 8.427×10−4) (2.501×10−3, 5.543×10−4) crack tip position of PSO result (x,y)PSO /cm (−2.713×10−2, 5.981×10−3) (−6.183×10−2, 1.237×10−2) (8.414×10−2, −1.315×10−2) -
[1] 史君林, 赵建平. 含三晶交多晶体沿晶断裂数值建模方法研究[J]. 机械强度, 2008, 40(4): 844-851. (SHI Junlin, ZHAO Jianping. Investigation on finite element modeling method of with triple junction polycrystalline intergranular fracture[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2008, 40(4): 844-851.(in Chinese) [2] LING X, KEANINI R G, CHERUKUR H P. A non-iterative finite element method for inverse heat conduction problems[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2003, 56(9): 1315-1334. doi: 10.1002/nme.614 [3] LIU J, SUN X S, HAN X, et al. A novel computational inverse technique for load identification using the shape function method of moving least square fitting[J]. Computers and Structures, 2014, 144: 127-137. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruc.2014.08.002 [4] 余波, 吴月, 聂川宝, 等. 动载荷识别的非迭代法研究[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2019, 40(5): 473-489. (YU Bo, WU Yue, NIE Chuanbao, et al. A non-iterative method for dynamic load identification[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2019, 40(5): 473-489.(in Chinese) [5] FLETCHER R, REEVES C M. Function minimization by conjugate gradients[J]. The Computer Journal, 1964, 7(2): 149-154. doi: 10.1093/comjnl/7.2.149 [6] YANG Y C. Solving the two-dimensional inverse heat source problem through the linear least squares error method[J]. International Journal of Heat & Mass Transfer, 1998, 41(2): 393-398. [7] CUI M, ZHAO Y, XU B B, et al. Inverse analysis for simultaneously estimating multi-parameters of temperature-dependent thermal conductivities of an Inconel in a reusable metallic thermal protection system[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 125: 480-488. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.06.113 [8] UDAYRAJ, MULANI K, TALUKDAR P, et al. Performance analysis and feasibility study of ant colony optimization, particle swarm optimization and cuckoo search algorithms for inverse heat transfer problems[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 89: 359-378. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2015.05.015 [9] BONABEAU E, DORIGO M, MARCO D R D F, et al. Swarm Intelligence: From Natural to Artificial Systems[M]. New York: Oxford University Press, 1999. [10] KENNEDY J, EBERHART R C. Particle swarm optimization[C]// Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks. Piscataway, NJ, 1995. [11] PANDA T R, SWAMY A K. An improved artificial bee colony algorithm for pavement resurfacing problem[J]. International Journal of Pavement Research and Technology, 2018, 11(5): 509-516. doi: 10.1016/j.ijprt.2018.04.001 [12] 周焕林, 严俊, 余波, 等. 识别含热源瞬态热传导问题的热扩散系数[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2018, 39(2): 160-169. (ZHOU Huanlin, YAN Jun, YU Bo, et al. Identification of thermal diffusion coefficients for transient heat conduction problems with heat sources[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2018, 39(2): 160-169.(in Chinese) [13] LIEU Q X, LEE J. Modeling and optimization of functionally graded plates under thermo-mechanical load using isogeometric analysis and adaptive hybrid evolutionary firefly algorithm[J]. Composite Structures, 2017, 179: 89-106. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.07.016 [14] MIRJALILI S, MIRJALILI S M, LEWIS A. Grey wolf optimizer[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2014, 69: 46-61. doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2013.12.007 [15] MIRJALILI S, SAREMI S, MIRJALILI S M, et al. Multi-objective grey wolf optimizer: a novel algorithm for multi-criterion optimization[J]. Expert Systems With Applications, 2016, 47: 106-119. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2015.10.039 [16] OZSOYDAN F B. Effects of dominant wolves in grey wolf optimization algorithm[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2019, 83: 105658. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105658 [17] NIU P, NIU S, LIU N, et al. The defect of the Grey wolf optimization algorithm and its verification method[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2019, 171: 37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2019.01.018 [18] GILBERT S. An analysis of the finite element method[J]. Mathematics of Computation, 1974, 41(1): 115-126. [19] BREBBIA C A, TELLES J C F, WROBEL L C. Boundary Element Techniques: Theory and Applications in Engineering[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1984. [20] 郭历伦, 陈忠富, 罗景润, 等. 扩展有限元方法及应用综述[J]. 力学季刊, 2011, 32(4): 612-625. (GUO Lilun, CHEN Zhongfu, LUO Jingrun, et al. A review of the extended finite element method and its applications[J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics, 2011, 32(4): 612-625.