Study on Energy Absorption Performances of Conical Negative Stiffness Metamaterials
-
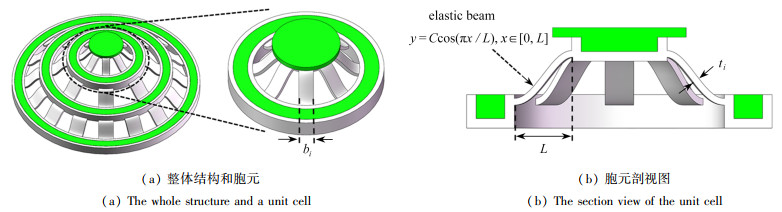
摘要: 由于负刚度超材料作为吸能材料具有可重复使用的特性,因此有必要对负刚度超材料的吸能性能和可重复使用性能进行深入研究. 采用3D打印技术制备了所设计的负刚度超材料,通过反复加载实验研究了超材料在多稳态模式和单稳态模式下的吸能性能,并采用自然时效的方法研究了残余应力对超材料吸能性能的影响. 结果表明,所设计超材料在反复加载时,随加载次数的增加,超材料的比吸能先下降后趋于稳定. 在多稳态模式和单稳态模式下,采用自然时效方法都可以有效释放超材料中的残余应力,从而提高其反复吸能性能.Abstract: Since negative stiffness metamaterials are reusable as energy-absorbing materials, it is necessary to investigate the energy-absorbing performances and reusability of negative stiffness metamaterials. The designed negative stiffness metamaterial was prepared with the 3D printing technology, and the energy absorption performance of the metamaterial in the multi-stable mode and the mono-stable mode was investigated by repeated loading experiments. The effect of the residual stress on the energy absorption performance of the metamaterial was studied with the natural aging method. The results show that, the specific energy absorption of the designed metamaterial first decreases and then stabilizes with the increase of the number of loading times in the case of repeated loading. In both the multi-stable mode and the mono-stable mode, the natural aging method can effectively release the residual stresses in the metamaterial, thus improving its repeated energy absorption performance.
-
Key words:
- negative stiffness /
- metamaterial /
- energy absorption
1) (我刊编委陈立明来稿) -
表 1 试件材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters of the specimen
material parameter TPU PLA density ρ/(kg/m3) 1 250 1 000 Poisson’s ratio ν 0.47 0.24 Young’s modulus E/MPa 75 1 024 -
[1] CHRONOPOULOS D, ANTONIADIS I, AMPATZIDIS T. Enhanced acoustic insulation properties of composite metamaterials having embedded negative stiffness inclusions[J]. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 2017, 12: 48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.eml.2016.10.012 [2] ESIN M, PASTERNAK E, DYSKIN A V. Stability of chains of oscillators with negative stiffness normal, shear and rotational springs[J]. International Journal of Engineering Science, 2016, 108: 16-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ijengsci.2016.08.002 [3] YANG H, MA L. Multi-stable mechanical metamaterials by elastic buckling instability[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 54: 3509-3526. doi: 10.1007/s10853-018-3065-y [4] CHEN B, CHEN L, DU B, et al. Novel multifunctional negative stiffness mechanical metamaterial structure: tailored functions of multi-stable and compressive mono-stable[J]. Composites(Part B): Engineering, 2021, 204: 108501. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108501 [5] SHAN S, KANG S H, RANEY J R, et al. Multistable architected materials for trapping elastic strain energy[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(29): 4296-4301. doi: 10.1002/adma.201501708 [6] TAN X, WANG B, YAO K, et al. Novel multi-stable mechanical metamaterials for trapping energy through shear deformation[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2019, 164: 105168. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.105168 [7] WANG B, TAN X, ZHU S, et al. Cushion performance of cylindrical negative stiffness structures: analysis and optimization[J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 227: 111276. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111276 [8] TAN X, WANG B, CHEN S, et al. A novel cylindrical negative stiffness structure for shock isolation[J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 214: 397-405. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.02.030 [9] TAN X, CHEN S, ZHU S, et al. Reusable metamaterial via inelastic instability for energy absorption[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2019, 155: 509-517. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.02.011 [10] HAGHPANAH B, SALARI-SHARIF L, POURRAJAB P, et al. Multistable shape-reconfigurable architected materials[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(36): 7915-7920. doi: 10.1002/adma.201601650 [11] RAFSANJANI A, PASINI D. Bistable auxetic mechanical metamaterials inspired by ancient geometric motifs[J]. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 2016, 9(2): 291-296. [12] 杨航, 马力. 多材料点阵结构的热可编程力学行为[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43(5): 534-552. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430104YANG Hang, MA Li. Multimaterial lattice structures with thermally programmable mechanical behaviors[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(5): 534-552. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430104 [13] AN X, LAI C, FAN H, et al. 3D acoustic metamaterial-based mechanical metalattice structures for low-frequency and broadband vibration attenuation[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2020, 191/192: 293-306. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2020.01.020 [14] LE T D, AHN K K. Experimental investigation of a vibration isolation system using negative stiffness structure[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2013, 70(5): 99-112. [15] FRENZEL T, FINDEISEN C, KADIC M, et al. Tailored buckling microlattices as reusable light-weight shock absorbers[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(28): 5865-5870. doi: 10.1002/adma.201600610 [16] JIANG H, LE BARBENCHON L, BEDNARCYK B A, et al. Bioinspired multilayered cellular composites with enhanced energy absorption and shape recovery[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2020, 36: 101430. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2020.101430 [17] ZHU S, WANG B, TAN X, et al. A novel bi-material negative stiffness metamaterial in sleeve-type via combining rigidity with softness[J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 262: 113381. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.113381 [18] 周世奇, 侯秀慧, 邓子辰. 一般宏观应力状态下凹角蜂窝结构的屈曲性能分析[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2023, 44(1): 12-24. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430202ZHOU Shiqi, HOU Xiuhui, DENG Zichen. Buckling analysis of re-entrant honeycomb structures under general macroscopic stress states[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2023, 44(1): 12-24. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430202 [19] 陈保才. 多稳态/单稳态可调控结构设计与吸能机制研究[D]. 硕士学位论文. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2021.CHEN Baocai. Study on the design and energy absorption mechanism in tailored multi-stable/mono-stable structure[D]. Master Thesis. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2021. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: