Active Vibration Control of Truss Structures for Large Space Telescopes Based on Cable Actuators
-
摘要:
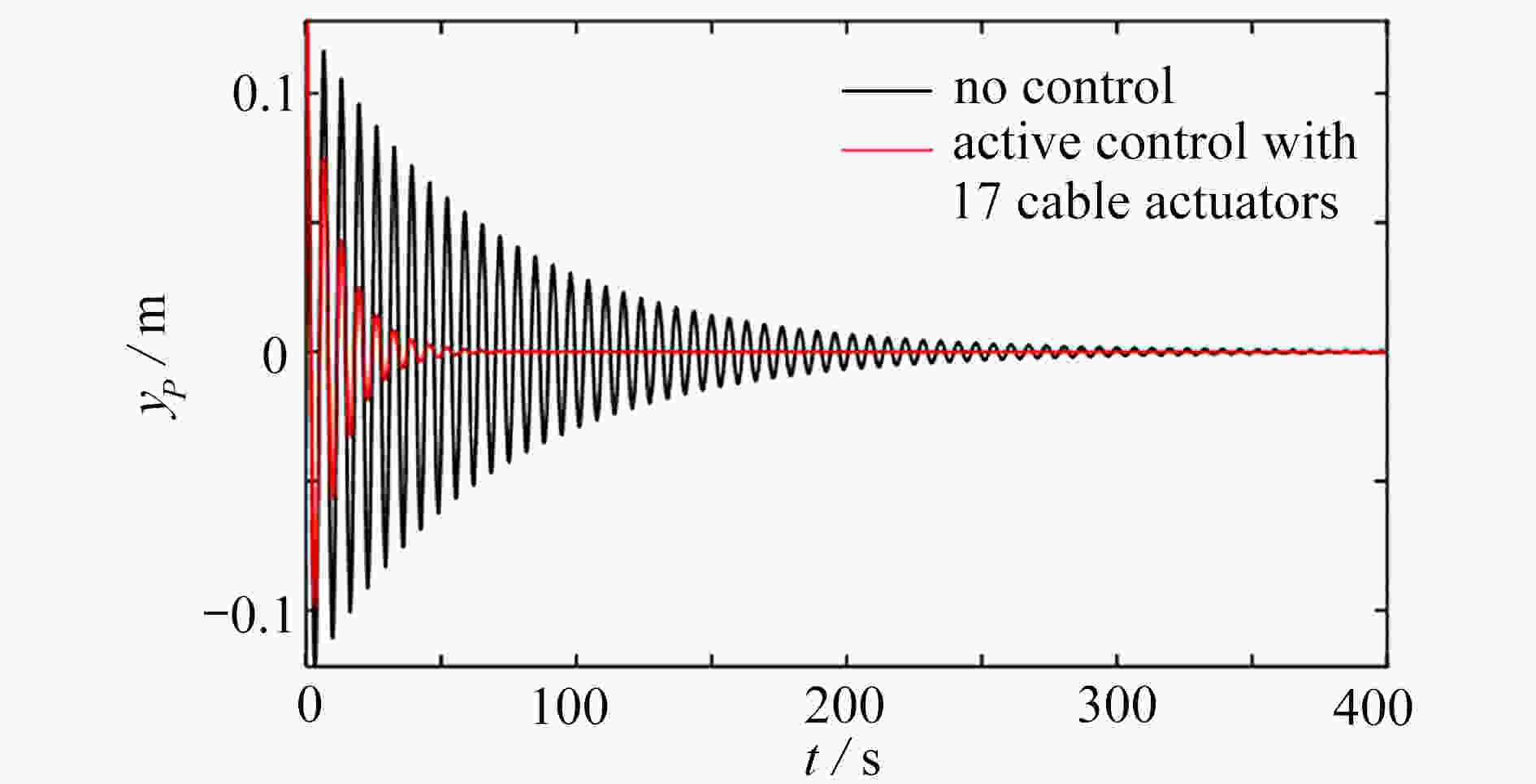
薄膜衍射是一种新型的太空望远镜的成像方式,它具有轻质、易折叠与展开、光学成像精度高等许多优点,是当今太空望远镜技术的研究热点。该文针对一类薄膜衍射太空望远镜桁架结构的振动主动控制进行了研究,提出了一种基于绳索作动器的振动主动控制策略。首先建立了望远镜桁架结构的动力学模型,然后采用粒子群优化算法研究了绳索作动器的优化布置,进而采用最优控制方法设计了结构振动的主动控制律,最后通过数值仿真验证了所给出方法的有效性,并详细研究了绳索作动器数量与结构振动稳定时间之间的对应关系。
Abstract:The membrane diffraction is a new imaging method for space telescopes. It makes a hot research topic in space telescope technology with lots of advantages, such as light weight, easy foldability and high optical imaging accuracy. The active vibration control of the truss structure of a kind of membrane diffraction space telescope was investigated, and an active vibration control strategy was proposed based on cable actuators. Firstly, the dynamic model for the telescope truss structure was established. Then the particle swarm optimization algorithm was used to study the arrangement optimization of cable actuators. The active control law for the structure vibration was designed with the classical linear quadratic regulator method. Finally, the numerical simulation results verify the effectiveness of the proposed method. In the numerical simulations, the relationship between the number of cable actuators and the required time for the structure to regain stability was studied in detail.
-
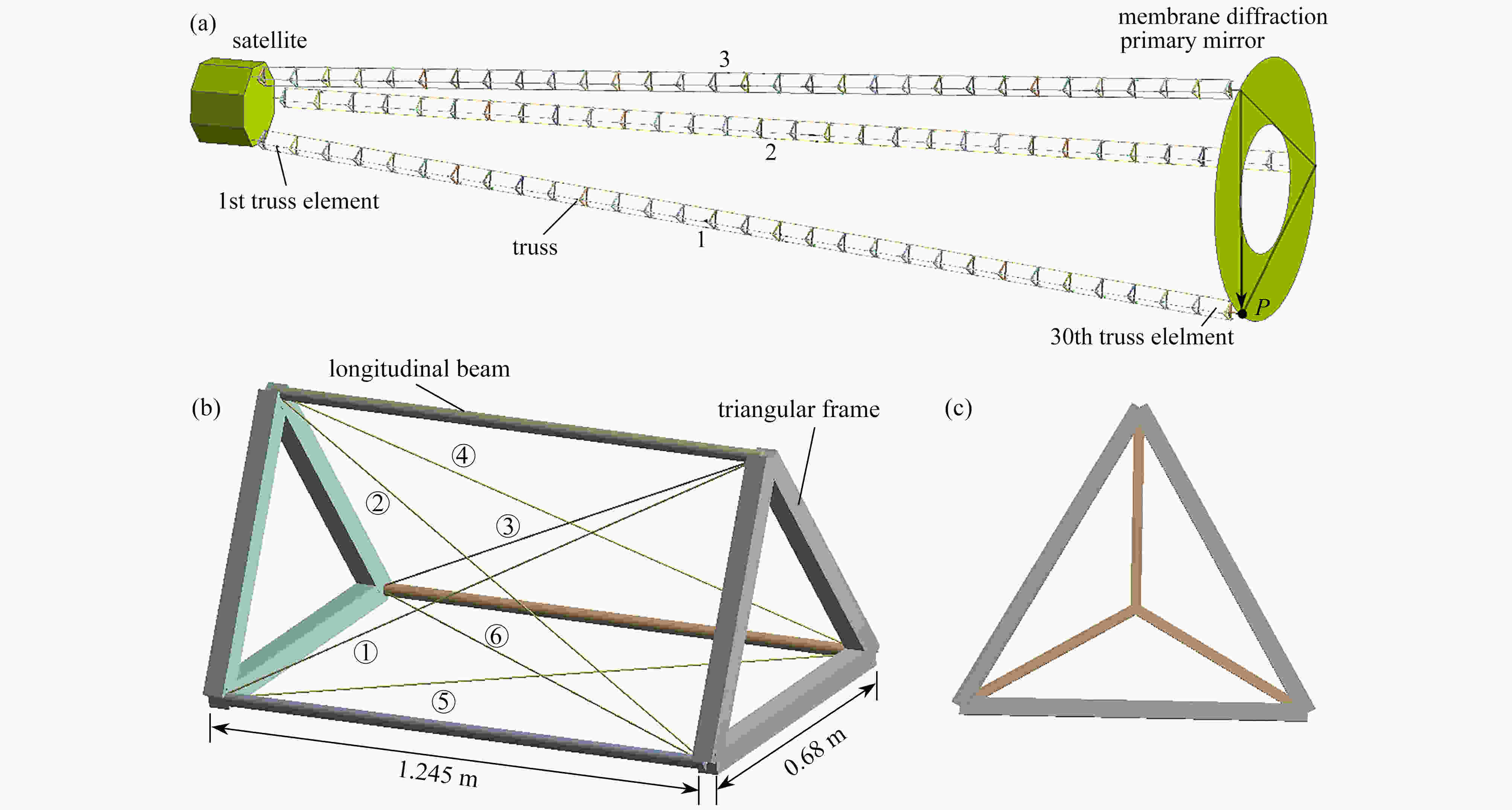
图 1 薄膜衍射太空望远镜结构示意图: (a) 薄膜衍射太空望远镜结构图;(b) 桁架单元结构图;(c) 桁架底部、顶部的三角框架结构图