(in Chinese) [21] SONG C M. The Scaled Boundary Finite Element Method: Introduction to Theory and Implementation[M/OL]. Wiley Online Library, 2018(2018-06-29) [2021-05-06]. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/book/10.1002/9781119388487. [22] SONG C M, WOLF J P. Semi-analytical representation of stress singularities as occurring in cracks in anisotropic multi-materials with the scaled boundary finite-element method[J]. Computers & Structures, 2002, 80(2): 183-197. [23] SONG C M. Evaluation of power-logarithmic singularities, T-stresses and higher order terms of in-plane singular stress fields at cracks and multi-material corners[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2005, 72(10): 1498-1530. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2004.11.002 [24] SONG C M. Analysis of singular stress fields at multi-material corners under thermal loading[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2006, 65(5): 620-652. doi: 10.1002/nme.1456 [25] DEEKS A J, CHENG L. Potential flow around obstacles using the scaled boundary finite-element method[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2003, 41(7): 721-741. doi: 10.1002/fld.468 [26] ANDREW J, DEEKS A J. Wave diffraction by vertical cylinder using the scaled boundary finite element method[C]//Proceeding CDROM of the Sixth World Congress on Computational Mechanics in Conjunction With the Second Asian Pacific Congress on Computational Mechanics. Beijing, China, 2004. [27] TAO L B, SONG H, CHAKRABARTI S. Scaled boundary FEM solution of short-crested wave diffraction by a vertical cylinder[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 197(1/4): 232-242. [28] SONG H, TAO L B, CHALRABARTI S. Modelling of water wave interaction with multiple cylinders of arbitrary shape[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2010, 229(5): 1498-1513. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2009.10.041 [29] 殷德胜, 尹栓, 周宜红. 裂缝分析的比例边界有限元与有限元耦合的虚拟结构面模型[J]. 计算力学学报, 2014, 31(6): 735-741, 748. (YIN Desheng, YIN Shuan, ZHOU Yihong. Coupled SBFEM and FEM for crack analysis based on virtual discontinuous surface method[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2014, 31(6): 735-741, 748.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7511/jslx201406009 [30] YU B, HU P M, SAPUTRA A A, et al. The scaled boundary finite element method based on the hybrid quadtree mesh for solving transient heat conduction problems[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2021, 89(1): 541-571. [31] WOLF J P, SONG C M. The scaled boundary finite-element method, a primer: derivations[J]. Computers and Structures, 2000, 78(1/3): 191-210. [32] GDOUTOS E E. Fracture Mechanics: an Introduction[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2005. [33] CHEN H L, YU B, ZHOU H L, et al. Identification of transient boundary conditions with improved cuckoo search algorithm and polynomial approximation[J]. Engineering Analysis With Boundary Elements, 2018, 95: 124-141. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2018.07.006 -




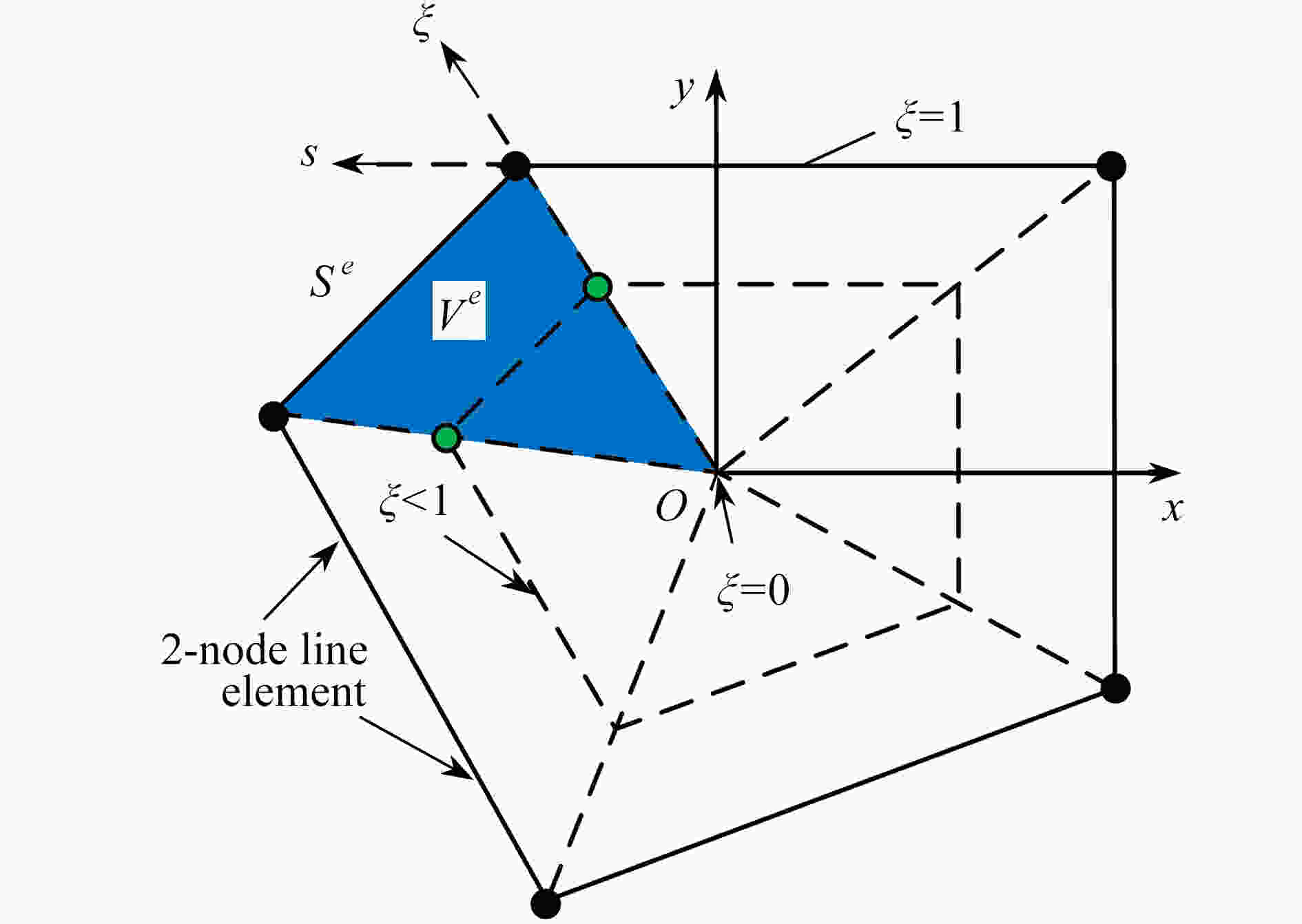
 下载:
下载:
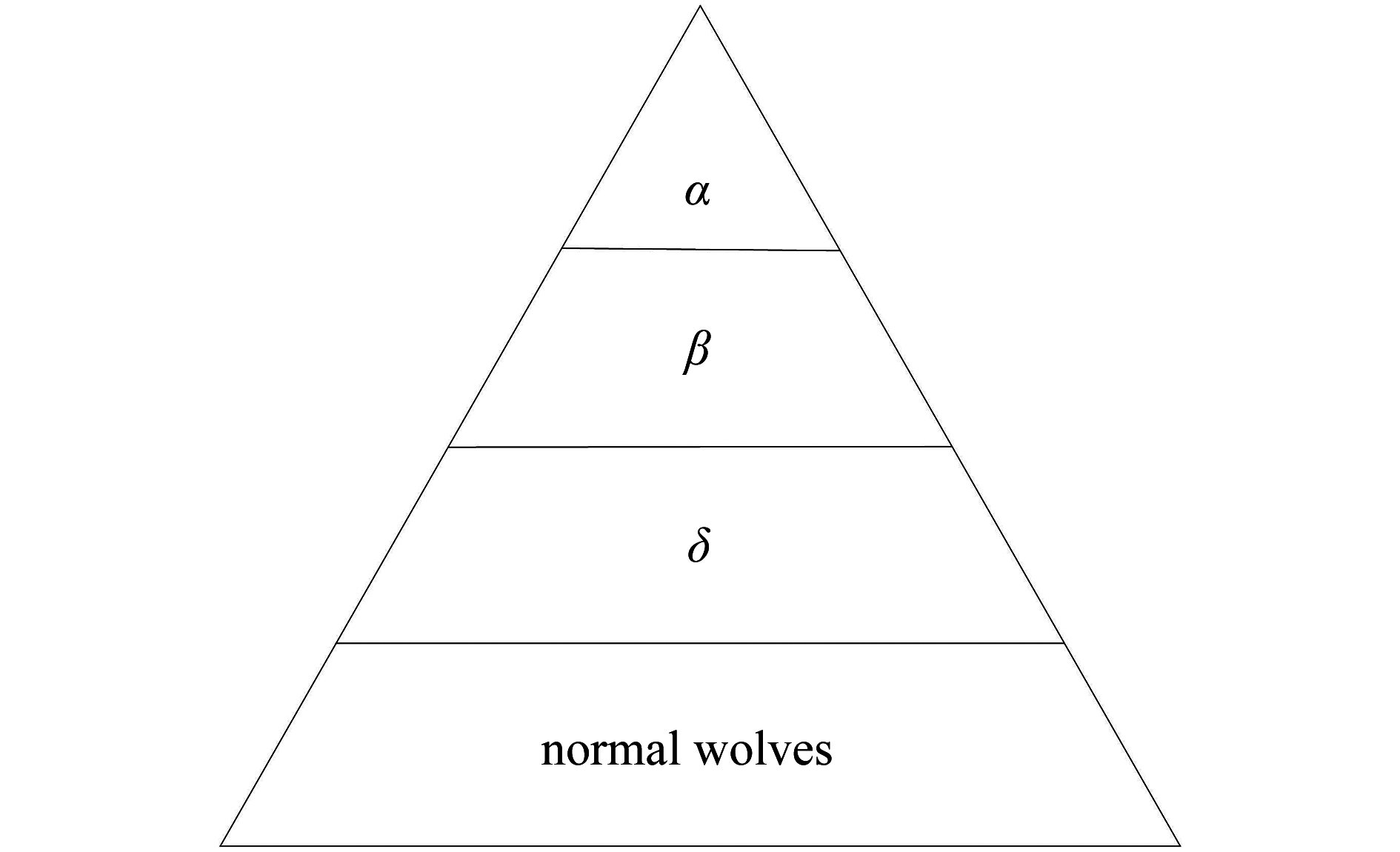
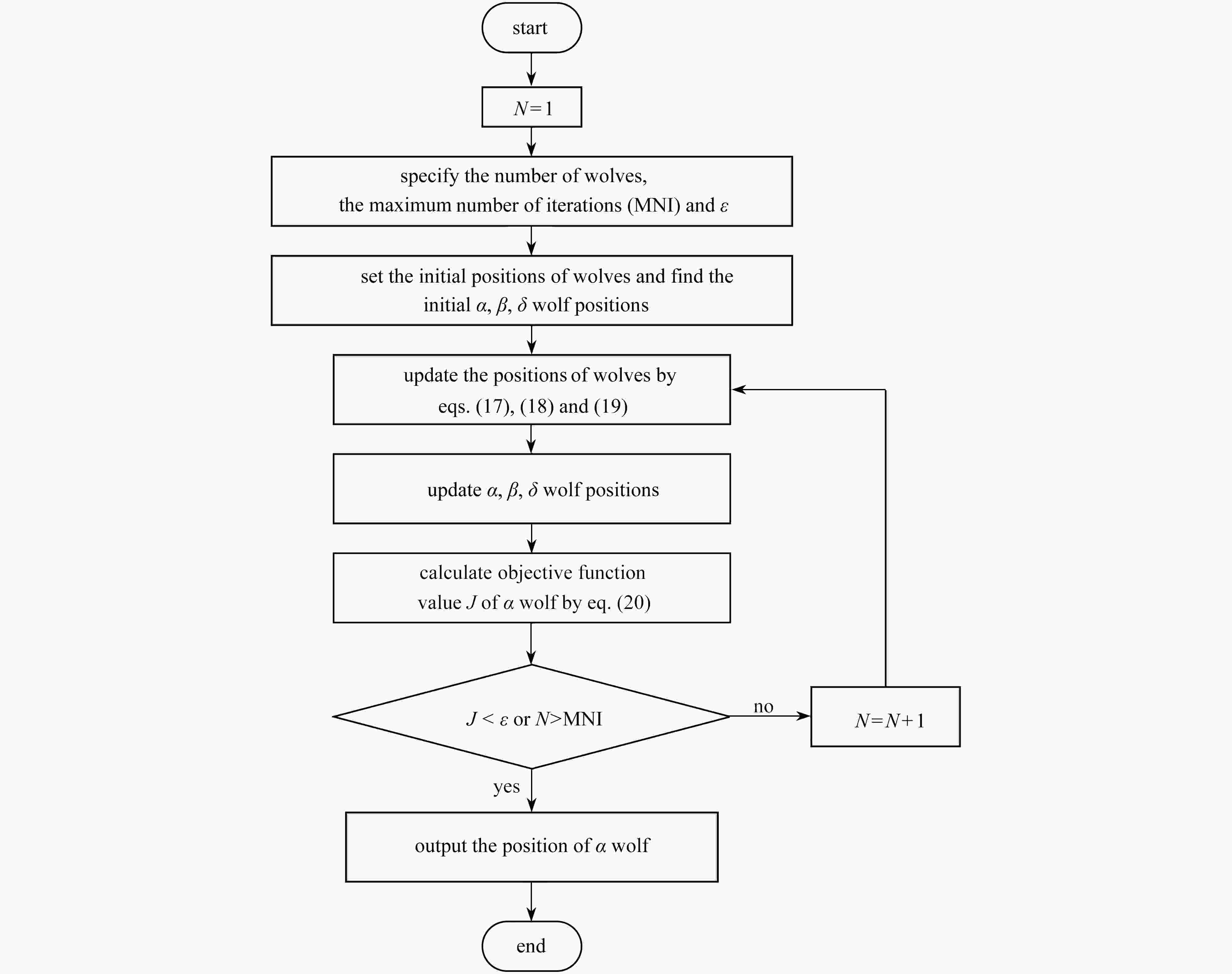
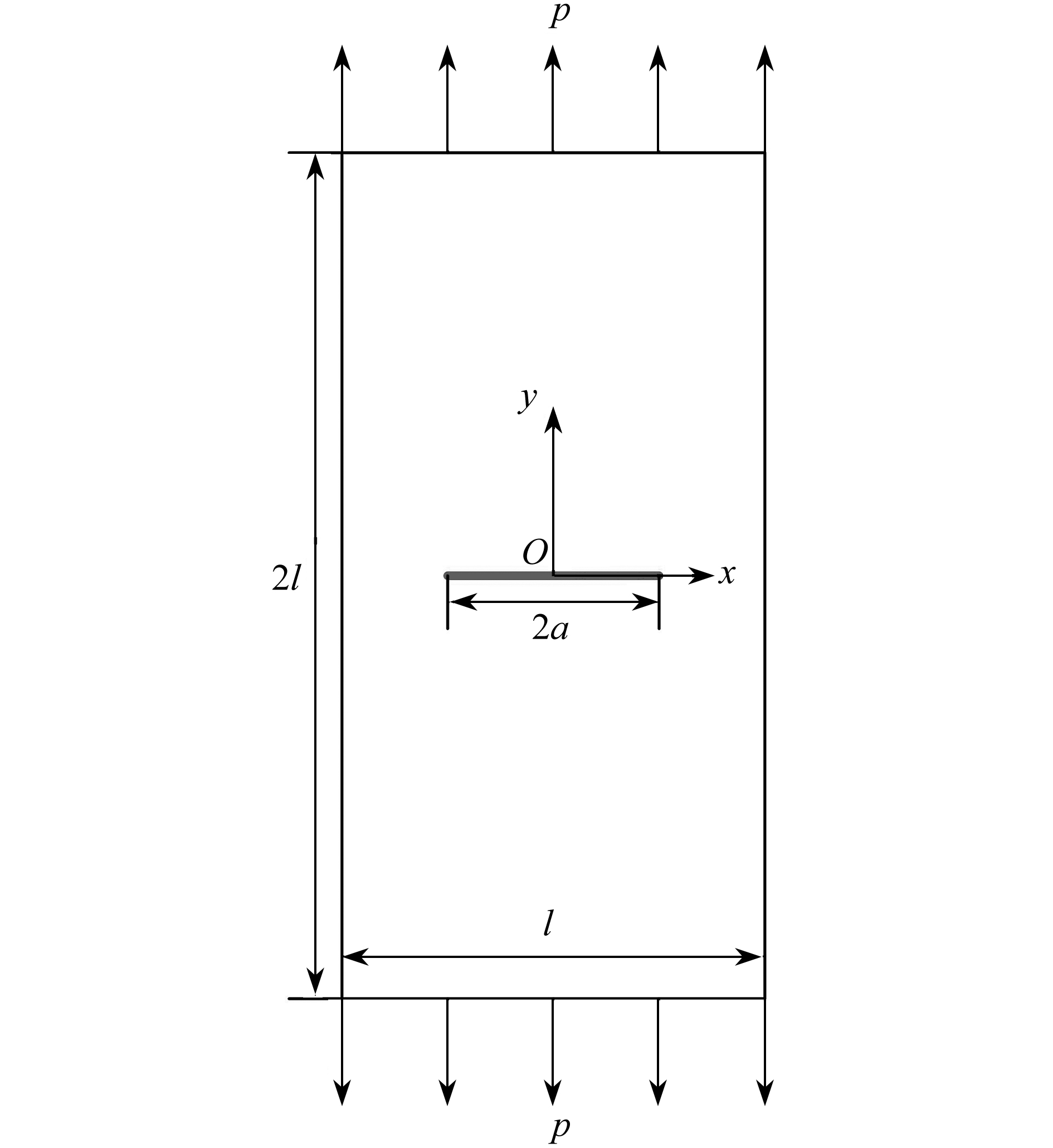







 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号