Study on the Influence Mechanism of Annular Solid Phase Settling on Deepwater Trapped Pressure and the Prediction Model
-
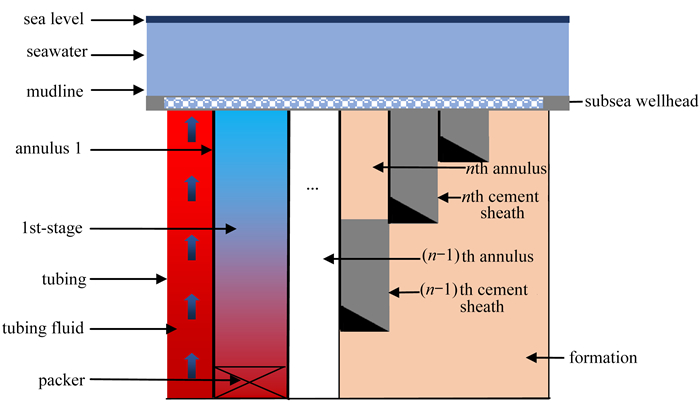
摘要: 深水油气开采作业中,精准预测环空圈闭压力对保障油气井安全、优化开采流程以及延长油气井使用寿命具有决定性意义. 本研究聚焦水基环空液体,系统测试了多种沉降时间下的密度及热物性参数,梳理出固相沉降对液体参数的影响规律. 基于定容热力学定律,考虑固相沉淀、液体热物性参数动态变化等关键因素,提出了适用于气井的多环空耦合圈闭压力计算方法. 将该方法的计算结果与水下井口实测圈闭压力对比,二者最大误差仅为8.91%. 以海上某典型采气井为具体实例,运用.Net语言编写程序,对所构建的模型进行求解运算. 结果表明,考虑固相沉降对环空液体密度影响极为显著,随着沉降时间的持续增加,液体密度呈现出明显的下降趋势. 经过7 d的测试,钻井液密度从初始的1.7 g/cm3逐步降低至1.23 g/cm3并趋于稳定,密度降幅高达27.65%. 随着井深增加、采气量上升、钻井液等压膨胀系数以及等温压缩系数增大,环空圈闭压力均呈现增大趋势. 在流体热物性相同的情况下,环空圈闭压力受环空封闭体积的影响尤为突出:第1环空圈闭压力达到23.2 MPa;第2环空圈闭压力为15.53 MPa;第3环空圈闭压力则为7.69 MPa. 对比井口油管位移与井底情况时发现,井口油管位移最大距离从1.69×10-6 m减小至6.1×10-7 m,井口油管位移距离约为井底的2.77倍. 环空圈闭压力的准确求解,能够为校核管柱安全系数、评估井口抬升风险以及优化水泥返高设计等实际工程作业,提供极为关键的理论依据与数据支撑,有力推进深水油气开采作业安全、高效开展.Abstract: In deepwater oil and gas production operations, accurately predicting the annular trapped pressure is of decisive significance for ensuring the safety of oil and gas wells, optimizing the production process, and extending the service life of oil and gas wells. The water-based annular fluids were investigated and the density and thermophysical property parameters under various settlement times were systematically tested, and the influence law of solid-phase settlement on the fluid parameters was sorted out. Based on the law of constant-volume thermodynamics, in view of key factors such as solid-phase settlement and dynamic changes in the thermophysical property parameters of the fluids, a calculation method for the multi-annular coupled trapped pressures applicable to gas wells was proposed. Through comparison of the calculation results of this method with the measured trapped pressure data at the underwater wellhead, the maximum error between the 2 is only 8.91%. With a typical offshore gas production well as a specific example, a program was developed with the.Net language to solve and operate the constructed model. The results show that, the solid-phase settlement has an extremely significant effect on the density of the annular fluid. With the continuous increase of the settlement time, the fluid density shows an obvious downward trend. After a 7 d test, the drilling fluid density gradually decreases from the initial value of 1.7 g/cm3 to 1.23 g/cm3 and tends to be stable, with a density reduction of up to 27.65%. With the well depth increase, the gas production rate rise, the isobaric expansion coefficient uplift and the drilling fluid isothermal compression coefficient growth, the annular trapped pressure always shows an increasing trend. Under the condition of the same thermophysical property of the fluid, the annular trapped pressure is particularly affected by the closed volume of the annulus. The trapped pressure in the 1st annulus is 23.2 MPa, that in the 2nd is 15.53 MPa, and that in the 3rd is 7.69 MPa. In addition, the comparison of the tubing displacement at the wellhead with that at the bottom of the well indicates that, the maximum tubing displacement at the wellhead decreases from 1.69×10-6 m to 6.1×10-7 m, and the tubing displacement at the wellhead is about 2.77 times that at the bottom. The accurate solution of the annular trapped pressure can provide an extremely crucial theoretical basis and data support for practical engineering operations such as checking the pipe string safety factor, evaluating the wellhead uplift risk, and optimizing the cement return height design, and effectively contribute to the safe and efficient development of deepwater oil and gas production operations.