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the membrane diffraction space telescope: (a) the structure of the membrane diffraction space telescope; (b) the structure of a truss element; (c) the triangular frame structure of the truss bottom and top
表 1 薄膜衍射太空望远镜结构的物理参数
Table 1. Physical parameters of the structure of the membrane diffraction space telescope
structural component size elastic modulus
E/GPadensity
ρ/(kg/m³)Poisson’s
ratio μRayleigh damping coefficient length
l/mcross-sectional area
A/m2α β triangular frame 0.68 2.5×10−3 70 2700 0.3 0.05 0.03 longitudinal beam 1.245 7.07×10−4 70 2700 connecting beam 0.3926 2.5×10−3 7000 2700 simplified beam of the rigid plate 0.3926 2.5×10−3 7000 2700 simplified beam of the
primary mirror7.9556 2.5×10−3 7000 2700 表 2 薄膜衍射太空望远镜的前四阶固有频率(单位:Hz)
Table 2. The 1st 4 natural frequencies of the membrane diffraction space telescope (unit: Hz)
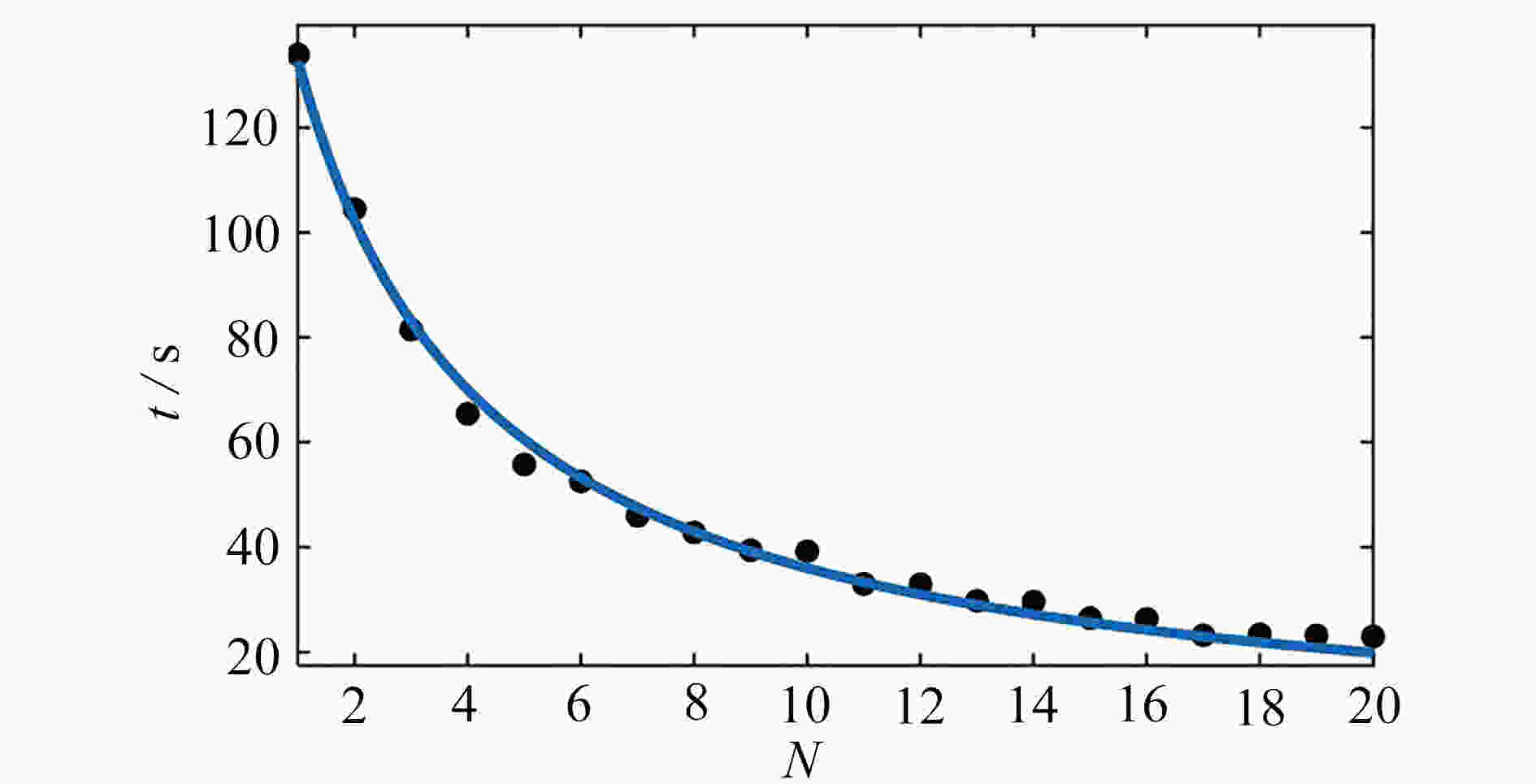
natural frequency 1st order 2nd order 3rd order 4th order theoretical model 0.15337 0.15337 0.22946 0.63599 ANSYS 0.15314 0.15314 0.23549 0.63464 error ε/% 0.15019 0.15019 2.56062 0.21272 表 3 绳索作动器的数量、最优位置与结构稳定所需时间
Table 3. Number of cable actuators, optimal positions and reqiured time for structural stabilization
number N cable actuator position time t/s number N cable actuator position time t/s 1 (3, 2, 5) 133.93 11 (1, 2, 6), (1, 5, 5), (1, 25, 4), (2, 2, 4), (2, 3, 1), (2, 8, 4), (2, 19, 4), (3, 1, 5), (3, 2, 3), (3, 4, 1), (3, 9, 1) 33.01 2 (3, 2, 1), (3, 27, 6) 104.48 12 (1, 1, 5), (1, 4, 6), (1, 22, 4), (1, 27, 1), (2, 4, 4), (2, 6, 4),
