An Airfoil Optimization Method Based on the Convolutional Neural Network Aerodynamic Reduced Order Model
-
摘要:
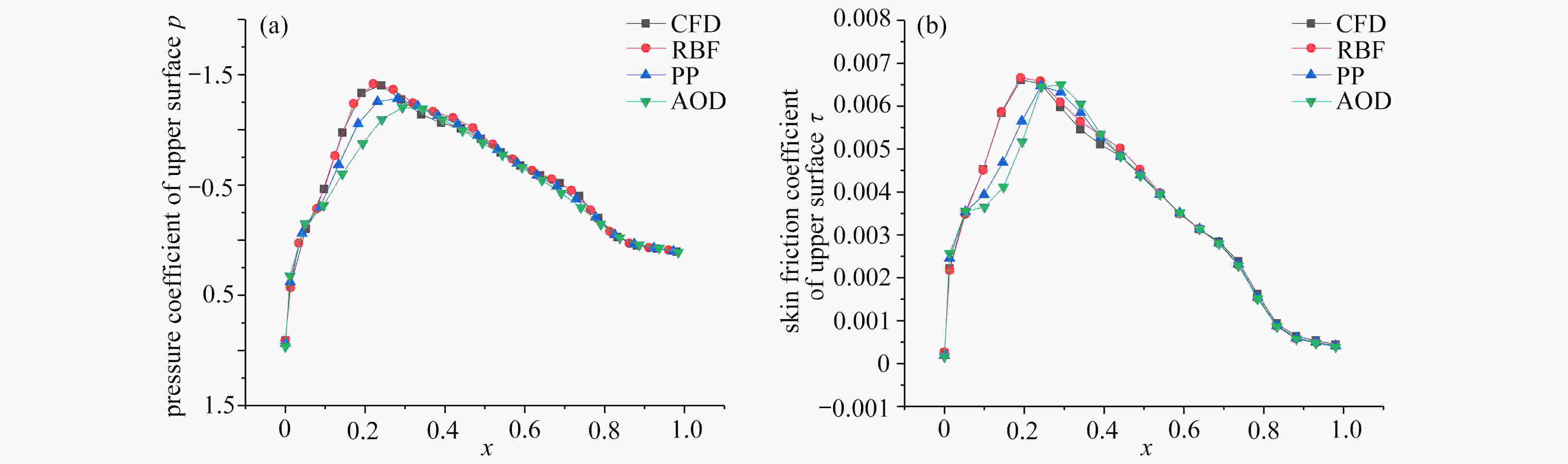
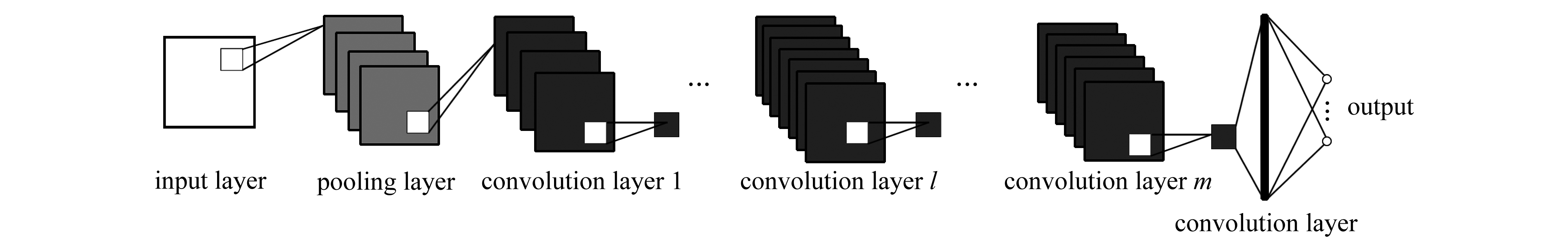
针对非线性大扰动翼型气动力优化问题,提出了基于卷积神经网络气动力降阶模型的优化方法。该方法用不同形状参数下翼型的气动力数据作为训练信号,训练卷积神经网络翼型气动力降阶模型。采用该气动力降阶模型,以最大升阻比为目标,对翼型进行优化,结果表明该方法可用于大扰动下翼型气动力的预测和优化。该文同时还讨论了池化法和径向基法的训练信号数据降维方法对降阶模型精度的影响,结果表明训练信号数据降维能够提高气动力降阶模型的精度。其原因在于训练信号数据降维可以减少神经网络模型的待定参数的个数,在相同数据量下神经网络模型收敛得更好。
Abstract:To solve the nonlinear problem of airfoil shape optimization induced by nonlinear large perturbation, an optimization method was proposed based on the convolutional neural network (CNN) aerodynamic reduced order model (ROM). In the method, the aerodynamic forces on different airfoils were used as the training data for the proposed ROM. For the sake of the maximum lift-drag ratios, the ROM was applied to optimize the airfoil shape. The results show the method applies well to the prediction and optimization of airfoil shape dynamics under large perturbation. The improving effects of the parameter pooling and the radial basis function method based training data method on the accuracy of the dimensionality reduction model, were discussed. The reason for the improvement is that, the training data dimensionality reduction can cut down the number of undetermined parameters in the CNN model and make the CNN model converge better under the same data volume.