-
表 1 第1—3环空管柱内外径特性参数
Table 1. Key parameters of tubing outer and inner diameters in the 1st to 3rd annuluses
parameter tube 1st annulus 2nd annulus 3rd annulus outer diameter/mm 88.9 177.8 244.5 339.7 inner diameter/mm 73 166.1 216.8 320.4 Poisson’s ratio 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.3 expansion coefficient 0.000 018 2 0.000 018 2 0.000 018 2 0.000 018 2 modulus/GPa 205 205 205 205 表 2 不考虑钻井液固相沉降圈闭压力误差数据对比表
Table 2. Comparison of pressure error data for solid phase settling traps without regard to drilling fluid solid phase settling
well depth/m 100 1 200 1 800 2 400 3 000 3 600 4 200 4 800 5 400 6 000 without settling trapped pressure /MPa 1.50 6.78 9.44 11.95 14.30 16.50 18.54 20.42 22.16 23.20 3 d of settling trapped pressure/MPa 1.10 5.24 7.28 9.16 10.89 12.46 13.88 15.15 16.26 16.90 without error/% 26.82 22.75 22.93 23.32 23.84 24.43 25.10 25.82 26.61 27.16 5 d of settling trapped pressure/MPa 0.84 4.29 5.96 7.47 8.83 10.03 11.07 11.97 12.70 13.10 without erro/% 44.24 36.70 36.90 37.48 38.28 39.21 40.26 41.41 42.66 43.53 7 d of settling trapped pressure/MPa 0.50 3.50 4.91 6.17 7.28 8.23 9.03 9.68 10.16 10.40 without erro/% 66.95 48.45 47.97 48.32 49.07 50.08 51.27 52.62 54.12 55.17 -
[1] 石榆帆, 唐宜家, 马天寿, 等. 深水环空圈闭压力的破裂盘泄压控制模型[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 42(5): 153-160.SHI Yufan, TANG Yijia, MA Tianshou, et al. Pressure relief control model of rupture disk for annular pressure build-up in deep-water wells[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2020, 42(5): 153-160. (in Chinese) [2] 陈彬, 王彪, 严德, 等. 海洋油气井圈闭压力最大许可值确定方法[J]. 中国科技论文, 2025, 20(1): 30-40.CHEN Bin, WANG Biao, YAN De, et al. Research on the determination method for maximum allowable value of trap pressure in offshore oil and gas wells[J]. China Sciencepaper, 2025, 20(1): 30-40. (in Chinese) [3] WILLIAMSON R, SANDERS W, JAKABOSKY T, et al. Control of contained-annulus fluid pressure buildup[C]//SPE/IADC Drilling Conference. Amsterdam, Netherlands. Richardson: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2003: SPE 79875-MS. [4] AZZOLA J H, TSELEPIDAKIS D P, PATTILLO P D, et al. Application of vacuum-insulated tubing to mitigate annular pressure buildup[J]. SPE Drilling & Completion, 2007, 22(1): 46-51. [5] HASAN A R, IZGEC B, KABIR C S. Ensuring sustained production by managing annular-pressure buildup[C]//EUROPEC/EAGE Conference and Exhibition. Amsterdam, The Netherlands. Richardson: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2009: SPE 121754-MS. [6] 孔祥伟, 林元华, 何龙, 等. 钻井多相流体运移特性及套压控制研究[J]. 应用力学学报, 2015, 32(5): 823-827.KONG Xiangwei, LIN Yuanhua, HE Long, et al. Migration characteristics and control of back pressure for multiphase fluid along wellbore in drilling operations[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2015, 32(5): 823-827. (in Chinese) [7] VARGO R F, PAYNE M, FAUL R, et al. Practical and successful prevention of annular pressure buildup on the marlin project[J]. SPE Drilling & Completion, 2003, 18(3): 228-234. [8] 宋闯, 张晓诚, 谢涛, 等. 渤海"三高"气井环空早期圈闭压力预测[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(5): 694-707.SONG Chuang, ZHANG Xiaocheng, XIE Tao, et al. Prediction of early annular trap pressure of three-high gas wells in Bohai Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(5): 694-707. (in Chinese) [9] ADAMS A J. How to design for annulus fluid heat-up[C]//SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. Dallas, Texas. Richardson: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 1991: 529-540. [10] 姜海龙, 朱培旺, 徐东华. 考虑气体加速效应的高压气井产能方程推导及其应用[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 41(2): 134-142. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.400030JIANG Hailong, ZHU Peiwang, XU Donghua. Derivation and application of productivity equations for high-pressure gas reservoirs with gas acceleration effects[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(2): 134-142. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.400030 [11] LODER T, EVANS J H, GRIFFITH J E. Prediction of and effective preventative solution for annular fluid pressure buildup on subsea completed wells-case study[C]//SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. Denver, Colorado. Richardson: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2003: SPE 84270-MS. [12] 张更, 李军, 柳贡慧, 等. 深水油气井全生命周期环空圈闭压力预测模型[J]. 石油机械, 2022, 50(4): 49-55.ZHANG Geng, LI Jun, LIU Gonghui, et al. Prediction model of annular trapped pressure in the whole life cycle of deepwater oil and gas wells[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2022, 50(4): 49-55. (in Chinese) [13] 杨进, 唐海雄, 刘正礼, 等. 深水油气井套管环空压力预测模型[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(5): 616-619.YANG Jin, TANG Haixiong, LIU Zhengli, et al. Prediction model of casing annulus pressure for deepwater well drilling and completion operation[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(5): 616-619. (in Chinese) [14] 张波, 管志川, 张琦. 深水油气井开采过程环空压力预测与分析[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(8): 1012-1017.ZHANG Bo, GUAN Zhichuan, ZHANG Qi. Prediction and analysis on annular pressure of deepwater well in the production stage[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(8): 1012-1017. (in Chinese) [15] 刘劲歌. 深水油气井开采期间环空压力预测及释放机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2017.LIU Jinge. Research on the annular pressure buildup and mitigation mechanism in deepwater wells[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2017. (in Chinese) [16] 曾静. 深水套管及水下井口温压效应研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2019.ZENG Jing. Coupling effect of temperature and pressure on deepwater casing and subsea wellhead[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2019. (in Chinese) [17] 孔祥伟, 刘祚才, 靳彦欣. 川渝裂缝性地层自动压井环空多相压力波速特性研究[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43(12): 1370-1379. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430006 KONG Xiangwei, LIU Zuocai, JIN Yanxin. Study on multiphase pressure wave velocity characteristics of automatic kill annulus in Chuanyu fractured formation[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(12): 1370-1379. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430006 [18] 朱德武, 何汉平. 凝析气井井筒温度分布计算[J]. 天然气工业, 1998, 18(1): 60-62.ZHU Dewu, HE Hanping. Calculation of well bore temperature distribution in condensate gas well[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 1998, 18(1): 60-62. (in Chinese) [19] 孔祥伟, 董巧玲, 叶佳杰. 储气库采-关作业油管气相波动压力分析[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2023, 51(6): 93-98.KONG Xiangwei, DONG Qiaoling, YE Jiajie. Analysis of gas phase fluctuation pressure in oil pipes during production and shutdown operations of gas storage[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2023, 51(6): 93-98. (in Chinese) [20] 邓元洲, 陈平, 张慧丽. 迭代法计算油气井密闭环空压力[J]. 海洋石油, 2006, 26(2): 93-96.DENG Yuanzhou, CHEN Ping, ZHANG Huili. Calculating the pressure in sealed annulus in oil well by iterative method[J]. Offshore oil, 2006, 26(2): 93-96. (in Chinese) [21] 周传义. 海上深水井环空圈闭压力研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2023.ZHOU Chuanyi. Annular pressure study of offshore deepwater wells[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2023. (in Chinese) [22] 刘书杰, 罗鸣, 马传华, 等. 深水高温高压气井环空圈闭压力下油管柱安全评价方法[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2024, 24(12): 4959-4968.LIU Shujie, LUO Ming, MA Chuanhua, et al. Safety evaluation method for tubing strings under annular trapping pressure in deep water high temperature and high pressure gas wells[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2024, 24(12): 4959-4968. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载:












 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号