A Symplectic Superposition Method for Vibration of the Orthotropic Rectangular Thin Plate Point-Supported at a Corner and Clamped at its Opposite Edges
-
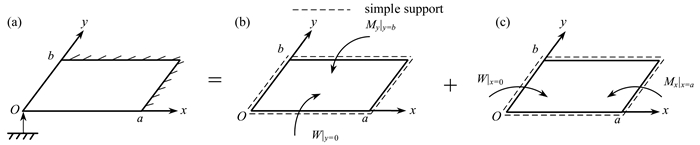
摘要: 运用辛叠加方法研究了一角点支撑对边两边固支的正交各向异性矩形薄板的振动问题. 首先由边界条件出发, 将原振动问题分解为两个对边简支的子振动问题, 再根据Hamilton体系的分离变量法分别得到两个子振动问题的级数展开解,然后利用叠加方法得到原振动问题的辛叠加解. 为了在具体计算中确定所得辛叠加的级数展开项, 对该解计算正交各向异性矩形薄板的情形进行了收敛性分析. 应用所得辛叠加解分别计算了一角点支撑对边两边固支的各向同性和正交各向异性矩形薄板的振动频率, 进而给出了正交各向异性方形薄板的前8阶振动频率所对应的模态.
-
关键词:
- 正交各向异性矩形薄板 /
- Hamilton体系 /
- 辛叠加方法 /
- 振动
Abstract: The symplectic superposition method was used to study the vibration problem of the orthotropic rectangular thin plate point-supported at a corner and clamped at its opposite edges. Firstly, based on the boundary conditions, the original vibration problem was decomposed into 2 subproblems with 2 opposite edges simply supported. Next, the series expansion solutions to the 2 sub-vibration problems were obtained based on the separation variable method in the Hamiltonian system. Then the symplectic superposition solution to the original vibration problem was obtained with the superposition method. To determine the terms of the series expansion of the obtained symplectic superposition solution in specific calculations, the convergence analysis of the solution for calculating orthotropic rectangular thin plates was performed. The symplectic superposition solution was also used to calculate the vibration frequencies of the isotropic and orthotropic rectangular thin plate point-supported at a corner and clamped at its opposite edges, respectively, and to give the modes corresponding to the 1st 8 vibration frequencies of an orthotropic square thin plate. -
表 1 一角点支撑对边两边固支各向同性矩形薄板的频率参数$ \omega a^{2} \sqrt{\rho h / D}$
Table 1. Values of frequency parameter $ \omega a^{2} \sqrt{\rho h / D}$ of the isotropic rectangular thin plates point-supported at a corner and clamped at its opposite edges
b/a reference mode 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 7th 8th 1.0 present 15.165 23.899 39.386 54.070 62.705 77.319 85.662 105.29 ref. [16] 15.165 23.902 39.388 54.083 62.705 77.321 85.695 105.29 1.5 present 9.197 8 18.191 26.293 31.679 44.141 53.626 59.007 68.345 ref. [16] 9.197 0 18.195 26.294 31.683 44.142 53.637 59.021 68.346 2 present 6.556 0 14.037 20.013 25.902 30.630 36.834 46.124 53.062 ref. [16] 6.555 1 14.035 20.026 25.897 30.637 36.829 46.133 53.048 2.5 present 5.355 7 10.465 16.927 21.726 24.924 30.121 33.694 40.362 ref. [16] 5.355 0 10.461 16.933 21.735 24.931 30.105 33.711 40.342 3 present 4.735 6 8.287 4 13.647 18.634 23.142 24.580 28.504 33.019 ref. [16] 4.734 9 8.283 6 13.642 18.657 23.142 24.583 28.512 32.994 3.5 present 4.379 8 6.954 0 11.056 16.006 19.980 23.211 25.428 27.318 ref. [16] 4.379 3 6.950 5 11.048 16.009 20.015 23.206 25.430 27.317 4 present 4.158 7 6.096 0 9.260 3 13.431 17.661 21.293 23.040 25.384 ref. [16] 4.158 2 6.092 9 9.252 7 13.422 17.687 21.319 23.047 25.369 4.5 present 4.012 5 5.517 2 8.009 7 11.399 15.373 18.887 22.411 23.053 ref. [16] 4.012 0 5.514 4 8.002 6 11.388 15.371 18.939 22.415 23.058 5 present 3.910 9 5.110 6 7.115 0 9.882 7 13.296 16.893 19.972 22.572 ref. [16] 3.910 4 5.108 1 7.108 4 9.871 1 13.284 16.914 20.033 22.568 表 2 一角点支撑对边两边固支正交各向异性矩形薄板的收敛性分析$ (\omega a^{2} \sqrt{\rho h / D_1})$
Table 2. Convergence analysis of the orthotropic rectangular thin plates point-supported at a corner and clamped at its opposite edges $ (\omega a^{2} \sqrt{\rho h / D_1})$
b/a number of series terms mode 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 7th 8th 1 50 18.929 31.932 50.967 65.823 81.800 99.774 114.65 124.19 55 18.929 31.932 50.967 65.824 81.800 99.775 114.65 124.19 60 18.929 31.933 50.967 65.824 81.800 99.775 114.65 124.19 65 18.928 31.933 50.967 65.825 81.800 99.776 114.65 124.19 70 18.928 31.933 50.967 65.825 81.800 99.776 114.65 124.19 75 18.928 31.933 50.967 65.825 81.800 99.776 114.65 124.19 80 18.928 31.933 50.967 65.825 81.800 99.777 114.65 124.19 85 18.928 31.933 50.967 65.825 81.800 99.777 114.65 124.19 2 50 8.869 7 17.901 24.683 31.580 41.419 49.502 58.218 66.804 55 8.869 6 17.901 24.683 31.580 41.419 49.502 58.220 66.804 60 8.869 6 17.901 24.683 31.580 41.419 49.502 58.221 66.805 65 8.869 5 17.901 24.684 31.580 41.419 49.502 58.222 66.805 70 8.869 5 17.901 24.684 31.580 41.420 49.501 58.222 66.805 75 8.869 4 17.901 24.684 31.580 41.420 49.501 58.223 66.805 80 8.869 4 17.901 24.684 31.580 41.420 49.501 58.223 66.805 85 8.869 4 17.901 24.684 31.580 41.420 49.501 58.223 66.805 表 3 一角点支撑对边两边固支正交各向异性矩形薄板的频率参数$ \omega a^{2} \sqrt{\rho h / D_1}$
Table 3. Values of frequency parameter $ \omega a^{2} \sqrt{\rho h / D_1}$ of the orthotropic rectangular thin plates point-supported at a corner and clamped at its opposite edges
b/a reference mode 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 7th 8th 1 present 18.928 31.933 50.967 65.825 81.800 99.776 114.65 124.19 1.5 present 12.483 21.692 33.851 42.947 55.604 67.520 75.576 81.878 2 present 8.869 4 17.901 24.684 31.580 41.420 49.501 58.223 66.805 2.5 present 7.011 4 14.240 20.654 26.545 31.025 38.707 46.258 53.475 3 present 5.968 4 11.404 17.931 22.735 26.481 32.009 36.404 43.731 3.5 present 5.329 5 9.499 4 15.130 20.180 24.293 26.740 31.518 36.249 4 present 4.910 4 8.204 4 12.804 17.934 21.977 24.366 28.082 30.721 4.5 present 4.620 8 7.291 0 11.059 15.659 19.907 23.216 24.836 27.953 5 present 4.412 4 6.623 4 9.757 3 13.696 17.948 21.468 23.445 25.887 -
[1] LEISSA A W. Vibration of plates: SP-160[R]. Washington DC: Office of Technology Utilization, NASA, 1960. [2] RAJU K K, RAO G V. Non-linear vibrations of orthotropic plates by a finite element method[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1976, 48 (2): 301-303. doi: 10.1016/0022-460X(76)90468-5 [3] LAL R, SAINI R. On the use of GDQ for vibration characteristic of non-homogeneous orthotropic rectangular plates of bilinearly varying thickness[J]. Acta Mechanica, 2015, 226: 1605-1620. doi: 10.1007/s00707-014-1272-4 [4] VALIZADEH N, BUI T Q, VU V T, et al. Isogeometric simulation for buckling, free and forced vibration of orthotropic plates[J]. International Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2013, 5 (2): 1350017. doi: 10.1142/S1758825113500178 [5] XING Y F, LIU B. New exact soltions for free vibrations of thin orthotropic rectangular plates[J]. Composite Structures, 2009, 89: 567-574. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2008.11.010 [6] LATIFI M, FARHATNIA F, KADKHODAEI M. Buckling analysis of rectangular functionally graded plates under various edge conditions using Fourier series expansion[J]. European Journal of Mechanics A: Solids, 2013, 41 (11): 16-27. [7] 钟万勰. 分离变量法与哈密尔顿体系[J]. 计算力学学报, 1991, 8 (3): 229-240. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJG199103000.htmZHONG Wanxie. Separation variable method and Hamilton system[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 1991, 8 (3): 229-240. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJG199103000.htm [8] LIU Yuemei, LI Rui. Accurate bending analysis of rectangular plates with two adjacent edges free and the others clamped or simply supported based on new symplecticapproach[J]. Applied Methematical Modelling, 2010, 34 (4): 856-865. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2009.07.003 [9] HU Z Y, YANG Y S, ZHOU C, et al. On the symplectic superposition method for new analytic free vibration solutions of side-cracked rectangular thin plates[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2020, 489: 115695. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2020.115695 [10] 周震寰, 李月杰, 范俊梅, 等. 双功能梯度纳米梁系统振动分析的辛方法[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2018, 39 (10): 1159-1171. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.390130ZHOU Zhenhuan, LI Yuejie, FAN Junmei, et al. A symplectic approach for free vibration of functionally graded double-nanobeam systems embedded in viscoelastic medium[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2018, 39 (10): 1159-1171. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.390130 [11] 刘明峰, 徐典, 倪卓凡, 等. 非Lévy型正交各向异性开口圆柱壳屈曲问题的辛叠加解析解[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2023, 44 (12): 1428-1440. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.440093 LIU Mingfeng, XU Dian, NI Zhuofan, et al. Symplectic superposition-based analytical solutions for buckling of non-Lévy-type orthotropic cylindrical shells[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2023, 44 (12): 1428-1440. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.440093 [12] XIONG Sijun, ZHENG Xinran, ZHOU Chao, et al. Buckling of non-Lévy-type rectangular thick plates: new benchmark solutions in the symplectic framework[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2024, 125: 668-686. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2023.09.009 [13] ALTEKIN M. Bending of orthotropic super-elliptical plates on intermediate point supports[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2010, 37 (11): 1048-1060. [14] LI R, WANG B, LI P. Hamiltonian system-based benchmark bending solutions of rectangular thin plates with a corner point-supported[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2014, 85: 212-218. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2014.05.004 [15] KOCATÜRK T, SEZER S, DEMIR C. Determination of the steady state response of viscoelastically point-sopported rectangular specially orthotropic plates with added concentrated masses[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2004, 278 (4/5): 789-806. [16] LI R, WANG B, LI G, et al. Analytic free vibration solutions of rectangular thin plates point-supported at a corner[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2015, 96/97: 199-205. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2015.04.004 [17] LI R, ZHENG X, WANG P, et al. New analytic free vibration solutions of orthotropic rectangular plates by a novel symplectic approach[J]. Acta Mechanica, 2019, 230: 3087-3101. doi: 10.1007/s00707-019-02448-1 [18] SU X, BAI E, CHEN A. Symplectic superposition solution of free vibration of fully clamped orthotropic rectangular thin plates on two-parameter elastic foundation[J]. International Journal of Structural Stability and Dynamics, 2021, 21 (9): 2150122. doi: 10.1142/S0219455421501224 [19] YAO W, ZHONG W, LIM C W. Symplectic Elasticity[M]. Singapore: World Scientific, 2009. -





 下载:
下载:


 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号