(2, 29, 6), (3, 2, 1), (3, 10, 2), (3, 10, 5), (3, 12, 2), (3, 21, 3)32.95 3 (1, 2, 5), (1, 29, 1), (3, 2, 2) 81.47 13 (1, 1, 6), (1, 5, 3), (1, 10, 5), (1, 29, 3), (2, 2, 3), (2, 6, 1), (2, 7, 3), (2, 8, 4), (2, 23, 5), (3, 3, 1), (3, 5, 1), (3, 15, 1), (3, 28, 5) 29.80 4 (1, 3, 8), (2, 4, 4), (3, 1, 1), (3, 27, 5) 65.45 14 (1, 2, 6), (1, 14, 6), (1, 26, 1), (2, 1, 2), (2, 2, 3), (2, 6, 4),
(2, 25, 2), (3, 2, 2), (3, 2, 6), (3, 6, 2), (3, 8, 1),
(3, 17, 3), (3, 25, 4), (3, 26, 5)29.64 5 (1, 3, 6), (1, 28, 2), (2, 2, 4), (3, 2, 2), (3, 3, 5) 55.78 15 (1, 4, 2), (1, 4, 5), (1, 8, 5), (2, 2, 4), (2, 2, 5), (2, 3, 4), (2, 22, 3), (2, 29, 6), (3, 1, 1), (3, 1, 4), (3, 2, 1), (3, 4, 2), (3, 5, 5), (3, 6, 4), (3, 29, 3) 26.49 6 (1, 1, 5), (1, 28, 4), (2, 1 ,4), (2, 3, 1), (3, 4, 1), (3, 28, 6) 52.56 16 (1, 2, 6), (1, 6, 5), (1, 7, 6), (1, 18, 4), (1, 26, 3), (1, 27, 2),
(2, 2, 4), (2, 20, 3), (2, 22, 3), (2, 27, 5), (3, 2, 1), (3, 2, 2),
(3, 2, 4), (3, 4, 2), (3, 7, 1), (3, 24, 6)26.38 7 (1, 3, 5), (1, 29, 3), (2, 2, 2), (2, 5, 4), (3, 2, 2), (3, 4, 5), (3, 29, 6) 45.97 17 (1, 2, 1), (1, 4, 4), (1, 6, 6), (2, 2, 3), (2, 2, 6), (2, 3, 3), (2, 5, 3), (2, 8, 2), (2, 13, 3), (2, 26, 1), (2, 30, 5), (3, 3, 2), (3, 4, 2),
(3, 10, 2), (3, 11, 2), (3, 23, 2), (3, 29, 4)23.24 8 (1, 2, 6), (1, 25, 2), (2, 3, 3), (2, 24, 6), (3, 1, 2), (3, 3, 2), (3, 4, 5), (3, 27, 4) 42.83 18 (1, 3, 6), (1, 4, 6), (1, 9, 5), (1, 13, 5), (1, 28, 2), (2, 1, 2), (2, 1, 3), (2, 2, 4), (2, 6, 1), (2, 11, 1), (2, 26, 6), (2, 30, 5), (3, 1, 4),