-
表 1 翼型优化结果
Table 1. Airfoil optimization results
parameter lower bound upper bound optimized upper surface a1
a2
a3
a4
a5
a6
a70
0
0
0
0
0
00.025
0.030
0.030
0.030
0.025
0.020
0.0150.025
0.030
0.030
0.030
0.025
0.020
0.015lower surface b1
b2
b3
b4
b5
b6
b70
0
0
0
0
0
00.025
0.030
0.030
0.030
0.025
0.020
0.0150.025
0.030
0.030
0.030
0.025
0.020
0.015lift-drag ratio $ {C_{\text{l}}}/{C_{\text{d}}} $ – – – 32.41 -
[1] ZHANG M C, GOU W X, LI L. Multidisciplinary design and multi-objective optimization on guide fins of twin-web disk using Kriging surrogate model[J]. Structural & Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2017, 55(1): 361-373. [2] DOWELL E H. Eigenmode analysis in unsteady aerodynamics: reduced order models[J]. AIAA Journal, 1996, 34(8): 1578-1583. doi: 10.2514/3.13274 [3] SILVA W A. Reduced-order models based on linear and nonlinear aerodynamic impulse responses[C]//40th Structures, Structureal Dynamics, and Materials Conference. St Louis, Missouri, 1999. [4] 陈志强, 刘战合, 苗楠. 基于增量学习的非定常气动力参数化降阶模型[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(12): 125103. (CHEN Zhiqiang, LIU Zhanhe, MIAO Nan. Parametric reduced-order modeling of unsteady aerodynamics based on incremental learning algorithm[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(12): 125103.(in Chinese) [5] CHEN Z Q, ZHAO Y H, HUANG R. Parametric reduced-order modeling of unsteady aerodynamics for hypersonic vehicles[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2019, 87: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2019.01.035 [6] HU J W, LIU H R, WANG Y G, et al. Reduced order model for unsteady aerodynamic performance of compressor cascade based on recursive RBF[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2021, 34(4): 341-351. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2020.08.022 [7] ZAHN R, WINTER M, ZIEHER M, et al. Application of a long short-term memory neural network for modeling transonic buffet aerodynamics[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 113: 106652. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2021.106652 [8] 李立州, 杨明磊, 张珺, 等. 尾流激励的叶片气动力降阶模型[J]. 计算力学学报, 2018, 35(3): 299-303. (LI Lizhou, YANG Minglei, ZHANG Jun, et al. Aerodynamic ROM of blade due to upstream wake[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2018, 35(3): 299-303.