Research on Deposition and Orientation Characteristics of Cylindrical Particles in Gas-Solid 2-Phase Turbulent Flow in Curved Tubes
-
摘要:
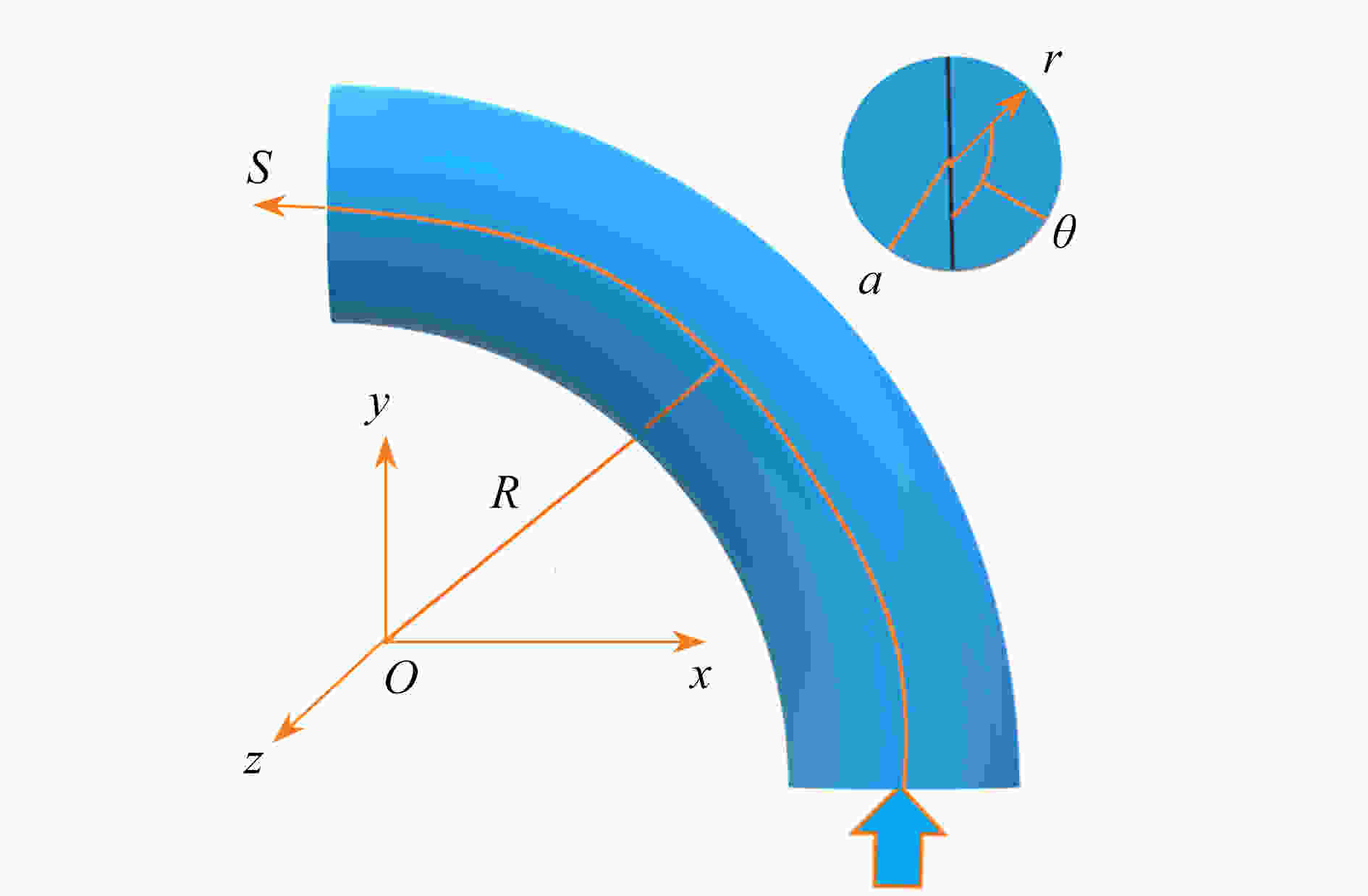
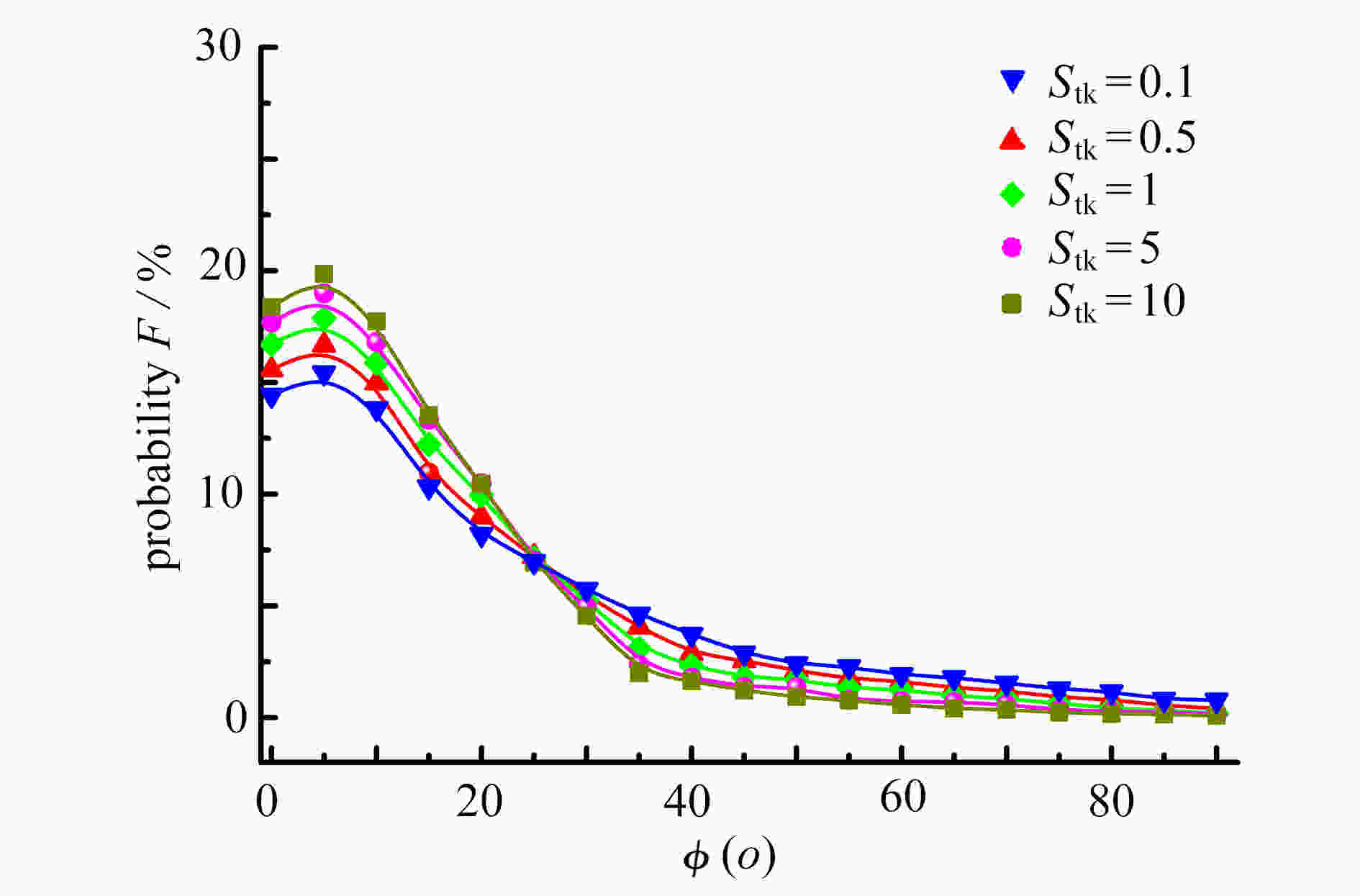
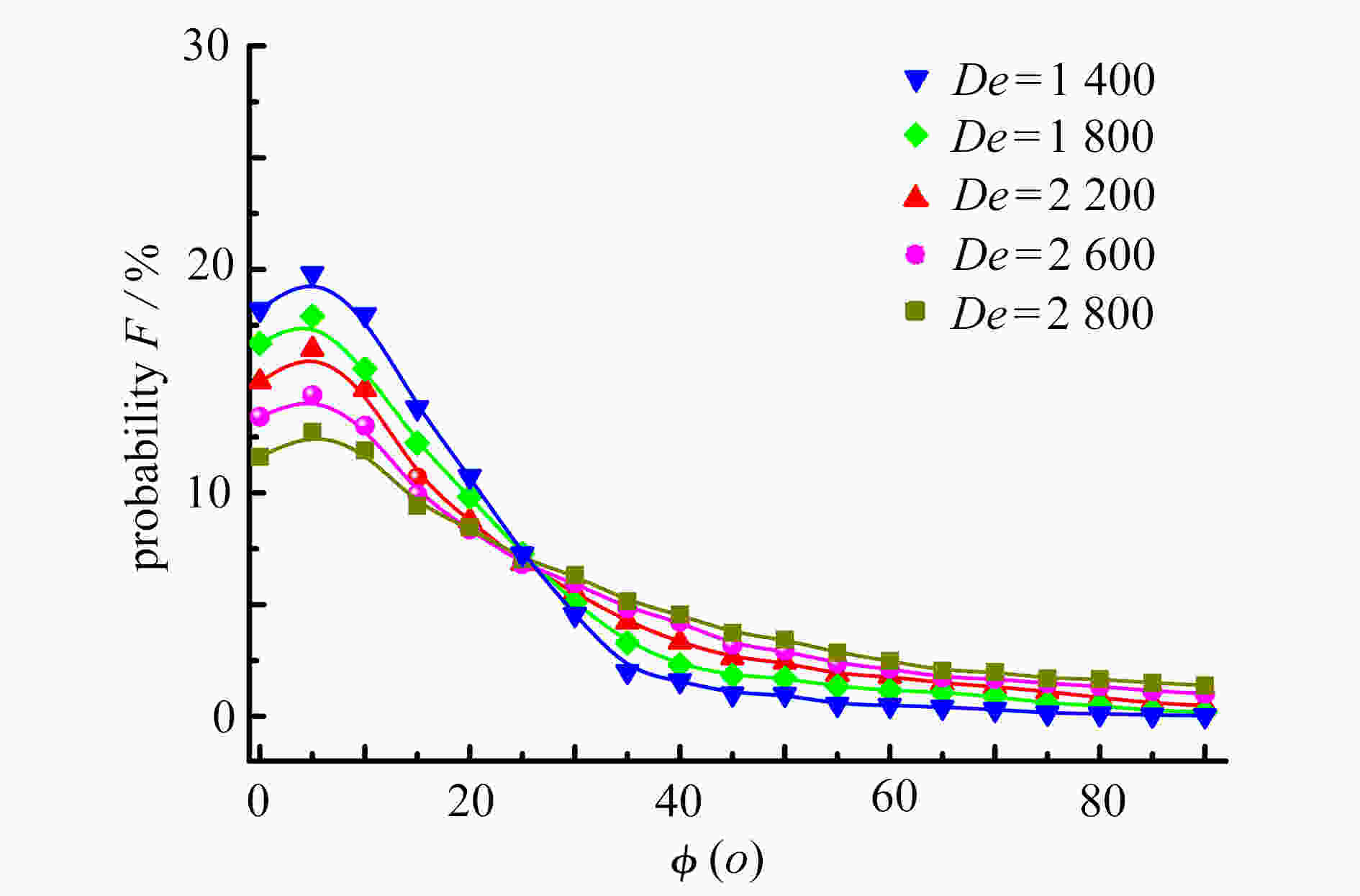
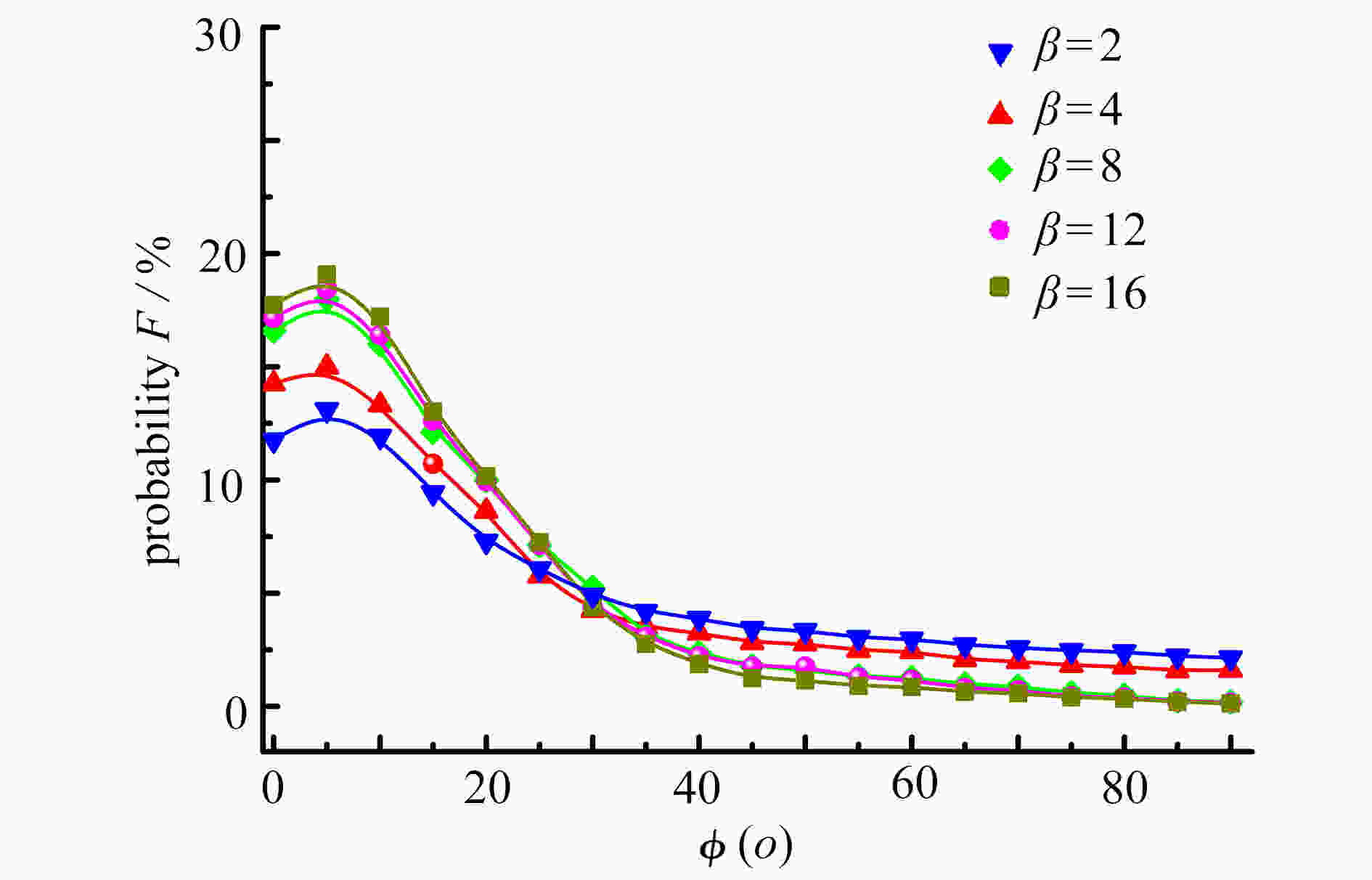
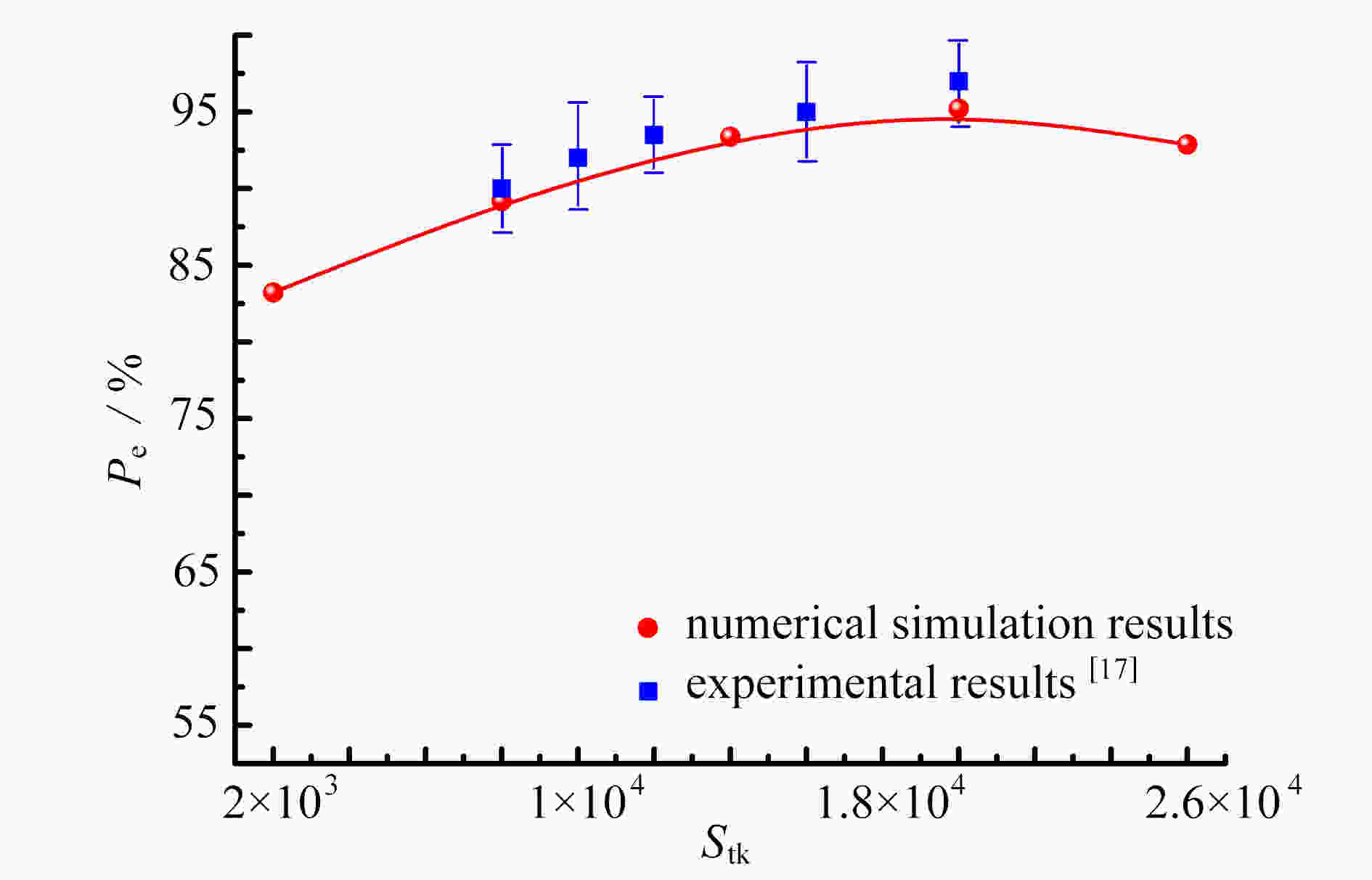
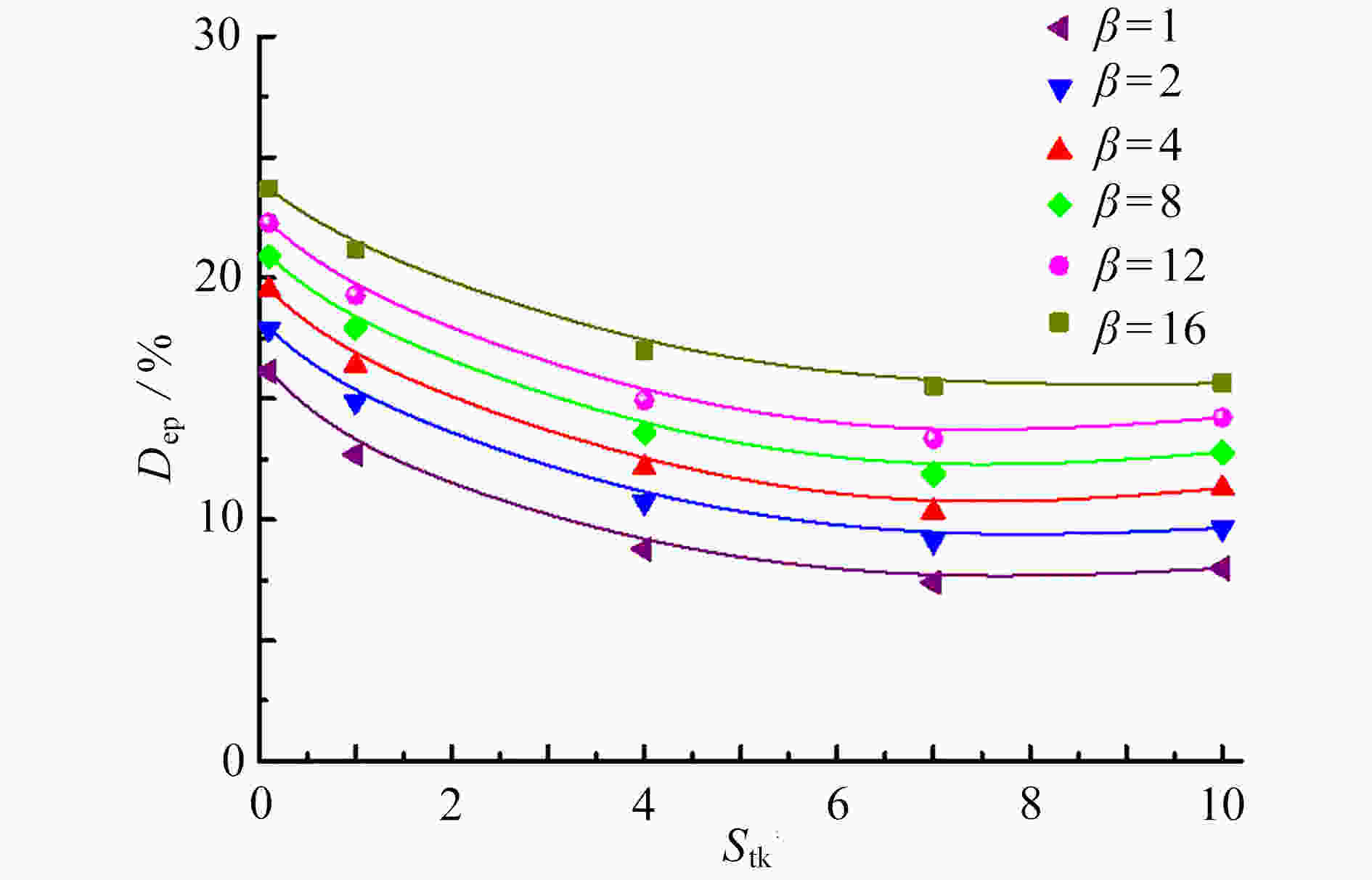
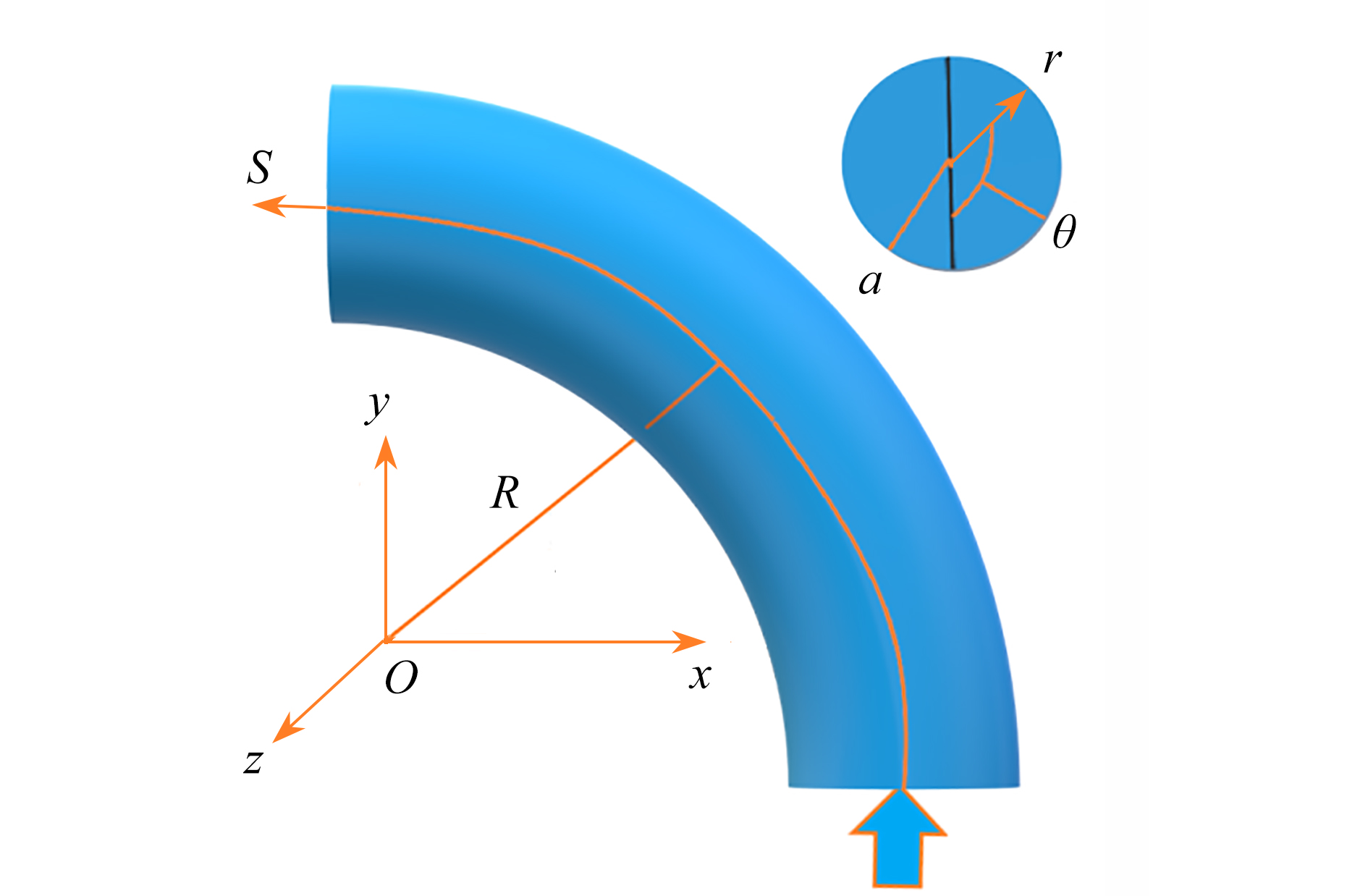
针对在Reynolds数Re=3000 ~ 50000、Stokes数Stk=0.1 ~ 10、Dean数De=1400 ~ 2800的情况下,长径比β=2 ~ 12的圆柱状颗粒流经弯管湍流场时的取向与沉积特性进行了研究。圆柱状颗粒的运动采用细长体理论结合Newton第二定律进行描述,取向分布函数由Fokker-Planck方程给出,平均湍流场通过求解Reynolds平均运动方程结合Reynolds应力方程得到,作用在颗粒上的湍流脉动速度由动力学模拟扫掠模型描述。通过求解湍流场以及颗粒的运动方程和取向分布函数方程,得到并分析了沿流向不同截面和出口处颗粒的取向分布,讨论了各因素对颗粒沉积特性的影响。研究结果表明,随着Stk和颗粒长径比β的增加、De和Re的减少,颗粒的主轴更趋向于流动方向。颗粒的沉积率随着De,Re,Stk和颗粒长径比的增大而增加,所得结论对于工程实际应用具有参考价值。
Abstract:In the cases of Reynolds number Re=3 000~50 000, Stokes number Stk=0.1~10, Dean number De=1 400~2 800, the orientation and deposition characteristics of cylindrical particles with aspect ratio β=2~12 in turbulent flow in curved tubes were studied. The motion of cylindrical particles was described under the slender body theory combined with Newton’s 2nd law. The orientation distribution function of cylindrical particles was given by the Fokker Planck equation. The mean velocity of the flow