Mean-Square Synchronization and Stochastically Passive Synchronization of Delayed Gene Regulatory Networks With Markovian Switching
-
摘要:
基因调控网络(GRNs)及其动力学模型的研究在后基因组时代是一个重要的研究领域。定性分析基因调控网络及其动力学对系统地认识生物体具有重要意义。该文提出了一类具有时变时滞和Markov切换的随机基因调控网络模型,研究了其均方同步和随机无源同步问题。通过设计合适的Lyapunov-Krasovskii泛函(LKF),并利用Lyapunov稳定性理论、线性矩阵不等式方法和随机分析技巧,得到了均方同步和随机无源同步的充分条件。此外,通过与其他文献进行比较,显示了该文结果的理论价值。数值模拟验证了所得充分条件的有效性。
Abstract:The research of gene regulatory networks (GRNs) and their dynamic models is important in the post-genome era. Qualitative analysis of GRNs and their dynamics is of great significance to the understanding of organisms from a systematic perspective. A stochastic GRN model with time-varying delay and Markovian switching was proposed to study the properties of mean-square synchronization and stochastically passive synchronization. Through the design of an appropriate Lyapunov-Krasovskii functional (LKF), the sufficient conditions for mean-square synchronization and stochastically passive synchronization were obtained by means of the Lyapunov stability theory, the linear matrix inequality method and the random analysis techniques. In addition, the comparison between the results of this paper and some other literatures shows that, the present results have markable theoretical meaning. The numerical simulation illustrates the validity of the obtained sufficient conditions.
-
[1] CHEN L, AIHARA K. Stability of genetic regulatory networks with time delay[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅰ: Fundamental Theory and Applications, 2002, 49(5): 602-608. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2002.1001949 [2] WANG G, CAO J. Robust exponential stability analysis for stochastic genetic networks with uncertain parameters[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2009, 14(8): 3369-3378. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2009.01.004 [3] YANG X L, SENTHILKUMAR D V, SUN Z K, et al. Key role of time-delay and connection topology in shaping the dynamics of noisy genetic regulatory networks[J]. Chaos, 2011, 21(4): 047522. doi: 10.1063/1.3629984 [4] YAO Y, LIANG J, CAO J. Robust stability of Markovian jumping genetic regulatory networks with disturbance attenuation[J]. Asian Journal of Control, 2011, 13(5): 655-666. doi: 10.1002/asjc.373 [5] YAO Y, LIANG J, CAO J. Stability analysis for switched genetic regulatory networks: an average dwell time approach[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2011, 348(10): 2718-2733. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2011.04.016 [6] LI C, CHEN L, AIHARA K. Stochastic synchronization of genetic oscillator networks[J]. BMC Systems Biology, 2007, 1(1): 1-11. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-1-1 [7] CHEN B S, HSU C Y. Robust synchronization control scheme of a population of nonlinear stochastic synthetic genetic oscillators under intrinsic and extrinsic molecular noise via quorum sensing[J]. BMC Systems Biology, 2012, 6(1): 1−15. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-6-115 [8] LU L, HE B, MAN C, et al. Passive synchronization for Markov jump genetic oscillator networks with time-varying delays[J]. Mathematical Biosciences, 2015, 262(1): 80-87. [9] REN F, CAO F, CAO J. Mittag-Leffler stability and