Study on the Motion Characteristics of Suction-Based Deep-Sea Polymetallic Nodule Mining
-
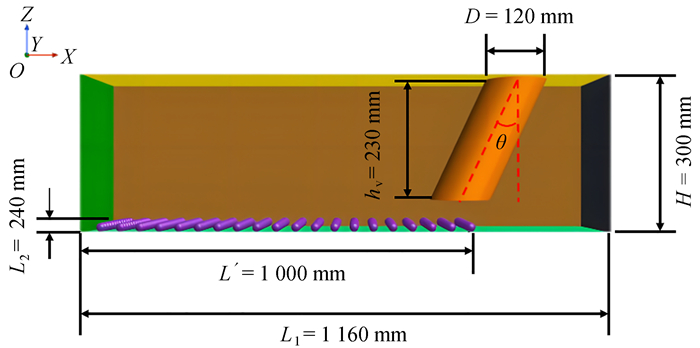
摘要: 多金属结核矿产资源以粗颗粒结核的形式呈面式分布于深海海床. 由于深海环境的脆弱和国际海底环境保护的紧迫性,研究集矿装置运动过程中的集矿特性和对海底的扰动具有实际意义. 采用计算流体动力学与离散元耦合方法(computational fluid dynamics and discrete element method, CFD-DEM)模拟了粗颗粒矿石在抽吸式集矿管作用下的采集过程. 结果表明,管道倾斜放置便于管道迎流侧抽吸大量矿石,有利于提高颗粒采集率. 集矿管水平运动和管道抽吸运动对流场形成叠加扰动,受该叠加扰动的影响,颗粒采集率随集矿管水平运动速度的增加先增大后减小,且一定程度上随集矿管倾斜角度的增加而增加. 海底流场的湍动能随集矿管水平运动速度的增加而减小,随集矿管倾斜角度的增加先增大后减小. 综合分析表明,集矿管水平运动速度为0.6 m/s和集矿管倾斜角度为45°是同时满足高采集率和低环境扰动的最佳工况,可为高性能深海多金属结核集矿装置的设计提供参考.Abstract: Polymetallic nodule mineral resources are distributed planarly in the form of coarse-grained nodules on the deep seabed. Owing to the fragility of the deep-sea environment and the urgency of environmental protection of the international seabed, it is of practical significance to study the collection rate and the disturbance of the seabed under different operating conditions during the movement of the mineral collecting device. A coupled computational fluid dynamics and discrete element method (CFD-DEM) was used to simulate the collection process of coarse-grained ore under the action of a suction collector pipe. The results show that, the tilted placement of the pipe facilitates the pumping of massive ores on the downstream side of the pipe, which is conducive to improving the particle collection rate. The horizontal movement of the collector pipe and the suction movement of the pipeline form a superposition of disturbances to the flow field; under the superposed disturbances, the particle collection rate increases and then decreases with the collector pipe horizontal movement speed, and increases with the collector pipe tilt angle to a certain extent. The turbulent kinetic energy of the seafloor decreases with the collector pipe horizontal movement speed, and increases and then decreases with the collector pipe tilt angle. Comprehensive analysis indicates that, the collector pipe horizontal movement speed of 0.6 m/s and the collector pipe tilt angle of 45° are the optimal working conditions to meet the requirements of high collection rates and low environmental disturbances in the parameter range of the study. The results can be used as a reference for the design of deep-sea polymetallic nodule collecting devices with high collection rates and low environmental disturbances.
-
Key words:
- deep-sea mining /
- suction collection /
- particle motion /
- collection rate /
- seafloor disturbance /
- CFD-DEM
edited-byedited-by1) (我刊青年编委邹遂丰推荐) -
表 1 多颗粒抽吸模型网格无关性验证
Table 1. Mesh independence verification of the multi-particle suction model
case number of cells time step/s flux/(kg/s) relative deviation/% E1 776 254 0.000 3 35.08 E2 868 943 0.000 3 35.56 1.37 E3 993 654 0.000 3 35.72 0.44 E4 1 245 964 0.000 3 35.79 0.19 表 2 多颗粒抽吸模型时间步长无关性验证
Table 2. Time step irrelevance verification of the multi-particle suction model
case time step/s number of cells flux/(kg/s) relative deviation/% M1 0.000 8 868 943 34.23 M2 0.000 5 868 943 35.12 2.60 M3 0.000 3 868 943 35.56 1.25 M4 0.000 1 868 943 35.76 0.56 -
[1] 刘少军, 刘畅, 戴瑜. 深海采矿装备研发的现状与进展[J]. 机械工程学报, 2014, 50(2): 8-18.LIU Shaojun, LIU Chang, DAI Yu. Status and progress on researches and developments of deep ocean mining equipments[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 50(2): 8-18. (in Chinese) [2] 胡经朝, 赵国成, 肖龙飞. 基于康达效应的海底集矿装置流场与集矿特性试验研究[J]. 海洋工程, 2022, 40(5): 132-138.HU Jingchao, ZHAO Guocheng, XIAO Longfei. Experimental investigation on flow field and collecting characteristics of mining device based on Coandǎ effect[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2022, 40(5): 132-138. (in Chinese) [3] CHEN Y X, XIONG H, CHENG H, et al. Effect of particle motion on the hydraulic collection of coarse spherical particles[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2020, 36(1): 72-81. doi: 10.1007/s10409-019-00922-6 [4] AMUDHA K, BHATTACHARYA S K, SHARMA R, et al. Influence of flow area zone and vertical lift motion of polymetallic nodules in hydraulic collecting[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 294: 116745. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.116745 [5] KUBICKI D, SIMON L. Slurry transport in a pipeline-comparison of CFD and DEM models[C]//Ninth International Conference on CFD in the Minerals and Process Industries. Melbourne, Australia, 2012. [6] RAMESH D R. Analysis of inferior vena cava filter using STAR CCM+'s Lagrangian particle tracking and DEM-CFD modelling approach[D]. Hyderabad, India: Birla Institute of Technology and Science, 2013. [7] 李亚林. 变曲率流道内固液两相CFD-DEM方法及在大型脱硫泵中的应用[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2015.LI Yalin. Effcet of continuously varying curvature on solid-liquid two-phase flow by CFD-DEM and its application in large desulfurization pump[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2015. (in Chinese) [8] AKHSHIK S, BEHZAD M, RAJABI M. CFD-DEM simulation of the hole cleaning process in a deviated well drilling: the effects of particle shape[J]. Particuology, 2016, 25: 72-82. doi: 10.1016/j.partic.2015.02.008 [9] ZHANG Y Y, DAI Y, ZHU X. Numerical investigation of recommended operating parameters considering movement of polymetallic nodule particles during hydraulic lifting of deep-sea mining pipeline[J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(5): 4248. doi: 10.3390/su15054248 [10] LI Y, LIU S, HU X. Solid-liquid two-phase flow in deep-sea mining pipelines based on CFD-DEM[J]. Ships and Offshore Structures, 2023, 18(11): 1617-1625. doi: 10.1080/17445302.2022.2129928 [11] 夏秋, 贾浩, 宿向辉, 等. 海底矿石颗粒水力采集运动特性研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2023, 44(3): 660-667.XIA Qiu, JIA Hao, SU Xianghui, et al. Motion characterization of seabed ore particle in hydraulic collecting[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2023, 44(3): 660-667. (in Chinese) [12] NINER H J, ARDRON J A, ESCOBAR E G, et al. Deep-sea mining with no net loss of biodiversity-an impossible aim[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2018, 5: 1-12. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00001 [13] 李雨瑶, 赵国成, 肖龙飞. 不同水力集矿模型的矿粒采集及环境扰动特性数值研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2024, 58(7): 1036-1046.LI Yuyao, ZHAO Guocheng, XIAO Longfei. Numerical study on collection and environmental disturbance characteristics of different nodule collecting models[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2024, 58(7): 1036-1046. (in Chinese) [14] ZHAO G, XIAO L, HU J, et al. Fluid flow and particle motion behaviors during seabed nodule pickup: an experimental study[J]. International Journal of Offshore and Polar Engineering, 2021, 31(2): 210-219. doi: 10.17736/ijope.2021.jc803 [15] 费龙, 郑成荣, 金强, 等. 深海多金属结核开采装备技术发展综述[J]. 船舶, 2024, 35(6): 1-14.FEI Long, ZHENG Chengrong, JIN Qiang, et al. Overview of the development of equipment and technology for deep-sea polymetallic nodule mining[J]. Ship & Boat, 2024, 35(6): 1-14. (in Chinese) [16] 刘唐京, 王企鲲, 邹赫. 高Re数层流管道中颗粒聚集特性的数值研究[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2023, 44(1): 70-79. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430075 LIU Tangjing, WANG Qikun, ZOU He. Numerical investigation of particle focusing patterns in laminar pipe flow with high Reynolds numbers[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2023, 44(1): 70-79. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430075 [17] 赵国成. 深海采矿水力集矿方法与流体-颗粒动力特性研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2022.ZHAO Guocheng. Research on hydraulic collecting methods and fluid-particle dynamic characteristics for deep-sea mining[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2022. (in Chinese) [18] Clift R, Grace J R, Weber M E. Bubbles, drops, and particles[J]. Drying Technology, 1978. [19] CROWE C T, SOMMERFELD M, TSUJI Y. Multiphase Flows With Droplets and Particles[M]. Boca Raton, FL: CRC, 1998. [20] CUNDALL P A, STRACK O D L. A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies[J]. Géotechnique, 1979, 29(1): 47-65. [21] HU J C, ZHAO G C, XIAO L F, et al. Experimental investigation on characteristics of flow field in 'suck-up-based' and 'coandǎ-effect-based' nodule pick-up devices[C]//ISOPE International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference, 2020: ISOPE-I-20-1110. -





 下载:
下载:

















 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号