Elastocapillary Deformation of Soft Matter Beams on Elastic Substrate
-
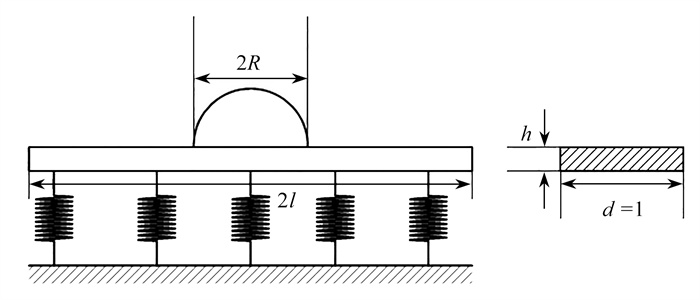
摘要: 当软物质微/纳米结构表面存在液滴时,需要考虑由润湿诱导的弹性毛细变形. 该文基于一个新的润湿方程,推导了液滴铺展半径与其表面曲率的关系,并得到了无重力影响时液滴保持球冠状的必要条件;结合Winkler地基模型,计算了弹性基底上软物质微梁的弹性毛细变形,得到了微梁挠度的解析解. 以聚苯乙烯(EPS)和聚乙烯(PE)梁为例,分析并讨论了液滴铺展半径、弹性模量和基底参数对微梁的挠曲变形以及从基底上脱黏的影响.
-
关键词:
- 润湿 /
- 弹性毛细变形 /
- Winkler地基模型 /
- 软物质 /
- 微梁
Abstract: With droplets on the surface of soft matter or micro/nanostructures, wetting-induced elastocapillary deformation should be considered. Based on a new wetting equation, the relationship between the droplet spreading radius and its surface curvature was determined, and the necessary conditions for the droplet to hold the spherical cap without the influence of gravity were obtained. Combined with the Winkler foundation model, the elastocapillary deformation of soft material microbeam on elastic substrate was calculated. The analytical solution for the deflection of the microbeam was given. With polystyrene and polyethylene beams as examples, the influences of the droplet spreading radius, the beam material elastic modulus and the Winkler foundation parameter on the microbeam deflections and detachments from the substrate, were analyzed and discussed.-
Key words:
- wetting /
- elastocapillary deformation /
- Winkler foundation model /
- soft matter /
- microbeam
-
表 1 EPS微梁的材料参数与几何参数
Table 1. Material and geometric parameters of the EPS micro-beam
l/mm E/MPa d/mm h/mm I/mm4 5 1.8 1 0.05 1/96 000 表 2 微梁最大挠度及黏附长度与液滴半径的对应关系
Table 2. Maximum deflections and adhesive lengths of the micro-beam vs. droplet radii
parameter R/mm 1 0.1 0.01 y(0)/mm 0.024 2 0.046 2 0.049 6 l1/mm 1.4 0.83 0.82 表 3 微梁的最大挠度及黏附长度随基床系数的变化
Table 3. Maximum deflections and adhesive lengths of the micro-beam vs. the bedding coefficient
parameter k/(10-3·N/mm3) 1 1.5 2 20 y(0)/mm 0.046 1 0.034 0 0.027 4 0.004 9 l1/mm 2.60 2.35 2.19 1.23 -
[1] FENG S L, DELANNOY J, MALOD A, et al. Tip-induced flipping of droplets on Janus pillars: from local reconfiguration to global transport[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(28): eabb4540. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb4540 [2] 余迎松. 液气界面张力垂直分量引起的基底弹性变形[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2012, 33(9): 1025-1042. doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2012.09.001YU Yingsong. Substrate elastic deformation due to vertical component of liquid-vapor interfacial tension[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2012, 33(9): 1025-1042. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2012.09.001 [3] LESTER G R. Contact angles of liquids at deformable solid surfaces[J]. Journal of Colloid Science, 1961, 16(4): 315-326. doi: 10.1016/0095-8522(61)90032-0 [4] RUSANOV A I. Theory of the wetting of elastically deformed bodies, 1: deformation with a finite contact angle[J]. Colloid Journal of the USSR, 1975, 37 : 614-622. [5] FORTES M A. Deformation of solid surfaces due to capillary forces[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1984, 100(1): 17-26. doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(84)90407-7 [6] STYLE R W, DUFRESNE E R. Static wetting on deformable substrates, from liquids to soft solids[J]. Soft Matter, 2012, 8(27): 7177-7184. doi: 10.1039/c2sm25540e [7] STYLE R W, BOLTYANSKIY R, CHE Y L, et al. Universal deformation of soft substrates near a contact line and the direct measurement of solid surface stresses[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2013, 