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7511/jslx20170609002 [9] HE L. Fourier methods for turbomachinery applications[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2010, 46(8): 329-341. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2010.04.001 [10] 王梓伊, 张伟伟. 适用于参数可调结构的非定常气动力降阶建模方法[J]. 航空学报, 2017, 38(6): 178-187. (WANG Ziyi, ZHANG Weiwei. Unsteady aerodynamic reduced-order modeling method for parameter changeable structure[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2017, 38(6): 178-187.(in Chinese) [11] ZHANG W W, CHEN K J, YE Z Y. Unsteady aerodynamic reduced-order modeling of an aero-elastic wing using arbitrary mode shapes[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2015, 58: 254-270. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2015.07.007 [12] YAO W G, JAIMAN R K. A harmonic balance technique for the reduced-order computation of vortex-induced vibration[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2016, 65: 313-332. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2016.06.002 [13] ZHANG W W, XU Y B, SU D, et al. Flutter analysis of tandem cascades based on a fluid-structure coupling method[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2019, 32(2): 04018147. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)AS.1943-5525.0000975 [14] 罗骁, 张新燕, 张珺, 等. 基于谐波平衡法的尾流激励的叶片振动降阶模型方法[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2018, 39(8): 892-899. (LUO Xiao, ZHANG Xinyan, ZHANG Jun, et al. A reduced-order model method for blade vibration due to upstream wake based on the harmonic balance method[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2018, 39(8): 892-899.(in Chinese) [15] 张鸿志, 周强, 陈刚, 等. 气动弹性系统本征正交分解降阶模型精度的参数影响研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2016, 50(11): 104-109. (ZHANG Hongzhi, ZHOU Qiang, CHEN Gang, et al. Effects of some parameters on accuracy of aeroelastic proper orthogonal decomposition reduced order model[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2016, 50(11): 104-109.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201611016 [16] LI L Z, LI J J, ZHANG J, et al. Aerodynamic shape optimization by continually moving ROM[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 99: 105729. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.105729 [17] 张珺, 李立州, 原梅妮. 径向基函数参数化翼型的气动力降阶模型优化[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2019, 40(3): 250-258. (ZHANG Jun, LI Lizhou, YUAN Meini. Optimization of RBF parameterized airfoils with the aerodynamic ROM[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2019, 40(3): 250-258.(in Chinese) [18] 韩力群. 人工神经网络理论、设计及应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2002.HAN Liqun. Artificial Neural Network Theory, Design and Application[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2002.(in Chinese) [19] 阎平凡. 人工神经网络与模拟进化计算[M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2005.YAN Pingfan. Artificial Neural Network and Evolutionary Computing[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2005.(in Chinese) [20] 尹明朗, 寇家庆, 张伟伟. 一种高泛化能力的神经网络气动力降阶模型[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2017, 35(2): 205-213.YIN Minglang, KOU Jiaqing, ZHANG Weiwei. A reduced-order aerodynamic model with high generalization capability based on neural network[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2017, 35(2): 205-213.(in Chinese) [21] KOU J Q, ZHANG W W. Multi-kernel neural networks for nonlinear unsteady aerodynamic reduced-order modeling[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2017, 67: 309-326. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2017.04.017 [22] 张磊, 王洪涛, 刘卫, 等. 基于高维数据和深度学习的短期电力负荷预测[J]. 科技通报, 2021, 37(3): 55-66. (ZHANG Lei, WANG Hongtao, LIU Wei, et al. Short-term power load forecasting based on high-dimensional data and deep learning[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2021, 37(3): 55-66.(in Chinese) [23] 翟高粤. 基于优化反向传播算法的物体识别技术[J]. 信息技术, 2021, 50(3): 5-7. (ZHAI Gaoyue. Object recognition based on optimized back propagation method[J]. Information Technology, 2021, 50(3): 5-7.(in Chinese) [24] 张有健, 陈晨, 王再见. 深度学习算法的激活函数研究[J]. 无线电通信技术, 2021, 47(1): 115-120. (ZHANG Youjian, CHEN Chen, WANG Zaijian. Research on activation function of deep learning algorithm[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2021, 47(1): 115-120.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2021.01.016 [25] 江泽涛, 秦嘉奇, 张少钦. 参数池化卷积神经网络图像分类方法[J]. 电子学报, 2020, 48(9): 1729-1734. (JIANG Zetao, QIN Jiaqi, ZHANG Shaoqin. Parameterized pooling convolution neural network for image classification[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(9): 1729-1734.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.09.009 -




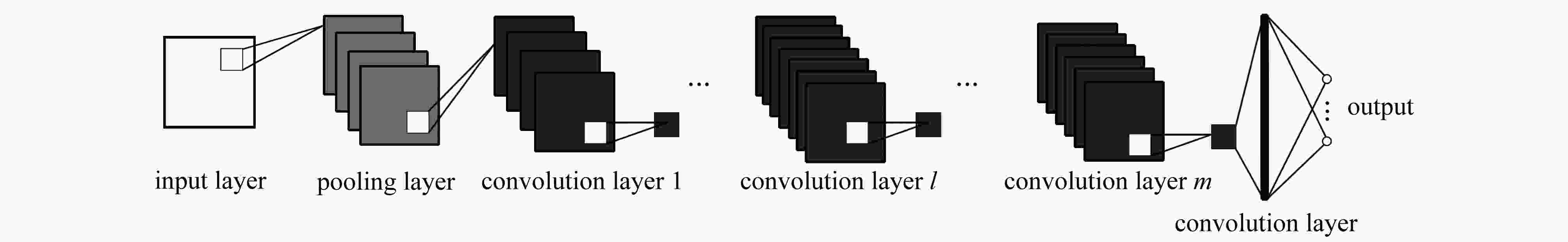
 下载:
下载:
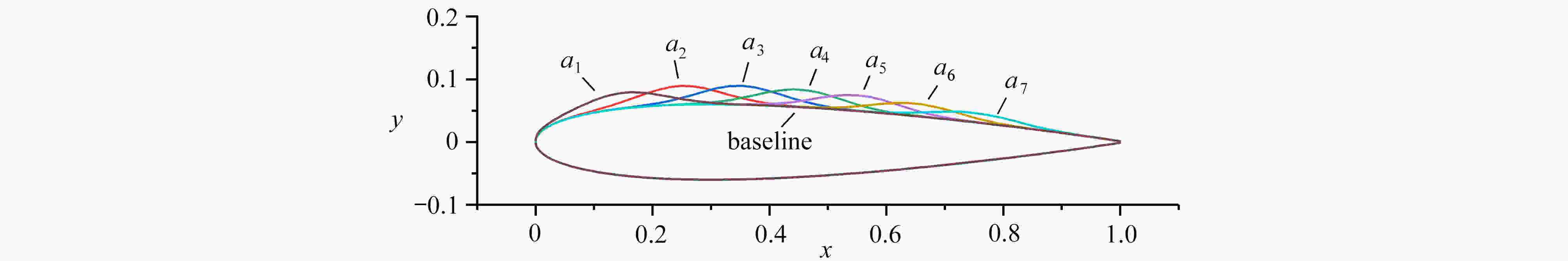
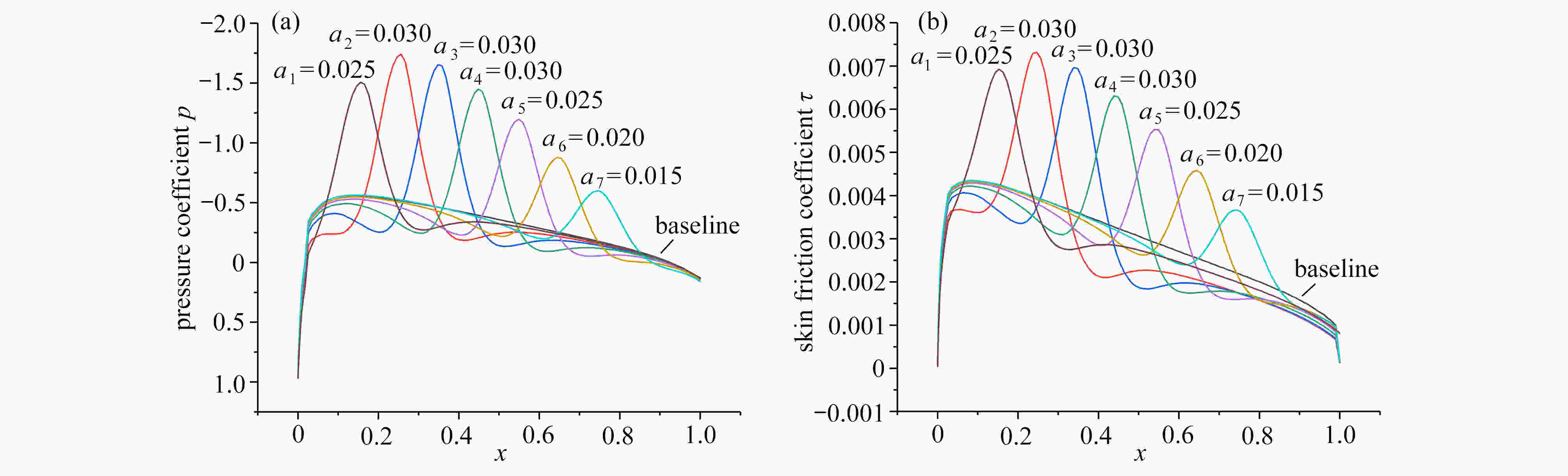


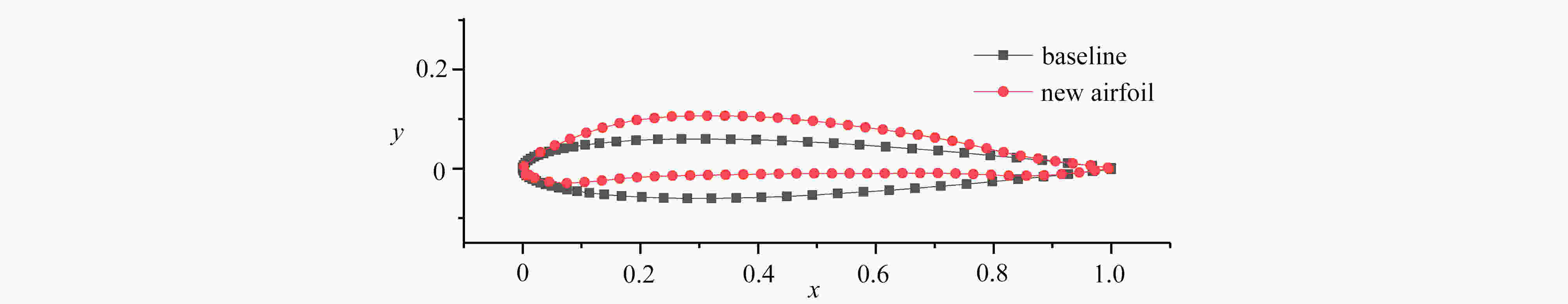



 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号