(3, 2, 1), (3, 7, 1), (3, 20, 1), (3, 27, 2), (3, 28, 5)23.42 9 (1, 2, 6), (1, 30, 1), (2, 1, 2), (2, 1, 3), (2, 2, 3), (2, 24, 6), (3, 3, 2), (3, 4, 1), (3, 30, 4) 39.42 19 (1, 2, 6), (1, 6, 3), (1, 6, 6), (1, 10, 5), (1, 30, 1), (2, 2, 3), (2, 5, 4), (2, 6, 4), (2, 8, 3), (2, 12, 3), (2, 23, 6), (2, 26, 3), (2, 29, 3),
(2, 30, 1), (3, 2, 1), (3, 3, 1), (3, 6, 2), (3, 20, 6), (3, 25, 3)23.20 10 (1, 5, 5), (1, 6, 5), (1, 25, 4), (2, 2, 4), (2, 3, 2), (3, 1, 2), (3, 3, 2), (3, 12, 2), (3, 23, 6), (3, 28, 3) 39.22 20 (1, 2, 6), (1, 4, 5), (1, 6, 5), (1, 9, 1), (1, 26, 4), (1, 28, 1), (2, 1, 6), (2, 3, 4), (2, 5, 3), (2, 7, 4), (2, 8, 2), (2, 16, 3), (2, 26, 2), (3, 2, 6), (3, 3, 1), (3, 5, 4), (3, 6, 2), (3, 12, 1), (3, 12, 6), (3, 15, 6) 23.02 -
[1] 孙莹, 张伟, 吴瑞琴. 六维系统环形桁架天线的非线性动力学分析[J]. 应用数学与力学, 2019, 40(3): 282-301. (SUN Ying, ZHANG Wei, WU Ruiqin. Analysis on nonlinear dynamics of circular truss antennae in 6D systems[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2019, 40(3): 282-301.(in Chinese) [2] AKIRA M, AKIO T, NAOKAZU H, et al. Technology status of the 13 m aperture deployment antenna reflectors for engineering test satellite Ⅷ[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2000, 27(2/9): 147-152. [3] 焦建超, 苏云, 王保华, 等. 地球静止轨道膜基衍射光学成像系统的发展与应用[J]. 国际太空, 2016, 450: 49-55. (JIAO Jianchao, SU Yun, WANG Baohua, et al. Development and application of GEO membrane based diffraction optical imaging system[J]. Space International, 2016, 450: 49-55.