was obtained by solving the Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes equation and the Reynolds stress equation. The turbulent fluctuating velocity acting on particles was described with the kinetic simulation sweeping model. By solving the equations of the turbulent flow, the particle motion and the orientation distribution function, the orientation distributions of particles on the cross sections in different axial positions and the outlet were obtained and analyzed. The effects of various parameters on the deposition rate of particles were discussed. The results showed that, the main axis of particles turns toward the flow direction with the increase of Stk and β, and the decrease of De and Re. The deposition rate of particles increases with De, Re and β. However, it shows a non-monotonic trend with the change of Stk
. The work has reference values for practical engineering application.
-
-
[1] AKSHAT T M, MISRA S, GUDIYAWAR M Y, et al. Effect of electrospun nanofiber deposition on thermo-physiology of functional clothing[J]. Fibers and Polymers, 2019, 20(5): 991-1002. doi: 10.1007/s12221-019-9100-z [2] TIAN L, AHMADI G, WANG Z C, et al. Transport and deposition of ellipsoidal particles in low Reynolds number flows[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2012, 45: 1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jaerosci.2011.09.001 [3] TU C X, YIN Z Q, LIN J Z, et al. A review of experimental techniques for measuring micro- to nano-particle-laden gas flows[J]. Applied Sciences, 2017, 7(2). DOI: 10.3390/app7020120. [4] SUN L, LIN J Z, BAO F B. Numerical simulation on the deposition of nanoparticles under laminar conditions[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2006, 18(6): 676-680. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6058(07)60006-7 [5] PHARES D J, SHARMA G. A DNS study of aerosol deposition in a turbulent square duct flow[J]. Aerosol Science and Technology, 2006, 40(11): 1016-1024. doi: 10.1080/02786820600919416 [6] ARMAND P, BOULAUD D, POURPRIX M, et al. Two-fluid modeling of aerosol transport in laminar and turbulent flows[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 1998, 29(8): 961-983. doi: 10.1016/S0021-8502(98)00006-8 [7] 罗万清, 李海燕, 梁剑寒. 基于Euler-Lagrange模型的电弧风洞喷管两相流模拟[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 41(1): 16-26. (LUO Wanqing, LI Haiyan, LIANG Jianhan. Simulation of 2-phase flow in the nozzle of the arc heated wind tunnel based on the Eulerian-Lagrange model[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(1): 16-26.(in Chinese)LUO Wanqing, LI Haiyan, LIANG Jianhan. Simulation of 2-phase flow in the nozzle of the arc heated wind tunnel based on the Eulerian-Lagrange model[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(1): 16-26. (in Chinese)) [8] LIN J Z, YIN Z Q, GAN F J, et al. Penetration efficiency and distribution of aerosol particles in turbulent pipe flow undergoing coagulation and breakage[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2014, 61: 28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2013.12.001 [9] PUI D Y H, ROMAY-NOVAS F, LIU B Y H. Experimental study of particle deposition in bends of circular cross section[J]. Aerosol Science and Technology, 1987, 7(3): 301-315. doi: 10.1080/02786828708959166 [10] BALÁSHÁZY I, MARTONEN T B, HOFMANN W. Inertial impaction and gravitational deposition of aerosols in curved tubes and airway bifurcations[J]. Aerosol Science and Technology, 1990, 13(3): 308-321. doi: 10.1080/02786829008959447 [11] LEE K W, GIESEKE J A. Deposition of particles in turbulent flow pipes[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2006, 25(4): 699-709. [12] SATO S, CHEN D R, PUI D Y H. Particle transport at low pressure: deposition in bends of a circular cross-section[J]. Aerosol Science and Technology, 2003, 37: 770-779. doi: 10.1080/02786820300911 [13] WANG J, FLAGAN R C, SEINFELD J H. Diffusional losses in particle sampling systems containing