Analysis of Wind Vibration Response of Large-Span Asymmetric Suspension Structures With Series Inerter Dampers
-
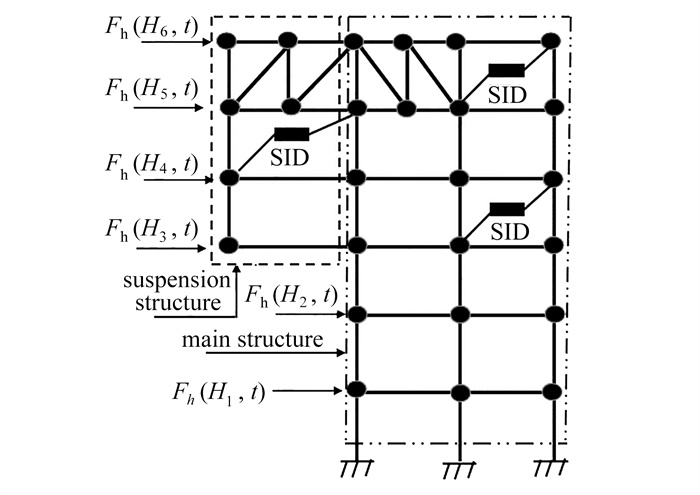
摘要: 针对非对称大跨悬挂结构双向随机风振响应显著的问题,提出了一种利用惯容系统来抑制结构振动的策略,并针对减振体系随机风振响应分析方法复杂的现状,提出了一种简明分析法. 首先,建立了顺风向脉动激励下结构水平和竖向耦合振动的动力学方程,借助有限元分析技术获得了大跨度悬挂结构的实模态动力参数,并基于实模态理论重构了减振体系的动力方程. 其次,基于复模态法和虚拟激励法,获得了大跨度悬挂结构的位移、层间位移和惯容系统出力等响应量频域统一解,并基于功率谱的二次式分解法获得了上述响应量0阶、2阶和4阶谱矩和方差简明封闭解. 最后,利用算例验证了所提封闭解的正确性,并基于此研究了惯容系统参数对抑制悬挂结构双向风振动的特征. 研究表明,大跨悬挂结构的悬挂部分水平和竖向振动加速度均显著影响舒适度,工程设计时需要考虑双向振动,设置惯容系统可有效降低双向振动.
-
关键词:
- 非对称大跨度悬挂结构 /
- 惯容系统 /
- Davenport风速谱 /
- 功率谱二次式分解法 /
- 封闭解
Abstract: Aimed at the significant problem of bidirectional random wind vibration responses of large-span asymmetric suspension structures, a strategy was proposed to suppress the vibration of large-span suspension structures with series inerter dampers (SIDs) as the energy damping system (EDS). For the complexity of the random wind vibration response analysis method, a concise closed-form solution was presented. Firstly, the dynamic equations for the horizontal and vertical coupled vibrations of the EDS under downwind excitation were established, and the finite element dynamic analysis technology was applied to obtain the real modal dynamic parameters of the large-span suspension structure to reconstruct the dynamic equations for the EDS based on the real modal theory. Secondly, based on the complex mode method and the pseudo-excitation method, the frequency domain unified solutions for the displacements, interlayer displacements and forces of the EDS were obtained. The quadratic decomposition method for the response power spectrum density function was used to obtain concise closed-form solutions for the 0th-, 2nd-, and 4th-order spectral moments and variances of the above responses of the EDS subjected to the Davenport spectrum. Finally, the correctness of the proposed method was verified through a numerical example, and based on this, the characteristics of SIDs in suppressing bidirectional vibrations of suspension structures were studied. The results show that, the horizontal and vertical vibration accelerations of the suspension parts of large-span suspension structures significantly affect vibration serviceability, so that bidirectional vibrations need to be considered in engineering design, and SIDs to reduce the horizontal vibrations can effectively reduce bidirectional vibrations. -
表 1 构件信息表
Table 1. Member Information
№. of elements material across section /mm №. of elements material across section /mm ① C30 box 650×400 ⑤ Q390 box 800×800×50 ② Q390 H 700×300×20×40 ⑥ Q390 box 1 000×1 000×80 ③ Q390 H 1 000×400×30×80 ⑦ Q390 box 600×600×20 ④ C35 box 1 400×1 400 ⑧ Q390 H 600×300×30×90 -
[1] 肖魁, 贾水钟, 贾君玉, 等. 上海图书馆东馆悬挂结构方案设计与研究[J]. 建筑结构, 2022, 52 (1): 1-6.XIAO Kui, JIA Shuizhong, JIA Junyu, et al. Design and research on suspended structure scheme of Shanghai East Library[J]. Building Structure, 2022, 52 (1): 1-6. (in Chinese) [2] 朱前坤, 蒲兴龙, 惠晓丽, 等. 基于人群-结构耦合作用甘肃省体育馆悬挂结构振动舒适度评估及控制[J]. 工程力学, 2018, 35 (S1): 46-52. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2017.06.S003ZHU Qiankun, PU Xinglong, HUI Xiaoli, et al. Serviceability evaluation and control of suspension structure of Gansu gymnasium based on pedestrian-structure coupled vibration[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2018, 35 (S1): 46-52. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2017.06.S003 [3] 刘郁馨, 吕志涛. 单段悬挂结构随机动力参数优化解[J]. 南京建筑工程学院学报(自然科学版), 2011, 56 (1): 1-8.LIU Yuxin, LÜ Zhitao. Optimal solution of random dynamic action for suspension building structures[J]. Journal of Nanjing Architectural and Civil Engineering Institute (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 56 (1): 1-8. (in Chinese) [4] GOODNO B J, GERE J M. Earthquake behavior of suspended-floor buildings[J]. Journal of the Structural Division, 1976, 102 (5): 973-992. [5] LIU Y X, LÜ Z T. Seismic performance and storey-based stability of suspended buildings[J]. Advances in Structural Engineering, 2014, 17 (10): 1531-1550. doi: 10.1260/1369-4332.17.10.1531 [6] CHEN M, LIANG X, YANG Z, et al. Analytical study on the random seismic responses of an asymmetrical suspension structure[J]. Buildings, 2023, 13 (6): 1435. doi: 10.3390/buildings13061435 [7] TIAN C, YAO W, PAN Y, et al. Dynamic response of asymmetric suspended structure subjected to random wind excitation[J]. The Structural Design of Tall and Special Buildings, 2024, 33 (10): e2106. doi: 10.1002/tal.2106 [8] KUMAR A, SAHA S K, MATSAGAR V A. Stochastic response analysis of elastic and inelastic systems with uncertain parameters under random impulse loading[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2019, 461 : 114899. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2019.114899 [9] 葛新广, 张梦丹, 龚景海, 等. 频响函数二次正交法在Davenport风速谱下结构系列响应简明封闭解的应用研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40 (21): 207-214.GE Xinguang, ZHANG Mengdan, GONG Jinghai, et al. Application of FRF quadratic orthogonal method in getting concise closed form solutions of structural series responses under Davenport wind speed spectrum[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40 (21): 207-214. (in Chinese) [10] GE X G, GONG J H, ZHAO C J, et al. Structural dynamic responses of building structures with non-viscous dampers under Kanai-Tajimi spectrum excitation[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2022, 517 : 116556. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2021.116556 [11] 李创第, 李宇翔, 杨雪峰, 等. 六参数实用黏弹性阻尼结构基于Davenport风谱风振响应的复模态法[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2023, 44 (3): 248-259. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420211LI Chuangdi, LI Yuxiang, YANG Xuefeng, et al. A complex mode method for wind-induced responses of 6-parameter practical viscoelastic damping energy dissipation structures based on the davenport wind speed spectrum[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2023, 44 (3): 248-259. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420211 [12] YANG W, DENG E, LEI M, et al. Transient aerodynamic performance of high-speed trains when passing through two windproof facilities under crosswinds: a comparative study[J]. Engineering Structures, 2019, 188 : 729-744. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.03.070 [13] 李创第, 王磊石, 邹万杰, 等. 广义Maxwell阻尼器高层结构随机风振响应解析法[J]. 广西大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 41 (4): 953-963.LI Chuangdi, WANG Leishi, ZOU Wanjie, et al. Analytic method for random wind-induced response of high-rise structure with general Maxwell dampers[J]. Journal of Guangxi University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 41 (4): 953-963. (in Chinese) [14] 赵中伟, 张永高. 基于本征-虚拟激励法的大跨钢结构风振响应分析[J]. 空间结构, 2020, 26 (1): 15-23.ZHAO Zhongwei, ZHANG Yonggao. Wind-induced response analysis of complex steel structures based on pod-pseudo excitation method[J]. Spatial Structures, 2020, 26 (1): 15-23. (in Chinese)) [15] GE X G, LI C D, AZIM I, et al. Structural dynamic responses of linear structures subjected to Kanai-Tajimi excitation[J]. Structures, 2021, 34 : 3958-3967. doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2021.08.092 [16] ZHANG R F, ZHAO Z P, PAN C, et al. Damping enhancement principle of inerter system[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2020, 27 (5): e2523. [17] 李创第, 江丽富, 王瑞勃, 等. 单自由度混联Ⅱ型惯容系统随机地震动响应分析[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2023, 44 (3): 260-271. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430166LI Chuangdi, JIANG Lifu, WANG Ruibo, et al. Responses of SDOF structures with SPIS-Ⅱ dampers under random seismic excitation[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2023, 44 (3): 260-271. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430166 [18] 葛新广, 龚景海, 李创第, 等. 功率谱二次正交化法在随机地震动响应的应用[J]. 振动工程学报, 2022, 35 (3): 616-624.GE Xinguang, GONG Jinghai, LI Chuangdi, et al. Application of quadratic orthogonalization method of response power spectrum to random ground motion response[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2022, 35 (3): 616-624. (in Chinese) [19] DAVENPORT A G. Past, present and future of wind engineering[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2002, 90 (12/13/14/15): 1371-1380. [20] LIEVENS K, LOMBAERT G, VAN NIMMEN K, et al. Robust vibration serviceability assessment of footbridges subjected to pedestrian excitation: strategy and applications[J]. Engineering Structures, 2018, 171 : 236-246. [21] 卢宇杰, 程逸建, 程正珲, 等. 悬挂结构组合楼盖人致振动舒适度试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2020, 41 (S2): 263-269.LU Yujie, CHENG Yijian, CHENG Zhenghui, et al. Experimental study on vibration serviceability of composite floor in a suspended structure[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2020, 41 (S2): 263-269. (in Chinese) [22] 高层民用建筑钢结构技术规程: JGJ 99—2015[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2016.Technical specification for steel structure of tall building: JGJ 99—2015[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2016. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载:















 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号