Fixed-Time Synchronization of Time-Delayed Memristive Neural Networks With Application to Confidential Communication
-
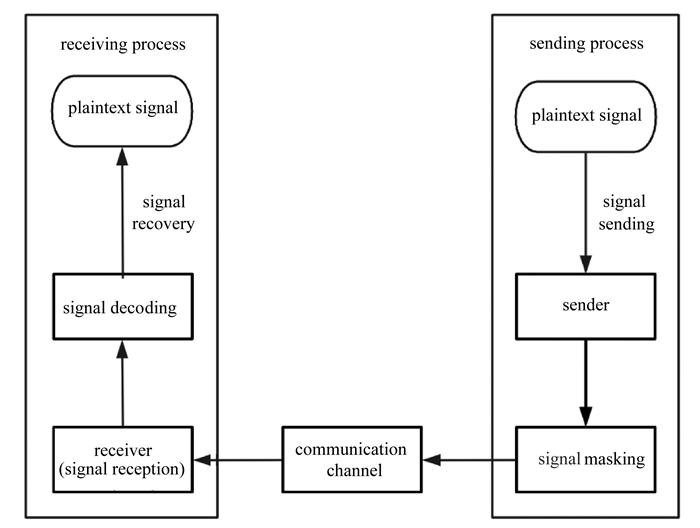
摘要: 针对具有时变时滞的忆阻神经网络,研究了其固定时间同步和在保密通信中的应用. 为了有效解决有限时间同步控制依赖初始条件的问题,利用Lyapunov稳定性理论,通过所设计的状态反馈控制器,得到了主从系统固定时间同步的充分条件和调整时间的上界. 在此基础上,以时滞忆阻神经网络为发射器,以响应系统为接收器,采用了混沌遮掩的方式实施信号加密,实现了在固定时间内恢复加密信号,确保了保密通信的安全性和时效性.
-
关键词:
- 忆阻神经网络 /
- 固定时间同步 /
- 保密通信 /
- Lyapunov稳定性理论
Abstract: The fixed-time synchronization of time-delayed memristive neural networks and its application in confidential communication was studied. To effectively solve the problem of finite-time synchronization control relying on initial conditions, the Lyapunov stability theory was used to obtain sufficient conditions for fixed-time synchronization of the master-slave system and upper bounds for the settling time through the designed state feedback controller. On this basis, the time-delayed memristive neural network was taken as the transmitter and its response system as the receiver, and the signal encryption was implemented by means of chaotic masking, to enable the recovery of the encrypted signal within a fixed time and ensure the security and timeliness of confidential communication. -
表 1 与其他文献控制器得到的调整时间对比
Table 1. Comparison of settling times obtained with other literature controllers
controller Tf ref. [17] ui(t)=-ζ1iei(t)-sign(ei(t))(ζ2i+ζ3i|ei(t)|d1+ζ4i|ei(t)|d2) 0.71 ref. [24] ui(t)=-ζ2isign(ei(t))-ζ4isign(ei(t))|ei(t)|d2 1.81 ref. [25] ui(t)=-ζ1iei(t)-sign(ei(t))(ζ2i+ζ4i|ei(t)|d2) 0.94 this paper $ \boldsymbol{u}_{i}(t)=-\zeta_{1 i} \boldsymbol{e}_{i}(t)-\operatorname{sign}\left(\boldsymbol{e}_{i}(t)\right)\left(\zeta_{2 i}+\zeta_{3 i}\left|\boldsymbol{e}_{i}(t)\right|^{d_{1}}+\zeta_{4 i}\left|\boldsymbol{e}_{i}(t)\right|^{d_{2}}+\sum\limits_{i=1}^{n} \zeta_{5 i}\left|\boldsymbol{e}_{j}(t-\mu(t))\right|\right)$ 0.65 -
[1] 谢川, 徐超, 周丹发, 等. 带襟翼导轨翼肋后缘尺寸-拓扑综合优化的摄动神经网络代理模型法[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2024, 45(1): 61-71. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.440033 XIE Chuan, XU Chao, ZHOU Danfa, et al. The perturbation neural network surrogate model method for size-topology synthetical optimization of wing rib trailing edges with flap tracks[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2024, 45(1): 61-71. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.440033 [2] 高兆瑞, 李铮, 姜永烽, 等. 基于人工神经网络的共振吸声超材料声学性能快速预测及结构优化设计[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2024, 45(8): 1058-1069. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.450170 GAO Zhaorui, LI Zheng, JIANG Yongfeng, et al. Acoustic performance rapid prediction and structural optimization for resonant sound-absorbing metamaterials based on artificial neural networks[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2024, 45(8): 1058-1069. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.450170 [3] JO S H, CHANG T, EBONG I, et al. Nanoscale memristor device as synapse in neuromorphic systems[J]. Nano Letters, 2010, 10(4): 1297-1301. doi: 10.1021/nl904092h [4] WANG L M, SHEN Y, YIN Q, et al. Adaptive synchronization of memristor-based neural networks with time-varying delays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(9): 2033-2042. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2361776 [5] SHI Y, ZHU P. Finite-time synchronization of stochastic memristor-based delayed neural networks[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2018, 29(6): 293-301. doi: 10.1007/s00521-016-2546-7 [6] ZHAO Y, REN S S, KURTHS J. Finite-time and fixed-time synchronization for a class of memristor-based competitive neural networks with different time scales[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2021, 148: 111033. [7] BATTISTON F, CENCETTI G, IACOPINI I, et al. Networks beyond pairwise interactions: structure and dynamics[J]. Physics Reports, 2020, 874: 1-92. doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2020.05.004 [8] 魏长江, 陈巧玉. 有限时间区间内马尔可夫跳变系统的异步滑模控制[J]. 