Low-Frequency Ultra-Wideband Underwater Acoustic Diffusion Stealth Based on Locally Resonant Encoded Metasurface
-
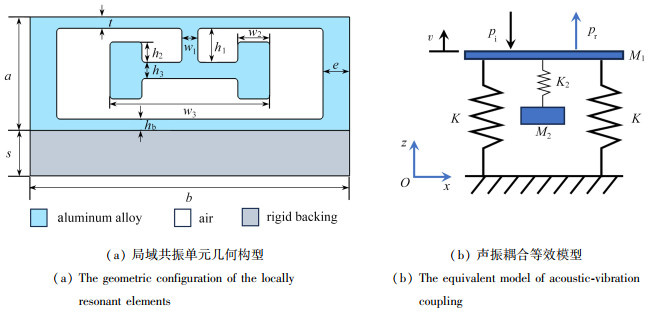
摘要: 水声隐身对提升水下设备的生存与工作能力意义重大. 该文提出了一种基于局域共振编码超表面的水下低频超宽带声扩散隐身方法. 首先,建立了局域共振超表面单元的声振耦合等效模型,揭示了倒“T”分形结构调制水下反射声波相位的力学机理,并基于遗传算法对宽频编码单元进行了协同优化设计. 进一步,依据编码调控理论,优化了宽频范围内具有良好扩散性能的超表面编码序列. 最后,针对该超表面开展了数值模拟和试验测试. 结果表明:具有倒“T”分形结构的超表面编码单元,在深亚波长尺度展现出良好的超宽频调相性能;编码超表面可在300~1 500 Hz的低宽频范围内实现水下扩散隐身;试验与仿真结果基本一致. 该工作为水下低频超宽带的声学隐身提供了新的途径.Abstract: Underwater acoustic stealth is of great significance for improving the survival and working capabilities of underwater devices. A method for underwater low-frequency ultra-wideband acoustic diffusion stealth based on the locally resonant coded metasurface was proposed. Firstly, an equivalent model of acoustic-vibration coupling for locally resonant metasurface elements was established, revealing the mechanical mechanism of an inverted T-shaped fractal structure in modulating the phases of underwater reflected acoustic waves. Then, a collaborative optimization design of the broadband coded elements was carried out based on the genetic algorithm. Furthermore, based on the coding theory, the coding sequence of the metasurface with superior diffusion performance within the broadband range was optimized. Finally, numerical simulations and experimental tests were conducted for this metasurface. The results show that, the metasurface coding element with an inverted T-shaped fractal structure can exhibit excellent ultra-wideband phase modulation performance at the deep sub-wavelength scale. The coded metasurface can achieve underwater diffusion stealth in the low broadband frequency range of 300~1 500 Hz. The experimental results are basically consistent with the simulation results. The research provides a new approach for underwater low-frequency ultra-wideband acoustic stealth.
-
Key words:
- acoustic diffusion stealth /
- low-frequency broadband /
- underwater acoustic metasurface /
- acoustic-vibration coupling /
- inverse design
edited-byedited-by1) (我刊青年编委王艳锋来稿) -
表 1 2-bit宽频单元表面的零阶法向位移D1,反射相位半解析解φana和模拟解φsim
Table 1. Zero-order normal displacements of the surface of the 2-bit broadband element, semi-analytical solutions of the reflection phase, and simulated solutions
frequency/Hz coding element “00” “01” “10” “11” 300 D1/(10-10 m) 0.318+7.036i -3.392+2.565i -1.498+0.334i 2.343+6.159i φana/(2π) 0 0.309 0.445 0.898 φsim/(2π) 0 0.308 0.445 0.899 600 D1/(10-10 m) 1.413+2.816i -0.848+3.307i -1.507+0.848i 1.370+0.654i φana/(2π) 0 0.229 0.486 0.790 φsim/(2π) 0 0.228 0.485 0.790 900 D1/(10-10 m) 0.983+0.531i 0.741+2.087i -0.946+1.872i -0.866+0.381i φana/(2π) 0 0.234 0.492 0.711 φsim/(2π) 0 0.234 0.491 0.710 1 200 D1/(10-10 m) -0.133+0.010i 0.872+0.755i 0.165+1.747i -0.830+1.177i φana/(2π) 0 0.251 0.494 0.720 φsim/(2π) 0 0.251 0.494 0.720 1 500 D1/(10-10 m) -0.669+0.482i 0.221+0.035i 0.670+0.925i -0.388+1.293i φana/(2π) 0 0.249 0.498 0.791 φsim/(2π) 0 0.249 0.499 0.792 表 2 水声扩散超表面厚度和频率等参数
Table 2. Parameters such as the thickness and frequency of the underwater acoustic diffusion metasurface
-
[1] 刘倩倩, 徐宁. 基于声隐身技术的水下无人系统防护功能材料研究[J]. 电声技术, 2020, 44(1): 19-23.LIU Qianqian, XU Ning. Research on functional materials of unmanned underwater system based on protection performance[J]. Audio Engineering, 2020, 44(1): 19-23. (in Chinese) [2] 焦达文. 分层海水环境中水下电场衰减规律和分布特性研究[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2021, 43(13): 137-142.JIAO Dawen. Research on attenuation law and distribution characteristics of underwater electric field in stratified seawater environment[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2021, 43(13): 137-142. (in Chinese) [3] 孙伟伟, 杨刚, 陈超, 等. 中国地球观测遥感卫星发展现状及文献分析[J]. 遥感学报, 2020, 24(5): 479-510.SUN Weiwei, YANG Gang, CHEN Chao, et al. Development status and literature analysis of China's earth observation remote sensing satellites[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 24(5): 479-510. (in Chinese) [4] 白鸿柏, 詹智强, 任志英. 金属橡胶声学性能研究进展与展望[J]. 振动与冲击, 2020, 39(23): 242-254.BAI Hongbai, ZHAN Zhiqiang, REN Zhiying. Progress and prospect of acoustic properties of metal rubber[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2020, 39(23): 242-254. (in Chinese) [5] QIN D H, PAN G, LEE S, et al. Underwater radiated noise reduction technology using sawtooth duct for pumpjet propulsor[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 188: 106228. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106228 [6] WANG W Q, XIE Y B, POPA B I, et al. Subwavelength diffractive acoustics and wavefront manipulation with a reflective acoustic metasurface[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2016, 120(19): 195103. doi: 10.1063/1.4967738 [7] CHEN J, XIAO J, LISEVYCH D, et al. Deep-subwavelength control of acoustic waves in an ultra-compact metasurface lens[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 4920. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07315-6 [8] ASSOUAR B, LIANG B, WU Y, et al. Acoustic metasurfaces[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2018, 3(12): 460-472. doi: 10.1038/s41578-018-0061-4 [9] TIAN Z H, SHEN C, LI J F, et al. Programmable acoustic metasurfaces[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(13): 1808489. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201808489 [10] CAI L, WEN J H, YU D L, et al. Beam steering of the acoustic metasurface under a subwavelength periodic modulation[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 111(20): 201902. doi: 10.1063/1.5001954 [11] ZHAO J J, LI B W, CHEN Z N, et al. Redirection of sound waves using acoustic metasurface[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 103(15): 151604. doi: 10.1063/1.4824758 [12] HUR S, CHOI H, YOON G H, et al. Planar ultrasonic transducer based on a metasurface piezoelectric ring array for subwavelength acoustic focusing in water[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 1485. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05547-7 [13] BAI Y Z, SONG A L, SUN C Y, et al. Broadband sound focusing with tunable focus based on reconfigurable acoustic coding metagrating[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2023, 122(26): 261705. doi: 10.1063/5.0152748 [14] TIAN Y, WEI Q, CHENG Y, et al. Acoustic holography based on composite metasurface with decoupled modulation of phase and amplitude[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 110(19): 191901. doi: 10.1063/1.4983282 [15] LI W B, LU G X, HUANG X D. Acoustic hologram of the metasurface with phased arrays via optimality criteria[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 180: 109420. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2022.109420 [16] LI J F, WANG W Q, XIE Y B, et al. A sound absorbing metasurface with coupled resonators[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2016, 109(9): 091908. doi: 10.1063/1.4961671 [17] YUAN T Y, SONG X, XU J J, et al. Tunable acoustic composite metasurface based porous material for broadband sound absorption[J]. Composite Structures, 2022, 298: 116014. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.116014 [18] CHEN H Y, CHAN C T. Acoustic cloaking and transformation acoustics[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2010, 43(11): 113001. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/43/11/113001 [19] SIECK C F, MARTIN T P, WISSMAN J P, et al. Aqueous acoustic metasurface for the anomalous reflection of sound[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2019, 146(4): 300. [20] DUAN M Y, YU C L, XIN F X, et al. Tunable underwater acoustic metamaterialsvia quasi-Helmholtz resonance: from low-frequency to ultra-broadband[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2021, 118(7): 071904. doi: 10.1063/5.0028135 [21] BALLESTERO E, JIMÉNEZ N, GROBY J P, et al. Metadiffusers for quasi-perfect and broadband sound diffusion[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2021, 119(4): 044101. doi: 10.1063/5.0053413 [22] SCHROEDER M R. Diffuse sound reflection by maximum-length sequences[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1975, 57(1): 149-150. doi: 10.1121/1.380425 [23] SCHROEDER M R. Binaural dissimilarity and optimum ceilings for concert halls: more lateral sound diffusion[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1979, 65(4): 958-963. doi: 10.1121/1.382601 [24] ZHU Y F, FAN X D, LIANG B, et al. Ultrathin acoustic metasurface-based schroeder diffuser[J]. Physical Review X, 2017, 7(2): 021034. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevX.7.021034 [25] JIMÉNEZ N, COX T J, ROMERO-GARCÍA V, et al. Metadiffusers: deep-subwavelength sound diffusers[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 5389. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05710-5 [26] XIAO L, CAO W K, HE S, et al. Absorption-diffusion integrated acoustic metasurface for scattering reduction[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2024, 224: 110136. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2024.110136 [27] YU G K, QIU Y P, LI Y, et al. Underwater acoustic stealth by a broadband 2-bit coding metasurface[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2021, 15(6): 064064. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.15.064064 [28] LI R C, JIANG Y T, ZHU R R, et al. Design of ultra-thin underwater acoustic metasurface for broadband low-frequency diffuse reflection by deep neural networks[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 12037. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16312-1 [29] LIANG T B, HE M, DONG H W, et al. Ultrathin waterborne acoustic metasurface for uniform diffuse reflections[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2023, 192: 110226. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2023.110226 [30] CHEN D C, ZHU X F, WEI Q, et al. Broadband tunable focusing lenses by acoustic coding metasurfaces[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2020, 53(25): 255501. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/ab8247 [31] ZHOU H T, FU W X, WANG Y F, et al. High-efficiency ultrathin nonlocal waterborne acoustic metasurface[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2021, 15(4): 044046. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.15.044046 [32] ZHOU H T, FU W X, LI X S, et al. Loosely coupled reflective impedance metasurfaces: precise manipulation of waterborne sound by topology optimization[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 177: 109228. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2022.109228 [33] 牛嘉敏, 吴九汇. 非对称类声学超材料的低频宽带吸声特性[J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(19): 45-49.NIU Jiamin, WU Jiuhui. Low frequency wide band sound absorption performance of asymmetric type acoustic metamaterials[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(19): 45-49. (in Chinese) [34] 林臻, 吴九汇. 含间隙非线性弹性超材料的低频宽带机理[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43(5): 524-533. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430103LIN Zhen, WU Jiuhui. The low-frequency broadband mechanism of nonlinear elastic metamaterials with gaps[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(5): 524-533. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430103 [35] LI J S, WEN X H, SHENG P. Acoustic metamaterials[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2021, 129(17): 171103. doi: 10.1063/5.0046878 [36] FAHY F J, GARDONIO P. Sound and Structural Vibration: Radiation, Transmission and Response[M]. Elsevier, 2007. [37] 姚谦, 杨钊, 王昕, 等. 力学超结构设计方法研究进展[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2024, 45(8): 974-1000. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.450307YAO Qian, YANG Zhao, WANG Xin, et al. The low-frequency a review of design methods for mechanical metastructures[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2025, 45(8): 974-1000. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.450307 [38] CHEN Z, GUAN S, XIE Q, et al. Locally resonant metasurface for low-frequency transmissive underwater acoustic waves[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2023, 10: 1098261. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2022.1098261 [39] CHEN Z, YAN F, NEGAHBAN M, et al. Resonator-based reflective metasurface for low-frequency underwater acoustic waves[J]. 2020, 128(5): 055305. [40] 胡博, 刘凯, 赵思缘, 等. 水下声学超表面异常折射方向调控研究[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2024, 45(1): 93-102.HU Bo, LIU Kai, ZHAO Siyuan, et al. Research on the regulation of abnormal refraction direction of underwater acoustic metasurface[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2024, 45(1): 93-102. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载:







 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号