generalized Mittag-Leffler stability of fractional-order gene regulatory networks[J]. Neurocomputing, 2015, 160(21): 185-190. [10] QIAN Y, YAN H, DUAN L, et al. Finite-time synchronization of fractional-order gene regulatory networks with time delay[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 126(2): 1-10. [11] XU G, H BAO, CAO J. Mean-square exponential input-to-state stability of stochastic gene regulatory networks with multiple time delays[J]. Neural Processing Letters, 2020, 51(1): 271-286. doi: 10.1007/s11063-019-10087-9 [12] KURASOV P, MUGNOLO D, WOLF V. Analytic solutions for stochastic hybrid models of gene regulatory networks[J]. Journal of Mathematical Biology, 2021, 82(1/2): 1-9. [13] HAO L, YANG Z, BI Y. Deterministic and stochastic dynamics in a gene regulatory network mediated by miRNA[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2021, 103(3): 2903-2916. doi: 10.1007/s11071-021-06239-z [14] MAO X C, LI X Y, DING W J, et al. Dynamics of a multiplex neural network with delayed couplings[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition) , 2021, 42(3): 441-456. doi: 10.1007/s10483-021-2709-6 [15] WANG Z H. Criteria for minimization of spectral abscissa of time-delay systems[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition) , 2021, 42(7): 969-980. doi: 10.1007/s10483-021-2751-9 [16] WANG Y, WANG Z, LIANG J. On robust stability of stochastic genetic regulatory networks with time delays: a delay fractioning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (Part B) , 2009, 40(3): 729-740. [17] LOU X, QIAN Y, CUI B. Exponential stability of genetic regulatory networks with random delays[J]. Neurocomputing, 2010, 73(4/6): 759-769. [18] ZHU Q, CAO J. Exponential stability of stochastic neural networks with both markovian jump parameters and mixed time delays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2011, 41(2): 341-353. [19] ZHU Q. Asymptotic stability in the pth moment for stochastic differential equations with Lévy noise[J]. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 2014, 416(1): 126-142. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2014.02.016 -




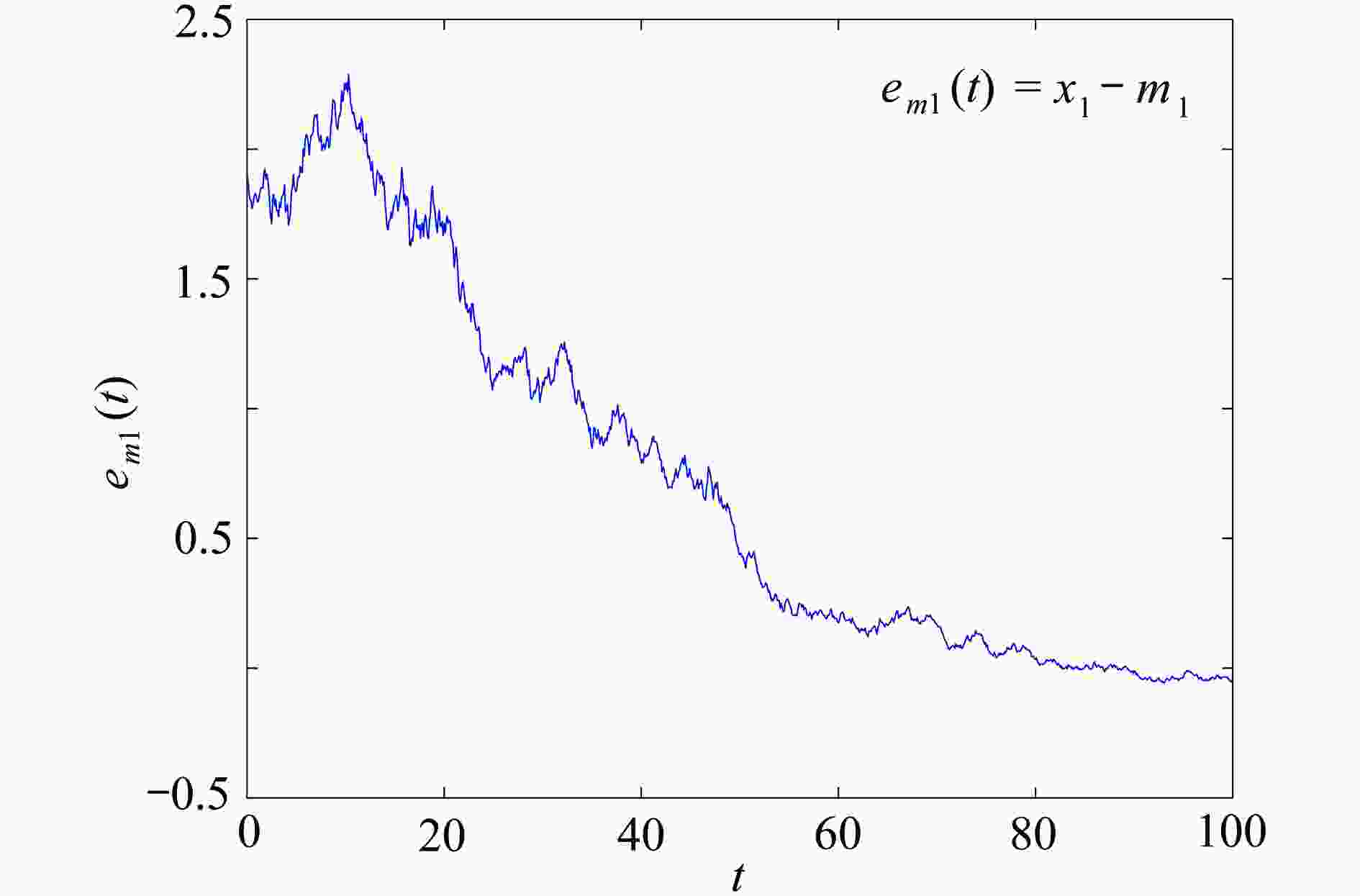
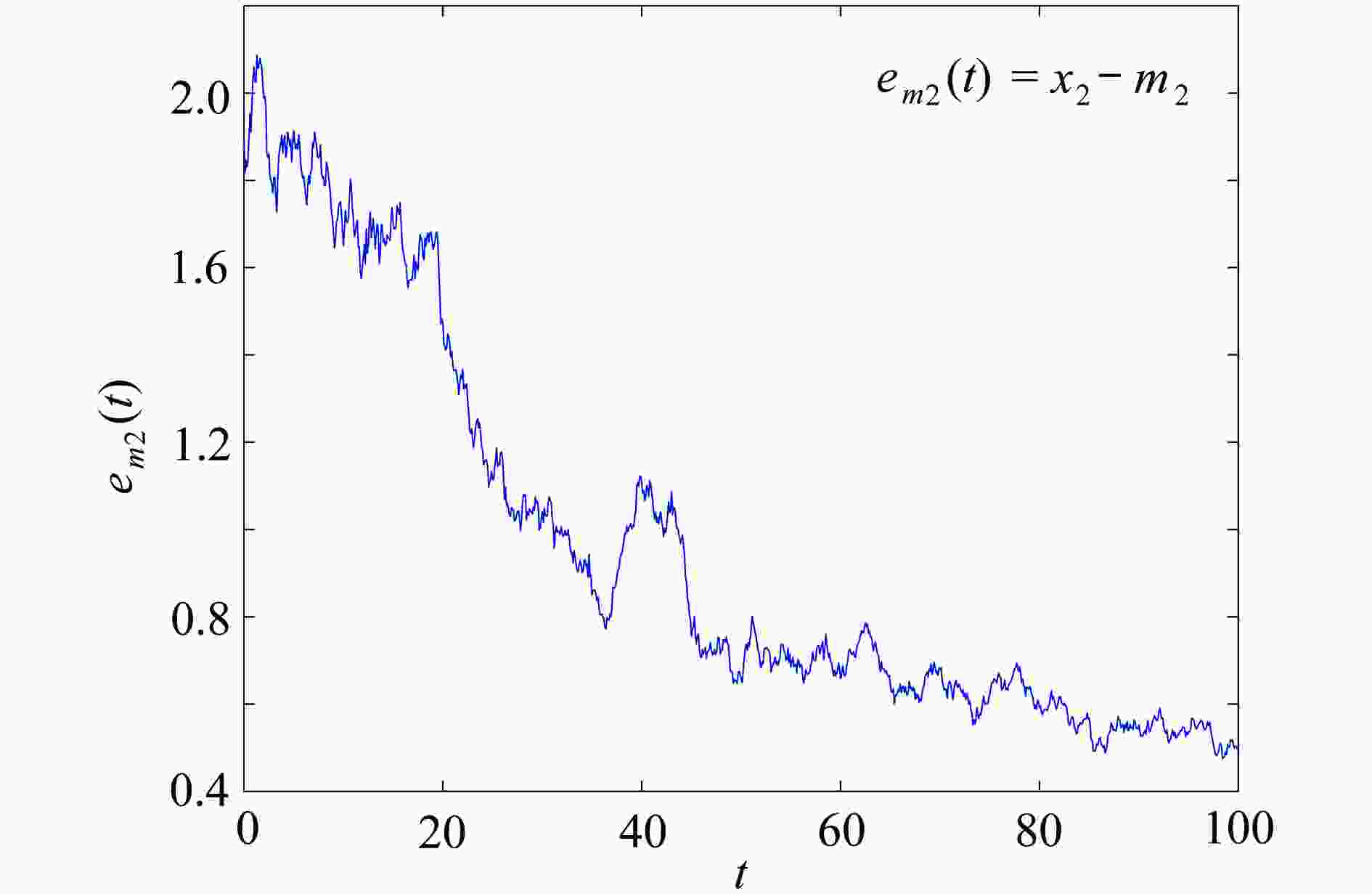
 下载:
下载:
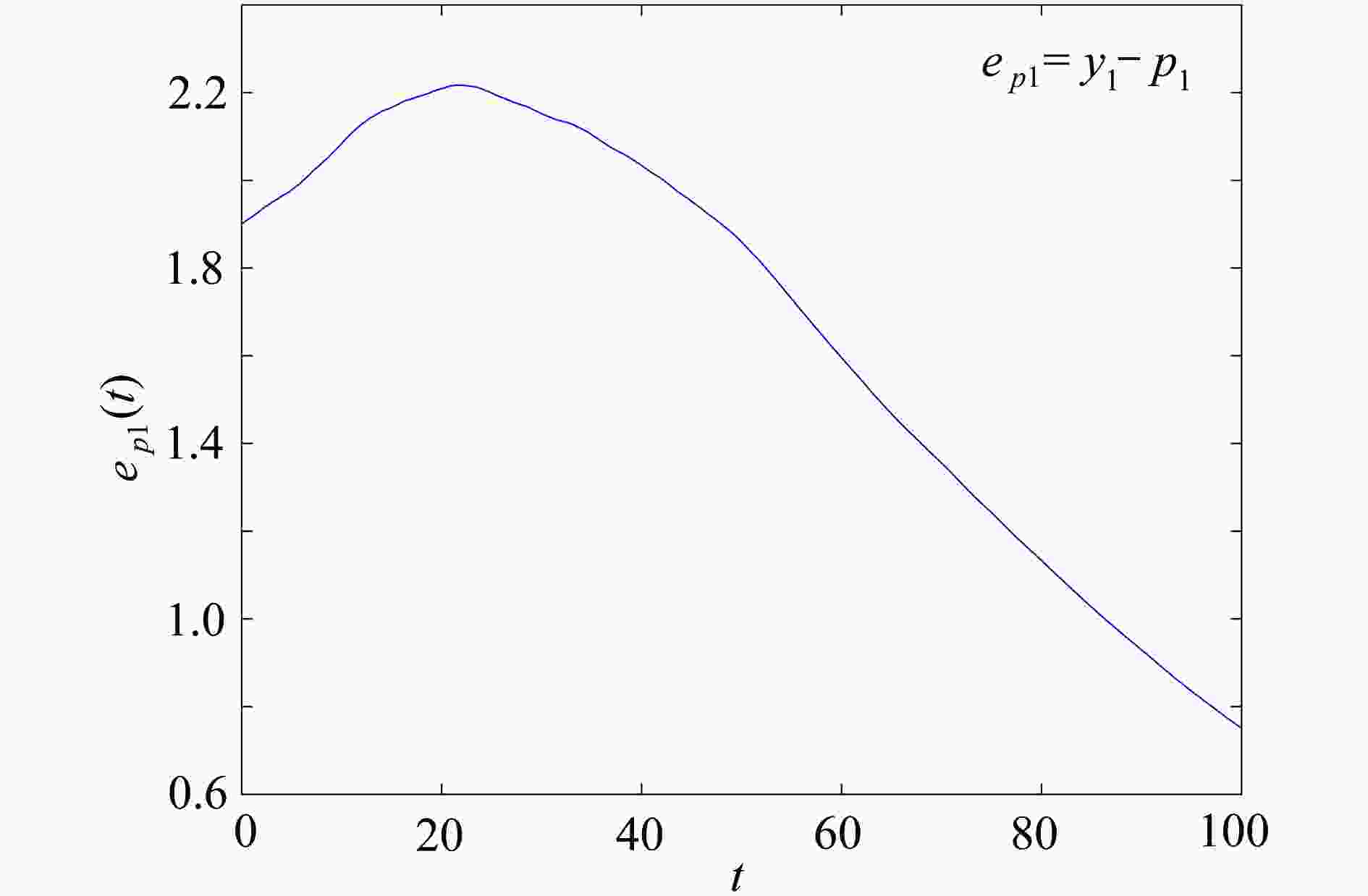
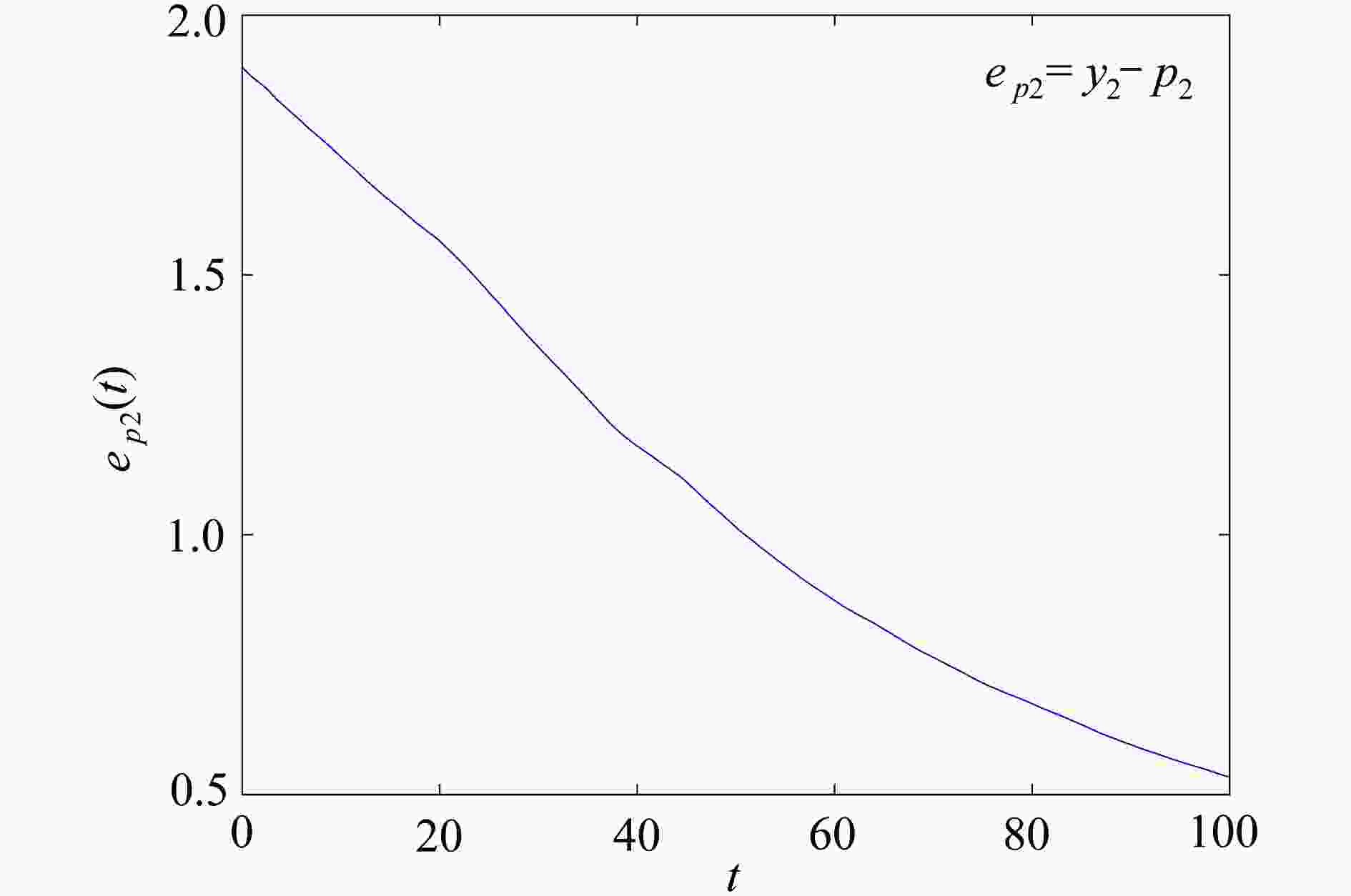
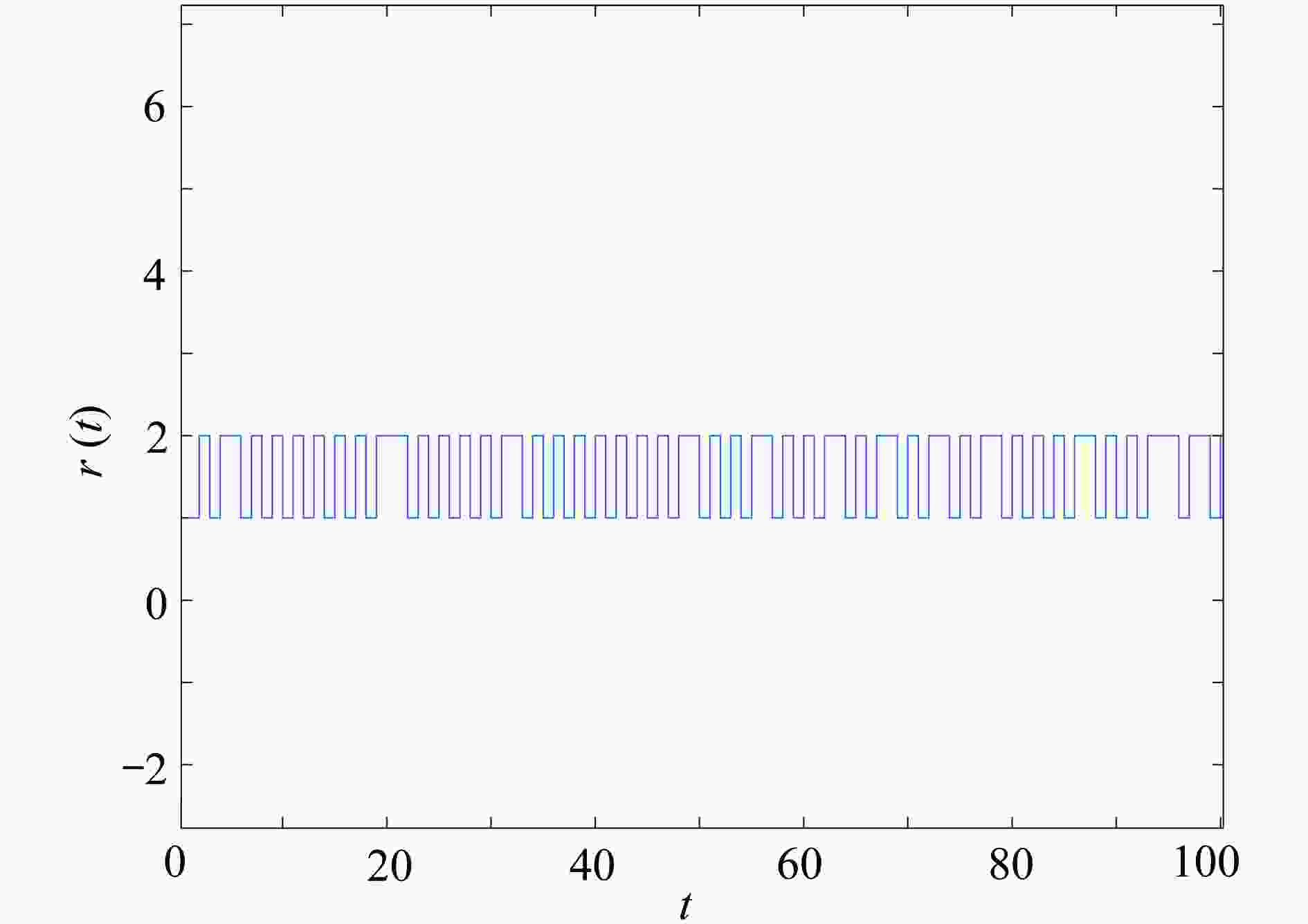
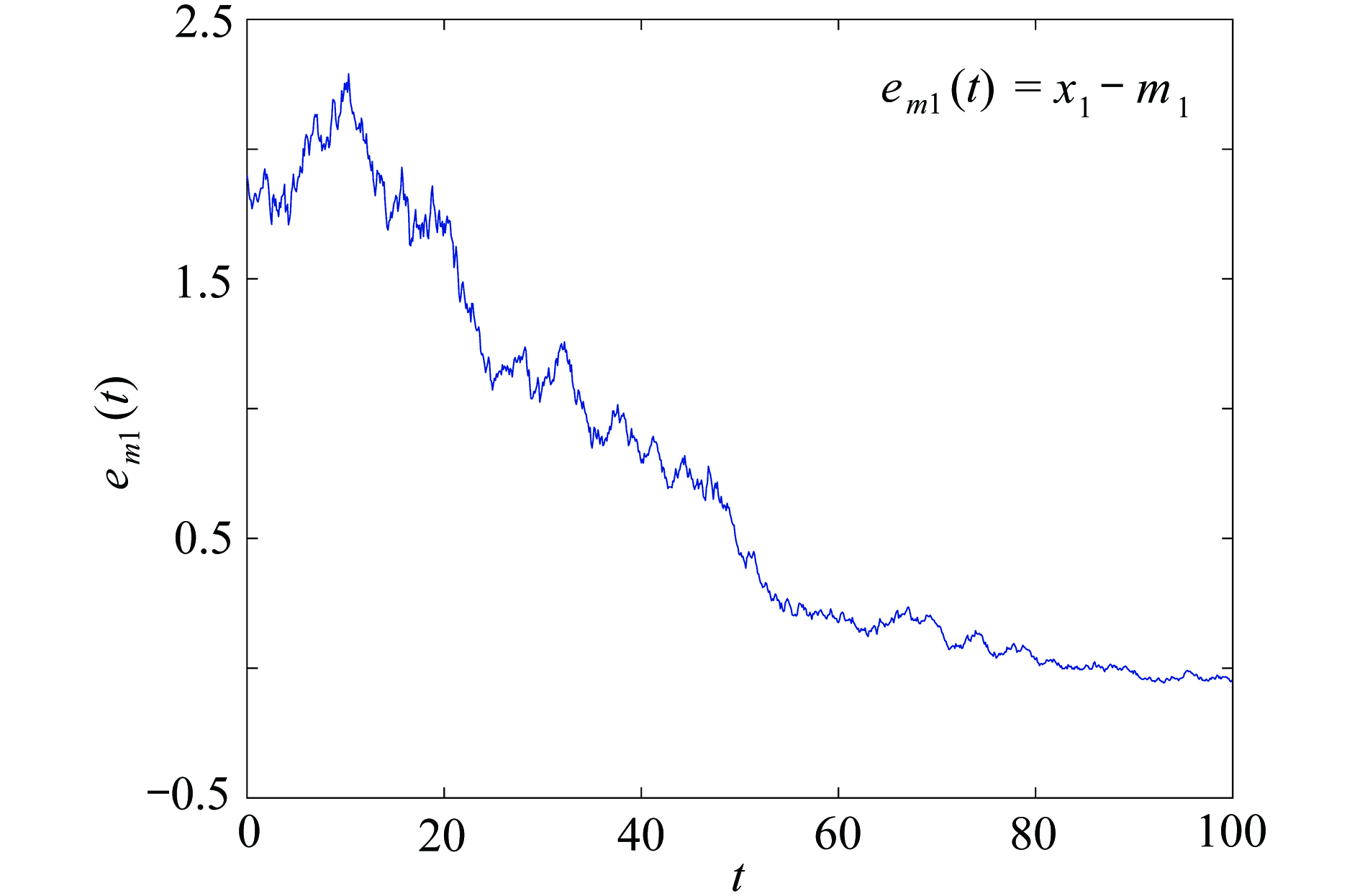

 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号