bends and elbows[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2002, 33(6): 843-857. doi: 10.1016/S0021-8502(02)00042-3 [14] YOOK S J, PUI D Y H. Experimental study of nanoparticle penetration efficiency through coils of circular cross-sections[J]. Aerosol Science and Technology, 2006, 40(6): 456-462. doi: 10.1080/02786820600660895 [15] LIN J Z, LIN P F, CHEN H J. Research on the transport and deposition of nanoparticles in a rotating curved pipe[J]. Physics of Fluid, 2009, 21(12): 122001. doi: 10.1063/1.3264110 [16] WILSON S R, LIU Y A, MATIDA E A, et al. Aerosol deposition measurements as a function of Reynolds number for turbulent flow in a ninety-degree pipe bend[J]. Aerosol Science and Technology, 2011, 45(3): 364-375. doi: 10.1080/02786826.2010.538092 [17] GHAFFARPASAND O, DREWNICK F, HOSSEINIEBALAM F, et al. Penetration efficiency of nanometer-sized aerosol particles in tubes under turbulent flow conditions[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2012, 50: 11-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jaerosci.2012.03.002 [18] LIN J Z, YIN Z Q, LIN P F, et al. Distribution and penetration efficiency of nanoparticles between 8~550 nm in pipe bends under laminar and turbulent flow conditions[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 85: 