(in Chinese) [4] HYDE R, DIXIT S, WEISBERG A, et al. Eyeglass: a very large aperture diffractive space telescope[C]//Conference on Highly Innovative Space Telescope Concepts. Waikoloa, HI, 2002. [5] MACEWEN H, BRECKINRIDGE J. Large diffractive/refractive apertures for space and airborne telescopes[C]//Conference on Sensors and Systems for Space Applications VI. Baltimore, MD, 2013. [6] DOMBER J, ATCHESON P, KOMMERS J. MOIRE: ground test bed results for a large membrane telescope[C]//Spacecraft Structures Conference. National Harbor, MD, USA, 2014. [7] 黄泽兵, 刘锦阳, 袁婷婷, 等. 太空衍射望远镜大型桁架展开过程动力学建模[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2021, 41(1): 55-63. (HUANG Zebing, LIU Jinyang, YUAN Tingting, et al. Dynamic modeling for the deployment of the folded truss of space diffraction telescope[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2021, 41(1): 55-63.(in Chinese) [8] 郑耀辉, 阮萍, 曹尚. 空间薄膜衍射望远镜展开结构设计与分析[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2016, 45(1): 121-125ZHENG Yaohui, RUAN Ping, CAO Shang. Deployable structure design and analysis for space membrane diffraction telescope[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2016, 45(1): 121-125. (in Chinese) [9] MAKAROW A L, KHOROSHILOV V S, ZAKRZHEVSKII A E. Spacecraft dynamics due to elastic ring antenna deployment[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2011, 69(7/8): 691-702. [10] KIM T H, SUH J E, HAN J H. Deployable truss structure with flat-form storability using scissor-like elements[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2021, 159: 104252. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2021.104252 [11] 杨静静, 王帅, 文良华, 等. 基于图像复原的衍射望远镜暗弱目标成像[J]. 光学学报, 2020, 40(14): 101-108.YANG Jingjing, WANG Shuai, WEN Lianghua, et al. Faint-object imaging of diffractive telescopes based on image restoration[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2020, 40(14): 101-108. (in Chinese) [12] ZHANG H L, LIU H, XU W B, et al. Error analysis of large-diameter subaperture stitching Fresnel diffractive elements[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(27): 7672-7678. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.007672 [13] LU G Y, ZHOU J Y, CAI G P. Active vibration control of a large space antenna structure using cable actuator[J]. AIAA Journal, 2021, 59(4): 1457-1468. doi: 10.2514/1.J059956 [14] LELEU S, ABOU-KANDIL H, BONNASSIEUX Y. Piezoelectric actuators and sensors location for active control of flexible structures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2001, 50(6): 1577-1582. doi: 10.1109/19.982948 [15] 黄泽兵. 太空衍射望远镜展开动力学建模与分析[D]. 硕士学位论文. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2021.HUANG Zebing. Dynamic modeling and analysis for the deployment of the space diffraction telescope[D]. Master Thesis. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2021. (in Chinese) [16] ZHOU J Y, LU G Y, CAI G P, et al. Static shape adjustment and actuator layered optimization for planar phased array satellite antenna[J]. International Journal of Aeronautical and Space Sciences, 2019, 20: 891-901. doi: 10.1007/s42405-019-00178-1 -




 下载:
下载:


 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号