上海工程技术大学学报, 2023, 37(3): 272-280.WEI Changjiang, CHEN Qiaoyu. Asynchronous sliding mode control for Markovian jumping systems in finite-time intervals[J]. Journal of Shanghai University of Engineering Science, 2023, 37(3): 272-280. (in Chinese) [9] XIONG X L, TANG R Q, YANG X S. Finite-time synchronization of memristive neural networks with proportional delay[J]. Neural Processing Letters, 2019, 50: 1139-1152. doi: 10.1007/s11063-018-9910-9 [10] POLYAKOV A. Nonlinear feedback design for fixed-time stabilization of linear control systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 57(8): 2106-2110. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2011.2179869 [11] WEI Y F, QING X, XIE C R, et al. Fixed-time synchronization of the new single-parameter chaotic system[J]. Complexity, 2020, 2020: 1067863. [12] HE W L, LUO T H, TANG Y, et al. Secure communication based on quantized synchronization of chaotic neural networks under an event-triggered strategy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(9): 3334-3345. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2943548 [13] PARK M J, LEE S H, KAVIARASAN B, et al. Secure communication in complex dynamical networks via time-delayed feedback control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(2): 1116-1125. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2022.3193056 [14] LIN C M, PHAM D H, HUYNH TT. Synchronization of chaotic system using a brain-imitated neural network controller and its applications for secure communications[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 75923-75944. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3080696 [15] LIU X X, LI C J, GE S S, et al. Time-synchronized control of chaotic systems in secure communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2022, 69(9): 3748-3761. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3175713 [16] ZHOU L L, TAN F, LI X H, et al. A fixed-time synchronization-based secure communication scheme for two-layer hybrid coupled networks[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 433: 131-141. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.12.033 [17] GAN Q T, LI L C, YANG J, et al. Improved results on fixed- /preassigned-time synchronization for memristive complex-valued neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(10): 5542-5556. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3070966 [18] YU Z Q, LIU P X, LING S, et al. Adaptive finite-time synchronisation of variable-order fractional chaotic systems for secure communication[J]. International Journal of Systems Science, 2024, 55(2): 317-331. doi: 10.1080/00207721.2023.2271621 [19] CHEN J J, ZENG Z G, JIANG P. Global Mittag-Leffler stability and synchronization of memristor-based fractional-order neural networks[J]. Neural Networks, 2014, 51: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2013.11.016 [20] CHEN C, LI L X, PENG H P, et al. A new fixed-time stability theorem and its application to the fixed-time synchronization of neural networks[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 123: 412-419. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.12.028 [21] POLYA G, LITTLEWOOD J E, HARDY G H. Inequalities[M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1952. [22] NADERI B, KHEIRI H. Exponential synchronization of chaotic system and application in secure communication[J]. Optik, 2016, 127(5): 2407-2412. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.11.175 [23] AHMAD I, SHAFIQ M, NADERI B. Finite-time synchronization of four-dimensional memristor-based chaotic oscillator and applied to secure communication systems[J]. Franklin Open, 2023, 3: 100015. doi: 10.1016/j.fraope.2023.100015 [24] HU C, HE H B, JIANG H J. Fixed/preassigned-time synchronization of complex networks via improving fixed-time stability[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(6): 2882-2892. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2977934 [25] XIAO Q Z, LIU H L, WANG Y K. An improved finite-time and fixed-time stable synchronization of coupled discontinuous neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(7): 3516-3526. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3116320 -





 下载:
下载:






 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号