61-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2015.01.033 [19] BATCHELOR G K. Slender-body theory for particles of arbitrary cross-section in Stokes flow[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1970, 44(3): 419-440. doi: 10.1017/S002211207000191X [20] MACKAPLOW M B, SHAQFEH E S G. A numerical study of the sedimentation of fiber suspension[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1988, 376(1): 149-182. [21] MICHAELIDES E E. Brownian movement and thermophoresis of nanoparticles in liquids[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 81: 179-187. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.10.019 [22] LEAL L G, HINCH E J. The effect of weak Brownian rotations on particles in shear flow[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1971, 46: 685-703. doi: 10.1017/S0022112071000788 [23] 高振宇, 林建忠, 李俊. 纤维悬浮剪切湍流中纤维旋转扩散系数的理论研究[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2007, 28(3): 263-269. (GAO Zhenyu, LIN Jianzhong, LI Jun. Theoretical research on the rotational dispersion coefficient of fiber in the turbulent shear flow of fiber suspension[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2007, 28(3): 263-269.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0887.2007.03.002GAO Zhenyu, LIN Jianzhong, LI Jun. Theoretical research on the rotational dispersion coefficient of fiber in the turbulent shear flow of fiber suspension[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2007, 28(3): 263-269. (in Chinese)) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0887.2007.03.002 [24] CHEN S B, JIANG L. Orientation distribution in a dilute suspension of fibers subject to simple shear flow[J]. Physics of Fluid, 1999, 11(10): 2878-2890. doi: 10.1063/1.870146 [25] LIEN F S, LESCHZINER M A. Assessment of turbulence-transport models including non-linear RNG eddy-viscosity formulation and second-moment closure for flow over a backward-facing step[J]. Computers and Fluids, 1994, 23(8): 983-1004. doi: 10.1016/0045-7930(94)90001-9 [26] LAUNDER B E. Second-moment closure and its use in modeling turbulent industrial flows[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 1989, 9(8): 963-985. doi: 10.1002/fld.1650090806 [27] LAUNDER B E. Second-moment closure: present and future[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 1989, 10(4): 282-300. doi: 10.1016/0142-727X(89)90017-9 [28] FUNG J C H, HUNT J C R, MALIK N A, et al. Kinematic simulation of homogeneous turbulence by unsteady random Fourier modes[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1992, 236: 281-318. doi: 10.1017/S0022112092001423 [29] WANG L P, STOCK D E. Numerical simulation of heavy particle dispersion-scale ration and flow decay considerations[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 1994, 116(1): 154-163. doi: 10.1115/1.2910224 [30] DONG S, FENG X, SALCUDEAN M, et al. Concentration of pulp fibers in 3D turbulent channel flow[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2003, 29(1): 1-21. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9322(02)00128-3 [31] WEBSTER D R, HUMPHREY J A C. Experimental observations of flow instability in a helical coil[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 1993, 115(3): 436-443. doi: 10.1115/1.2910157 [32] KRUSHKAL E M, GALLILY I. On the orientation distribution function of nonspherical aerosol particles in a general shear flow, Ⅱ: the turbulent case[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 1988, 19(2): 197-211. doi: 10.1016/0021-8502(88)90223-6 [33] PODGÓRSKI A, GRADOŃ L, GRZYBOWSKI P. Theoretical-study on deposition of flexible and stiff fibrous aerosol-particles on a cylindrical collector[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal and the Biochemical Engineering Journal, 1995, 58(2): 109-121. doi: 10.1016/0923-0467(95)02975-3 -




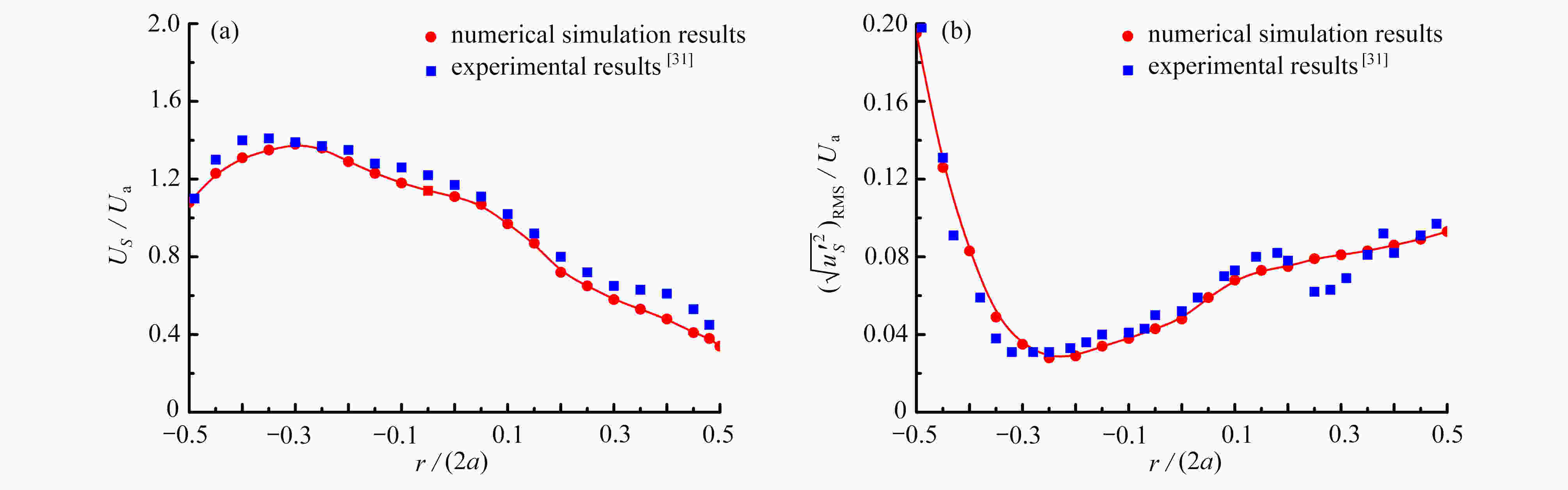
 下载:
下载:

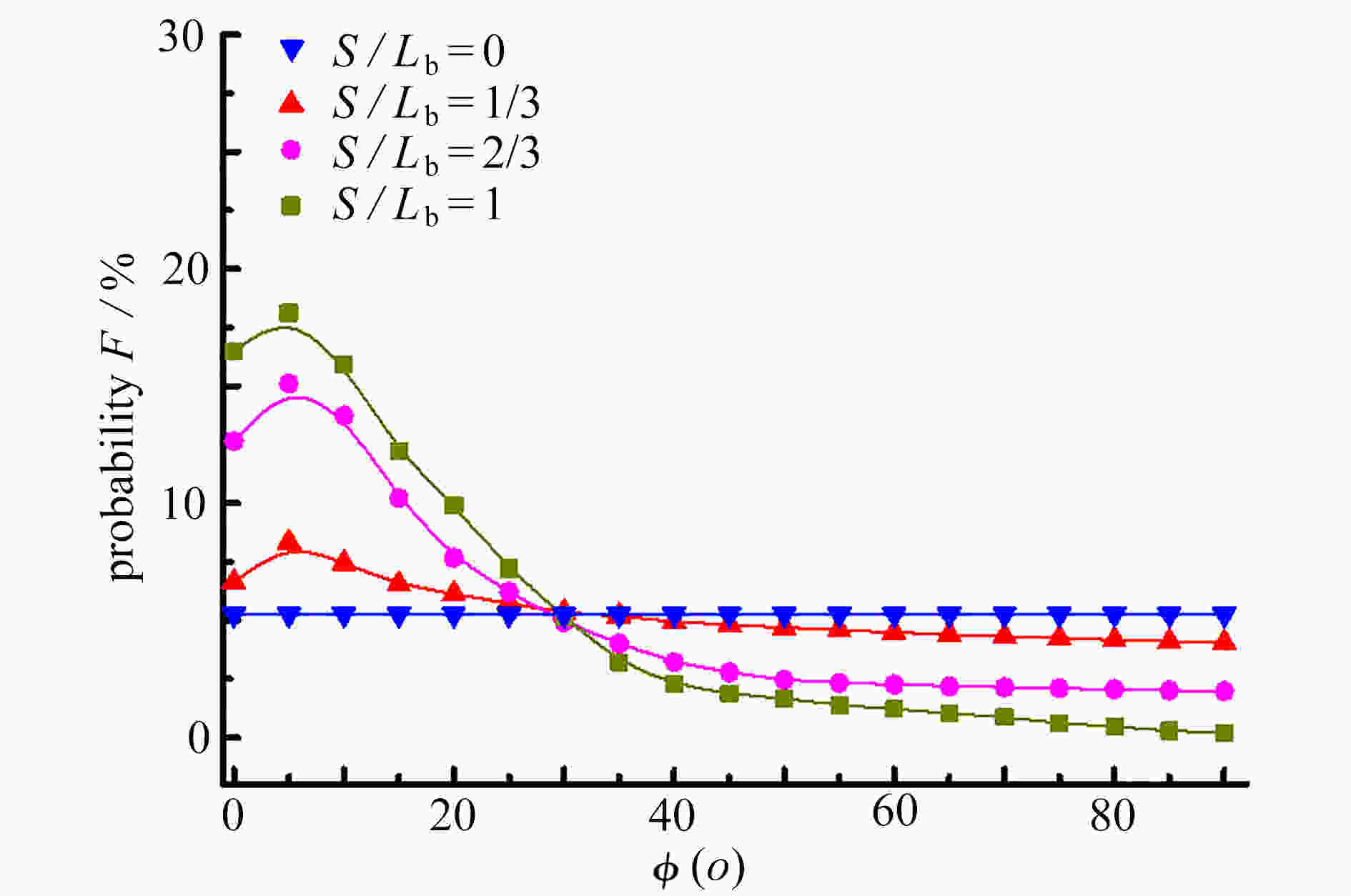




 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号