110(6): 066103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.066103 [8] BOSTWICK J B, SHEARER M, DANIELS K E. Elastocapillary deformations on partially-wetting substrates: rival contact-line models[J]. Soft Matter, 2014, 10(37): 7361-7369. doi: 10.1039/C4SM00891J [9] KERN R, MVLLER P. Deformation of an elastic thin solid induced by a liquid droplet[J]. Surface Science, 1992, 264(3): 467-494. doi: 10.1016/0039-6028(92)90203-I [10] OLIVES J. Capillarity and elasticity. The example of the thin plate[J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 1993, 5 : 2081-2094. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/5/14/007 [11] LIU J L, NIE Z X, JIANG W G. Deformation field of the soft substrate induced by capillary force[J]. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2009, 404(8/11): 1195-1199. [12] LIU J L, XIA R, MEI Y, et al. Droplet-induced abnormal bending of micro-beams[J]. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology, 2013, 27(13): 1418-1431. doi: 10.1080/01694243.2012.742400 [13] 陶泽, 李墨筱, 提飞, 等. 充液弹性毛细管低温相变的力学分析[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2021, 42(10): 1045-1061. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420301TAO Ze, LI Moxiao, TI Fei, et al. Mechanics of low-temperature phase transition in liquid-filled elastic capillary tubes[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2021, 42(10): 1045-1061. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420301 [14] YU Y S, ZHAO Y P. Deformation of PDMS membrane andmicrocantilever by a water droplet: comparison between Mooney-Rivlin and linear elastic constitutive models[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2009, 332(2): 467-476. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2008.12.054 [15] LIU J L, XIA R, ZHOU X H. A new look on wetting models: continuum analysis[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics and Astronomy, 2012, 55(11): 2158-2166. doi: 10.1007/s11433-012-4895-2 [16] HUANG Z X. New equations of wetting[J]. Philosophical Magazine Letters, 2020, 100 (4): 181-188. doi: 10.1080/09500839.2020.1740811 [17] HUANG Z X. Formulation and a new solving approach to the problem of the wetting-induced deformation[J]. Philosophical Magazine, 2021, 101(24): 2560-2583. doi: 10.1080/14786435.2021.1980238 [18] DRELICH J. The significance and magnitude of the line tension in three-phase (solid-liquid-fluid) systems[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 1996, 116(1/2): 43-54. [19] OKUBO T. Surface tension of structured colloidal suspensions of polystyrene and silica spheres at the air-water interface[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1995, 171(1): 55-62. doi: 10.1006/jcis.1995.1150 [20] VERA-GRAZIANO R, MUHL S, RIVERA-TORRES F. The effect of illumination on contact angles of pure water on crystalline silicon[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1995, 170(2): 591-597. doi: 10.1006/jcis.1995.1139 [21] DRELICH J, MILLER J D. The line/pseudo-line tension in three-phase systems[J]. Particulate Science and Technology, 1992, 10(1): 1-20. doi: 10.1080/02726359208906593 [22] DRELICH J, MILLER J D. The effect of solid surface heterogeneity and roughness on the contact angle/drop (bubble) size relationship[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1994, 164(1): 252-259. doi: 10.1006/jcis.1994.1164 -





 下载:
下载:










 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号